資料2-2-4 医療機器研究報告[1.8MB] (86 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_53225.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事審議会 医療機器・再生医療等製品安全対策部会(令和6年度第2回 3/6)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
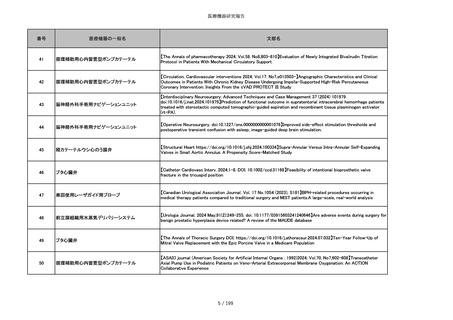
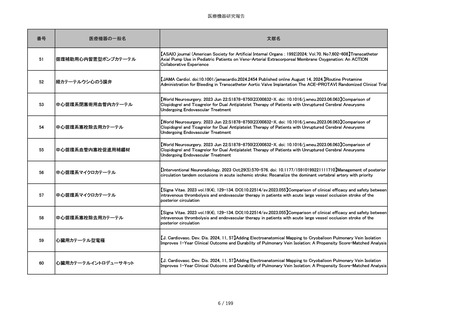
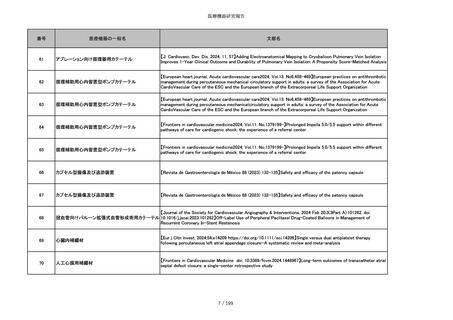
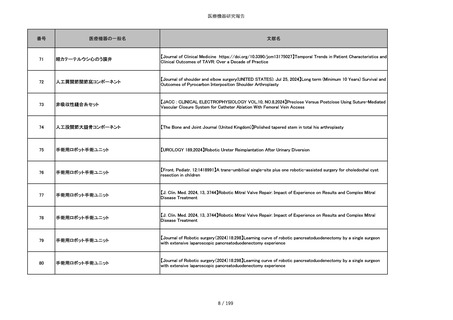
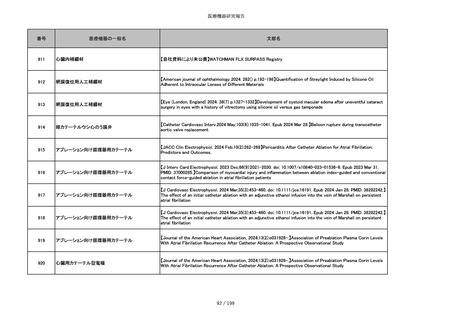
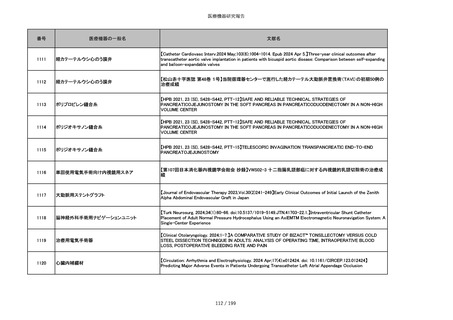
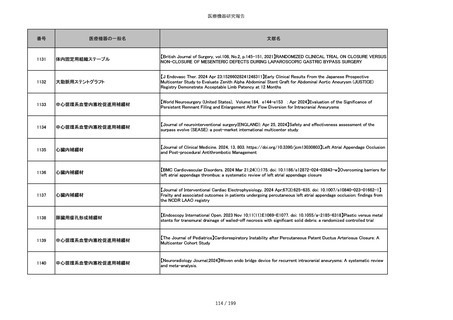
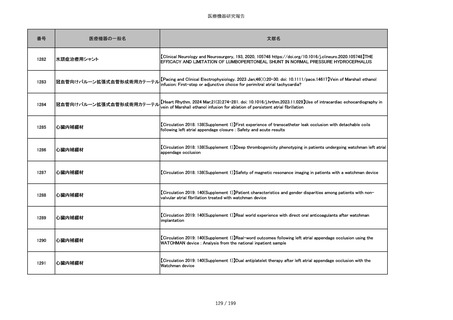
