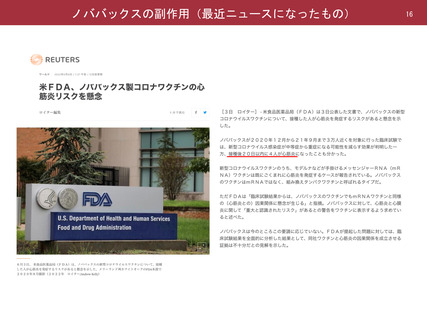
よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
参考資料1-1 新型コロナウイルスワクチン(ノババックス、J&J)接種後の採血制限期間について(令和4年7月22日開催 大隈班会議資料) (23 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_27504.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事・食品衛生審議会 薬事分科会血液事業部会安全技術調査会(令和4年度第2回 8/23)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
Frederikus A Kiok Menaka Pai Menno VHuisman, Michaer Makris
Epidemiology
Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Lancet Haematol 2021: 9: 73-80
Published Online
Niovember 11, 2021
https://doi.org/10.1016/
52352-3026(21)00306-9
Age restrictions for vaccination with
AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine introduced
bythe UK for people younger than
30 years (April 7 2021)
Agqe restriction increased to
Identification of VITT announced patients youngerthan 40 years
as new syndrome by scientists from intheUKforvaccination with
Norway, Germany, and the UK AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine
(March 19, 2021) (May 7 2021)
In Norway, Schultz and colleagues 4 reported five cases of VITT among 130 000
individuals who received the AstraZeneca- Oxford vaccine giving an incidence
of one in 26.000
In the UK, the MHRA reported 367 VITT cases after 24.7 million of the first
vaccination and 44 cases after the second AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccination,
giving rates of one case_ per 67.302 vaccinations and one case_per 518.181
vaccinations, resDectively.
From the USA, reported 12 cases of VITT after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine
after 7 million doses, suggesting a rate of one case_per 583.000 vaccinations.
The MHRA gives the risk of VITT after the first dose of AstraZeneca-Oxford
vaccination as one in 100.000 for people older than 50 years and one in 50.000
for those aged 49 years or younger.
Platelets Adenoviral
Vector
アデ FRIIA
人 (promotes platelet
8 NNN Tissue factor
“アン 人 ・ Y ア fa
milieu caused by * (activates platelets)
Vaccine components |
lymph node 『 PF4-viral Tissue PF4
Protein complex
Y\
Anti-PF4
factor
ForRI ア
(activates monocytes) 人 FcYRIla
(induces NETosis)
。 (VITT)
Anti-PF4 antibodies
memory
B cels レコ =
W
ュー
Figure 2: Proposed pathophysiology of vaccine-induced immunethrombotic thrombocytopenia
PF4=platelet factor 4.
0 典穫6
December Januay March ] で
。 2020 2021 2021 。 2021 。 202
EMA aPproves MHRA and EMA announce
AstraZeneca-Oxford new syndrome of thrombosis
vaccine (jan 29, 2021) thrombocytopenia, and anti-PF4
antibodies (April 7 2021)
MHRA approves
AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine MHRA and EMA announce
(Dec 30, 2020) no increase in thrombotic risk
after COVID-19 vaccination
MHRA approves (March 11, 2021)
Pfzer-BioNTech vaccine
(Dec 2. 2020)
Figure 1: Timeline of the development of adenovirus-based coronavirus vaccines and first recognition of
Vaccine-induced immune thromboticthrombocytopenia
On August 12, 2021, the full report from the first 294 UK cases was published.* EMA=European Medicines Agency.
MHRA=Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency.VITTsvaccine-induced immune thrombotic
thrombocytopenia.