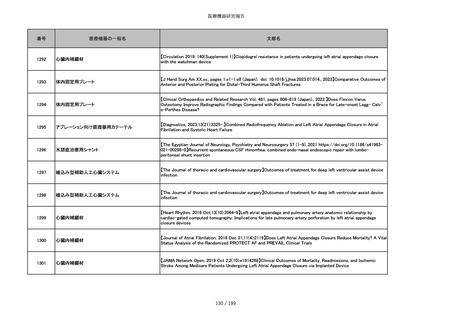
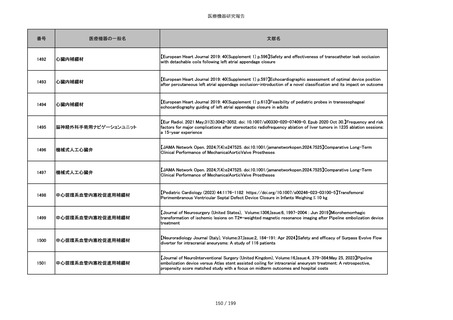
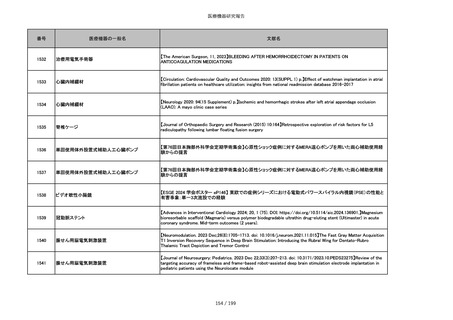
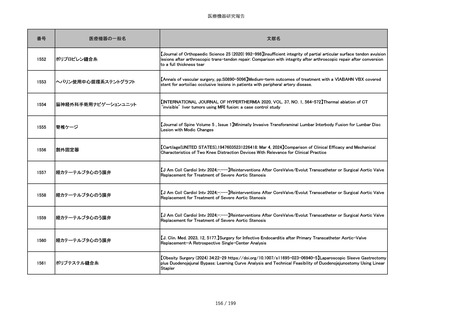
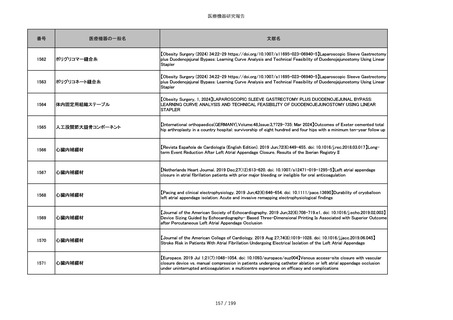
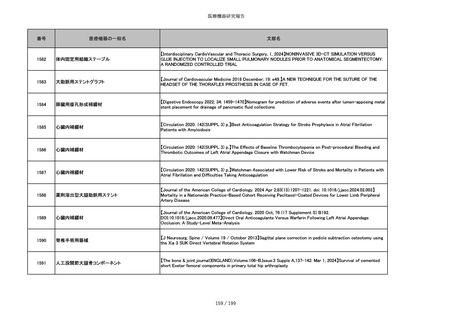
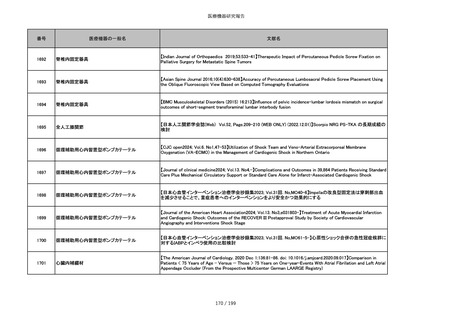
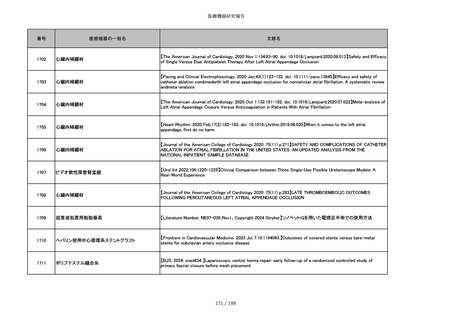
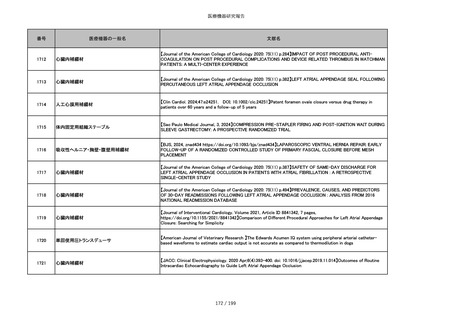
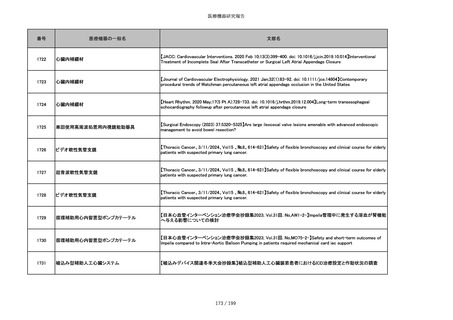
番号
医療機器の一般名
文献名
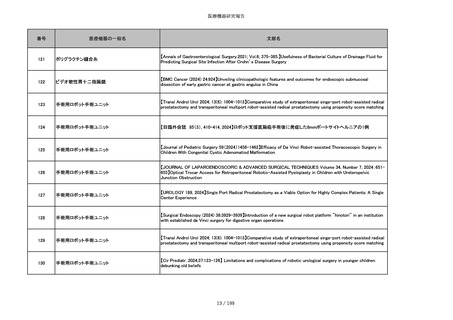
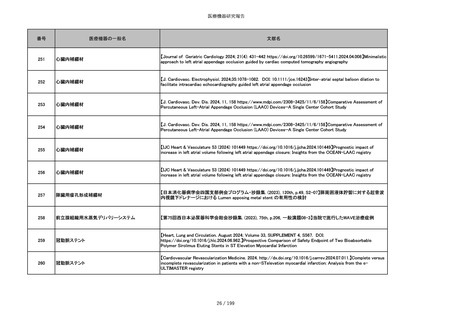
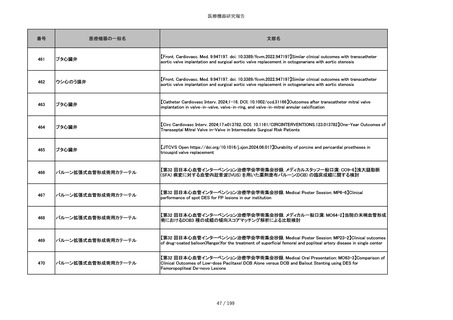
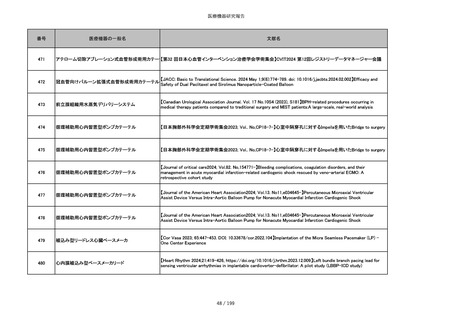
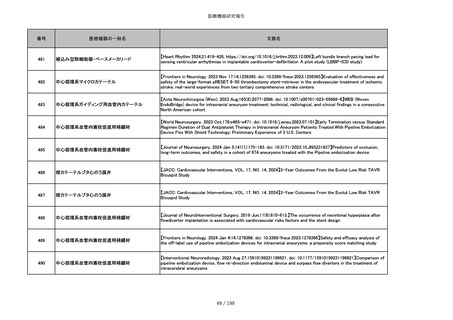
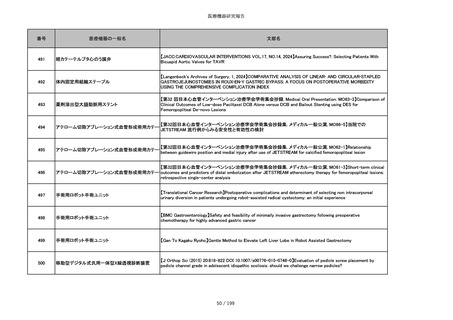
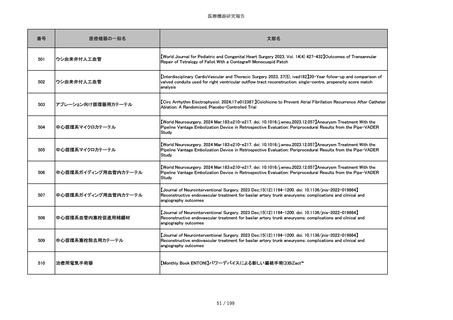
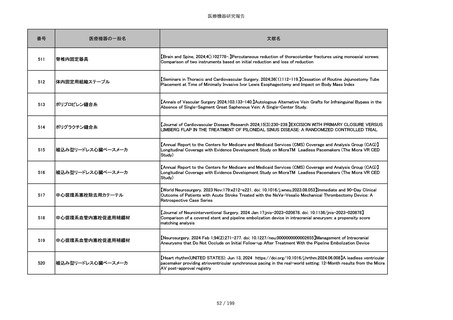
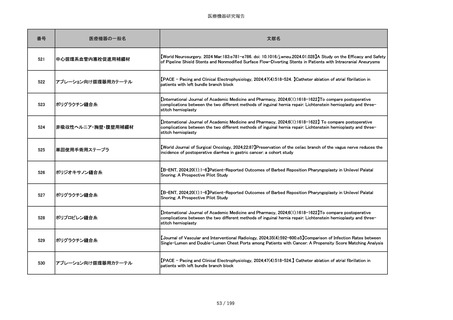
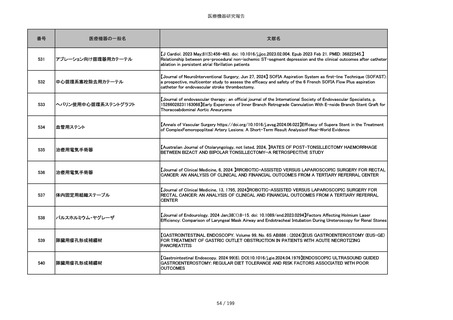
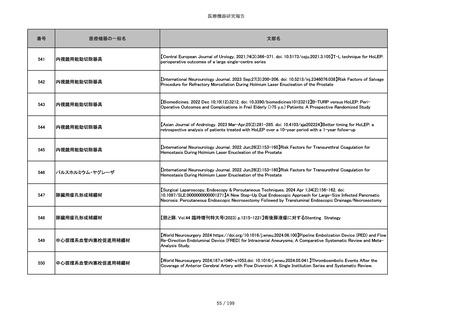
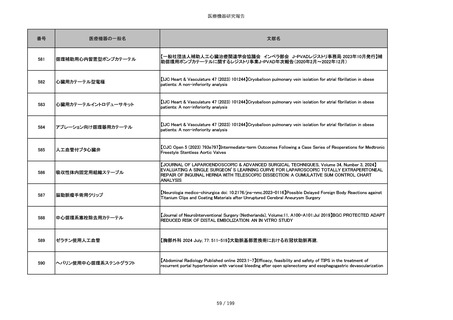
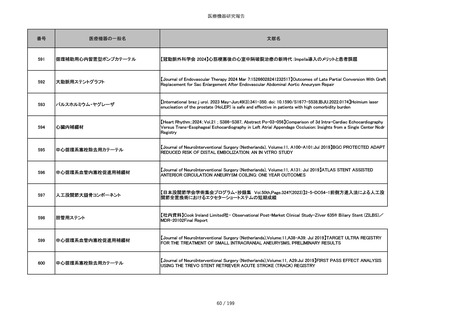
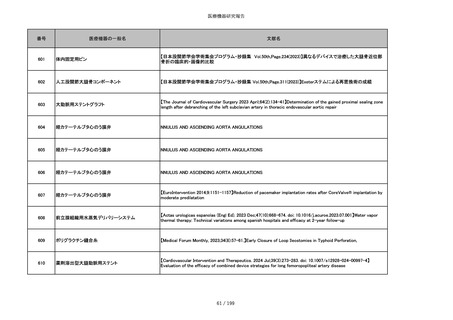
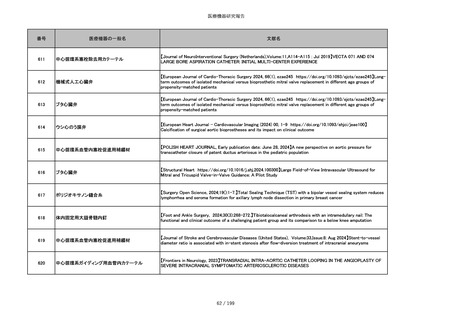
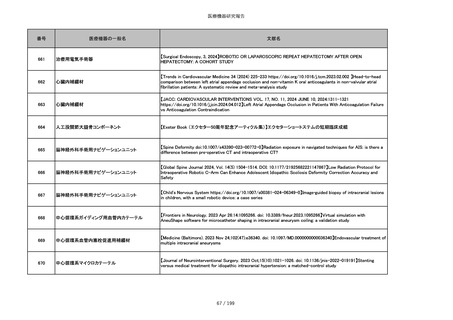
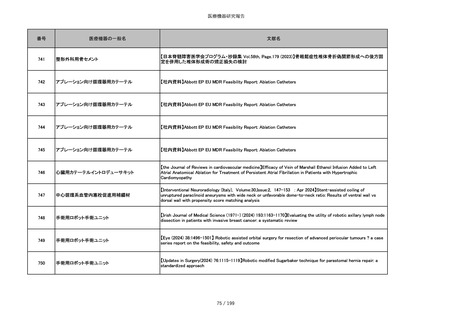