UK Expert Haematology Panel
Suspected VITT in case of Required tests in diagnostic VITT diagnostic criteria
work-up of VITT
AstraZeneca-Oxford or Full blood count andblood Thrombocytopenia (platelet
訓m, liver or renal function count <150 x10? cells per L),
5-30 days before onset of D-dimer >4000 FEU
symptoms (fbrinogen-equivalent units),
venous (or arterial)
3 thrombosis, ELISA positive,
Siqnsofvenous or arterial Activated partial functionaltest positive
thrombosis, such as severe thromboplastin time,
headache or other prothrombin time,
neurological symptoms fbrinogen concentrations,
(or both) D-dimer concentrations
New bleedinqg tendency or Heparin-induced
Petechiae thrombocytopenia ELISA test
for anti-platelet factor 4
antibodies and functional
SSay
Figure 3: Overview ofthe diagnostic investigation of VITT
Functional assays might involve a functional heparin-induced platelet activation assay, a serotonin-release assay,
or a flow-based platelet activation assay. FEU=fibrinogen-equivalent units.VITT=vaccine-induced immune
thrombotic thrombocytopenia. 23
23
Epidemiology
Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Lancet Haematol 2021: 9: 73-80
Published Online
Niovember 11, 2021
https://doi.org/10.1016/
52352-3026(21)00306-9
Age restrictions for vaccination with
AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine introduced
bythe UK for people younger than
30 years (April 7 2021)
Agqe restriction increased to
Identification of VITT announced patients youngerthan 40 years
as new syndrome by scientists from intheUKforvaccination with
Norway, Germany, and the UK AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine
(March 19, 2021) (May 7 2021)
In Norway, Schultz and colleagues 4 reported five cases of VITT among 130 000
individuals who received the AstraZeneca- Oxford vaccine giving an incidence
of one in 26.000
In the UK, the MHRA reported 367 VITT cases after 24.7 million of the first
vaccination and 44 cases after the second AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccination,
giving rates of one case_ per 67.302 vaccinations and one case_per 518.181
vaccinations, resDectively.
From the USA, reported 12 cases of VITT after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine
after 7 million doses, suggesting a rate of one case_per 583.000 vaccinations.
The MHRA gives the risk of VITT after the first dose of AstraZeneca-Oxford
vaccination as one in 100.000 for people older than 50 years and one in 50.000
for those aged 49 years or younger.
Platelets Adenoviral
Vector
アデ FRIIA
人 (promotes platelet
8 NNN Tissue factor
“アン 人 ・ Y ア fa
milieu caused by * (activates platelets)
Vaccine components |
lymph node 『 PF4-viral Tissue PF4
Protein complex
Y\
Anti-PF4
factor
ForRI ア
(activates monocytes) 人 FcYRIla
(induces NETosis)
。 (VITT)
Anti-PF4 antibodies
memory
B cels レコ =
W
ュー
Figure 2: Proposed pathophysiology of vaccine-induced immunethrombotic thrombocytopenia
PF4=platelet factor 4.
0 典穫6
December Januay March ] で
。 2020 2021 2021 。 2021 。 202
EMA aPproves MHRA and EMA announce
AstraZeneca-Oxford new syndrome of thrombosis
vaccine (jan 29, 2021) thrombocytopenia, and anti-PF4
antibodies (April 7 2021)
MHRA approves
AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine MHRA and EMA announce
(Dec 30, 2020) no increase in thrombotic risk
after COVID-19 vaccination
MHRA approves (March 11, 2021)
Pfzer-BioNTech vaccine
(Dec 2. 2020)
Figure 1: Timeline of the development of adenovirus-based coronavirus vaccines and first recognition of
Vaccine-induced immune thromboticthrombocytopenia
On August 12, 2021, the full report from the first 294 UK cases was published.* EMA=European Medicines Agency.
MHRA=Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency.VITTsvaccine-induced immune thrombotic
thrombocytopenia.
UK Expert Haematology Panel
Suspected VITT in case of Required tests in diagnostic VITT diagnostic criteria
work-up of VITT
AstraZeneca-Oxford or Full blood count andblood Thrombocytopenia (platelet
訓m, liver or renal function count <150 x10? cells per L),
5-30 days before onset of D-dimer >4000 FEU
symptoms (fbrinogen-equivalent units),
venous (or arterial)
3 thrombosis, ELISA positive,
Siqnsofvenous or arterial Activated partial functionaltest positive
thrombosis, such as severe thromboplastin time,
headache or other prothrombin time,
neurological symptoms fbrinogen concentrations,
(or both) D-dimer concentrations
New bleedinqg tendency or Heparin-induced
Petechiae thrombocytopenia ELISA test
for anti-platelet factor 4
antibodies and functional
SSay
Figure 3: Overview ofthe diagnostic investigation of VITT
Functional assays might involve a functional heparin-induced platelet activation assay, a serotonin-release assay,
or a flow-based platelet activation assay. FEU=fibrinogen-equivalent units.VITT=vaccine-induced immune
thrombotic thrombocytopenia. 23
23