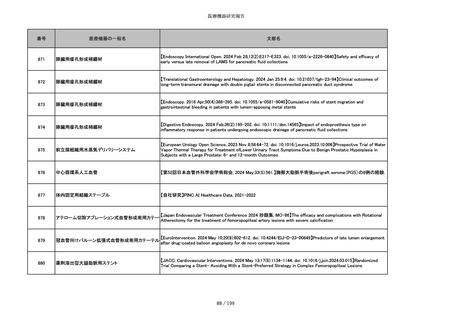
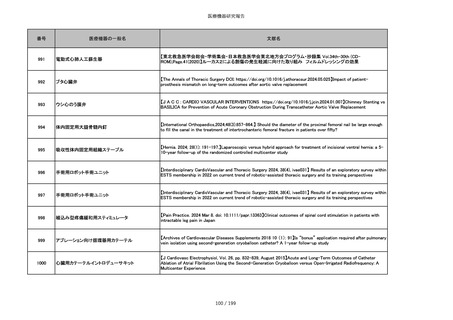
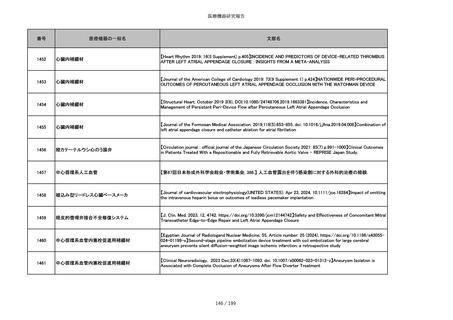
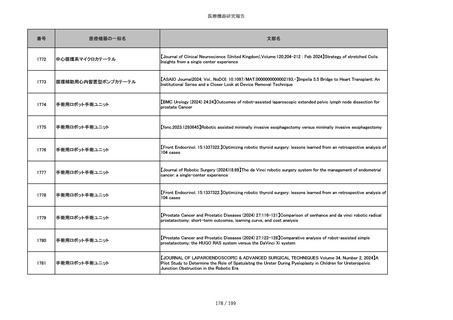
851
ペースメーカ・除細動器リード抜去キット
【Heart Rhythm. 2024 1-9】Transvenous lead extraction safety and efficacy in infected and noninfected patients
using mechanical-only tools: Prospective registry from a high-volume center
852
吸収性組織補強材
【J Neurosurg Pediatr 30:507–516, 2022 https://doi.org/10.3171/2022.7.PEDS22231】Association between synthetic
sealants and increased complication rates in posterior fossa decompression with duraplasty for Chiari malformations
regardless of graft type
853
整形外科用骨セメント
【日本骨粗鬆症学会雑誌 Vol.9, No.Suppl.1 (CD-ROM), Page.311 (2023.09.08)】骨粗鬆症に対するBKP(Balloon
Kyphoplasty)の適応,一年成績と問題点
854
整形外科用骨セメント
【日本骨粗鬆症学会雑誌 Vol.9, No.Suppl.1 (CD-ROM), Page.311 (2023.09.08)】Balloon kyphoplasty後に骨形成促進
薬投与を行った症例についての検討
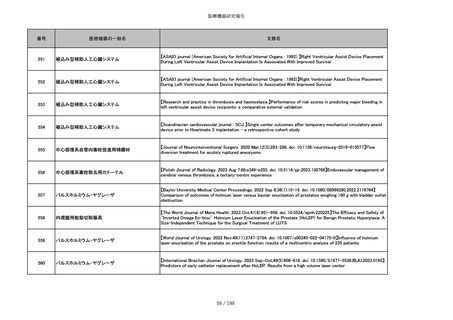
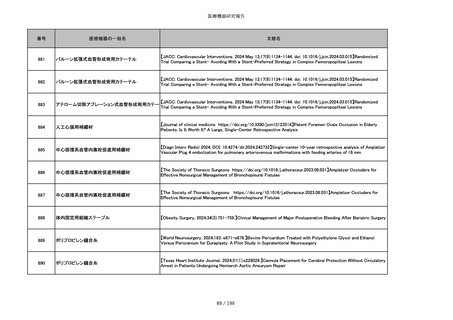
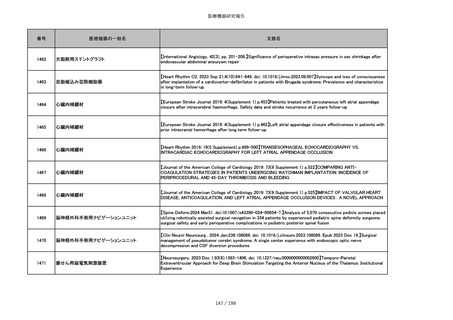
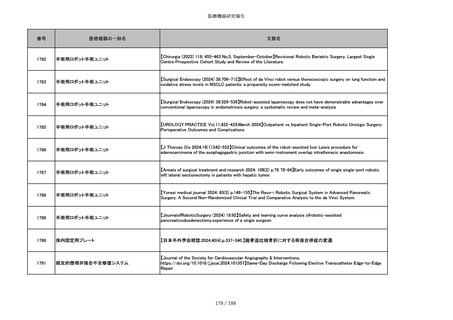
855
ポリグリコネート縫合糸
【Children 2024, 11, 35.】Use of Barbed Sutures for Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Repair
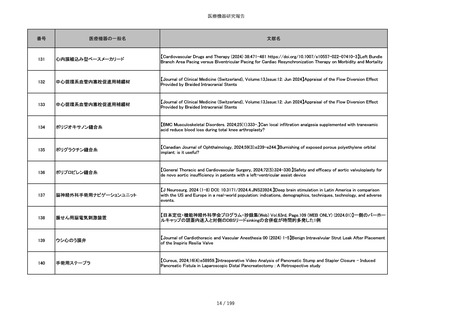
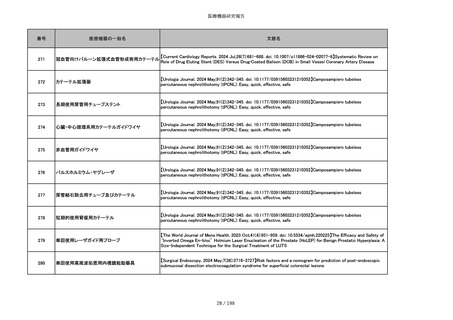
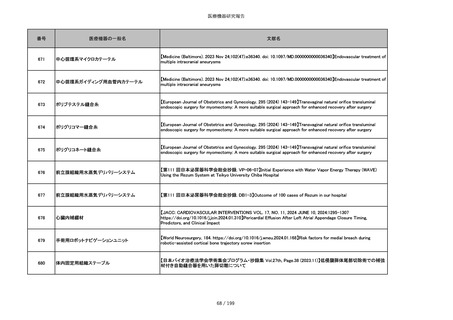
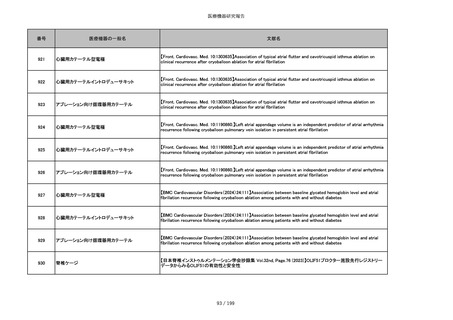
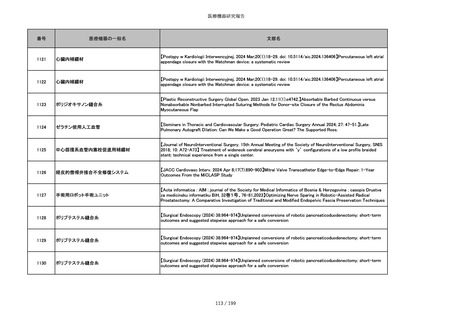
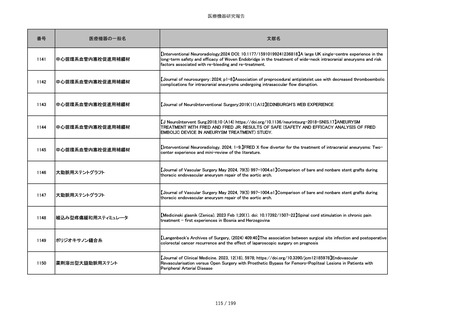
856
ポリグリコマー縫合糸
【Children 2024, 11, 35.】Use of Barbed Sutures for Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Repair
857
ポリブテステル縫合糸
【Children 2024, 11, 35.】Use of Barbed Sutures for Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Repair
858
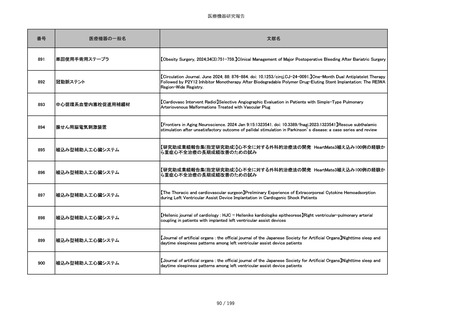
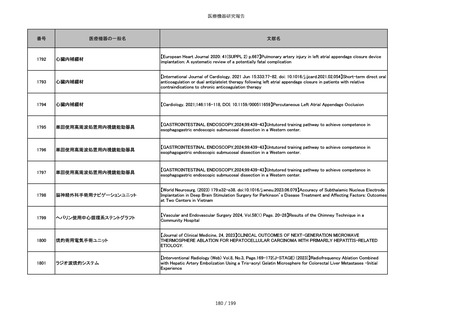
吸収性靭帯固定具
【Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, 2024;144(3):987-995.】A retrospective comparative study of surgical
outcomes following femoral fascia patching and iliotibial ligament bony patching for primary irreparable rotator cuff
tears in a geriatric population
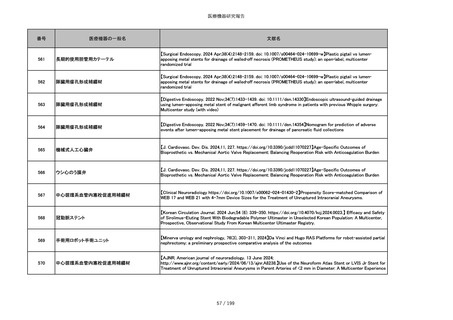
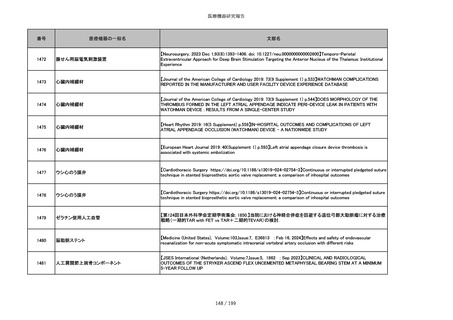
859
靭帯固定具
【Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, 2024;144(3):987-995.】A retrospective comparative study of surgical
outcomes following femoral fascia patching and iliotibial ligament bony patching for primary irreparable rotator cuff
tears in a geriatric population
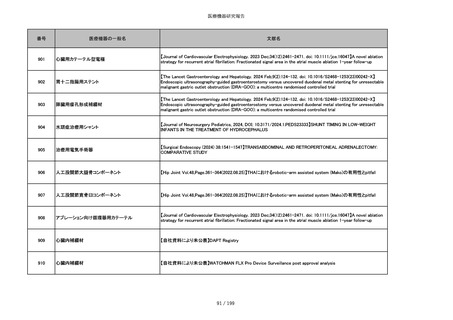
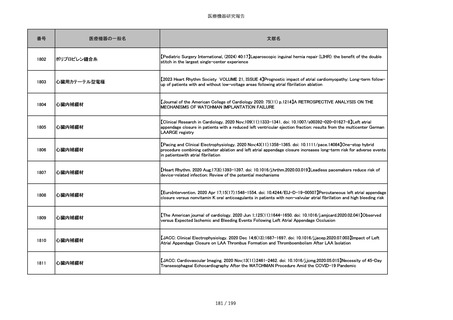
860
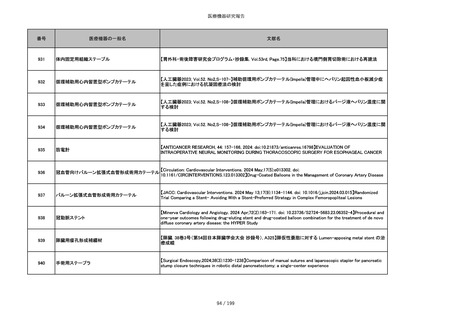
吸収性靭帯固定具
【Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, 2024;144(3):987-995.】A retrospective comparative study of surgical
outcomes following femoral fascia patching and iliotibial ligament bony patching for primary irreparable rotator cuff
tears in a geriatric population
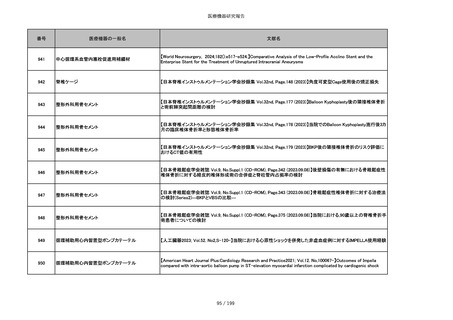
86 / 199