よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料2 超音波検査による乳がん検診の有効性を検証する比較試験(J-START)の進捗状況について. (10 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_34640.html |
| 出典情報 | がん検診のあり方に関する検討会(第39回 8/9)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
Sensitivity and specifcity of mammography and adjunctive
ultrasonography to screen for breast cancer in the japan
Strategic Anti-cancer Randomized Trial (」-START):
a randomised controlled trial
Norigki Ohuchi AK罰小o Suzuki Tommotaka Sobue, MasaakiKawai Seiichiro Yamannoto, Yjng-Fang Znend, Yoko Narikawa Shjono, 月jrosi Sito,
Shinichi Kuriyanma, ErikoTohno, Tokiko Endo, Akirg Fukao, chiroTsuji Takuhiro Yamaguchi Yasuo Ohashi Mamoru Fukuda, Takanojj jshida,
jor tneナSTART investigator grouDs
Sumimary
Backqround Mammopraphy is the only proven method for breast cancer screeninp that reduces mortality, althouph
it is inaccurate in young women or women with dense breasts. We investipated the efcacy of adjunctive
ultrasonography.
Methods Between july, 2007, and March, 2011, we enrolled asymptomatic women aged 40-49 years at 42 study sites
in 23 prefectures into the japan Strategic Anti-cancer Randomized Trial (j-START). Elipible women had no history of
any cancer in the previous 5 years and were expected to live for more than 5 years. Randomisation was done centrally
by the japan CHinical Research Support Unit. ParHicipants were randomly assigned im 1:1 ratio to underpo
mammooraphy and ultrasonopraphy (intervention proup) or mammography alone (control proup) hyice in 2 years.
The primary outcome was sensitivity, specihcity, cancer detection rate, and stage distribution at the frst round of
screeninp. Analysis was by intention to treat. This study is regpistered, number UMIN000000757.
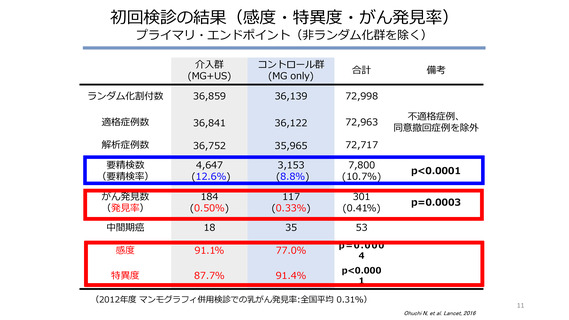
Findings Of 72 998 women enrolled, 36 859 were assipgned to the imtervention group and 36 139 to the control group.
Sensitivity was signihcantly hipgher in the intervention group than in the control group (91・1926, 959% CI 87・2-95・0 rs
77・096, 70・3-83・7: p=0・0004), whereas specihcity was signihcantly lower (87・79%6, 87・3-88・0 rs 91・496, 91・1-91・7:
p<0・0001). More cancers were detected in the intervention group than in the control group (184 [0・5026] rs 117 [0 ・3296],
p=0・0003) and were more frequently stage 0 and 1 (144 [71・396] rs 79 [52・0%], p=0・0194). 18 (0・05%) inmterval cancers
were detected in the intervention group compared with 35 (0・10%) in the control group (p=0・034).
O/zc// ん er g/ /g/7ceをた クの7の
⑲ ^
CrossiMark
Published Online
November 4, 2015
http:/dx.doi.orq/10.1016/
SO140-6736(15)00774-6
See Online/Comment
http/dx.doi.orq/10.1016/
S0140-6736(15)00787-4
Department of Surgical
Oncology (Prof N Ohuchi PhD,
A Suzuki PhD, Y-FZheng PhD,
Y N Shiono PhD, T Ishida PhD),
Department of Public Health
(ProflTsuji PhD), and
Department of Biostatistics
(ProfTYamaguchi PhD),
Graduate 5chool of Medicine,
Tohoku University, Sendai
Japan: Department of
Disaster- Related Public
Health, International Research
Institute of Disaster Science,
Tohoku University, Sendai
ultrasonography to screen for breast cancer in the japan
Strategic Anti-cancer Randomized Trial (」-START):
a randomised controlled trial
Norigki Ohuchi AK罰小o Suzuki Tommotaka Sobue, MasaakiKawai Seiichiro Yamannoto, Yjng-Fang Znend, Yoko Narikawa Shjono, 月jrosi Sito,
Shinichi Kuriyanma, ErikoTohno, Tokiko Endo, Akirg Fukao, chiroTsuji Takuhiro Yamaguchi Yasuo Ohashi Mamoru Fukuda, Takanojj jshida,
jor tneナSTART investigator grouDs
Sumimary
Backqround Mammopraphy is the only proven method for breast cancer screeninp that reduces mortality, althouph
it is inaccurate in young women or women with dense breasts. We investipated the efcacy of adjunctive
ultrasonography.
Methods Between july, 2007, and March, 2011, we enrolled asymptomatic women aged 40-49 years at 42 study sites
in 23 prefectures into the japan Strategic Anti-cancer Randomized Trial (j-START). Elipible women had no history of
any cancer in the previous 5 years and were expected to live for more than 5 years. Randomisation was done centrally
by the japan CHinical Research Support Unit. ParHicipants were randomly assigned im 1:1 ratio to underpo
mammooraphy and ultrasonopraphy (intervention proup) or mammography alone (control proup) hyice in 2 years.
The primary outcome was sensitivity, specihcity, cancer detection rate, and stage distribution at the frst round of
screeninp. Analysis was by intention to treat. This study is regpistered, number UMIN000000757.
Findings Of 72 998 women enrolled, 36 859 were assipgned to the imtervention group and 36 139 to the control group.
Sensitivity was signihcantly hipgher in the intervention group than in the control group (91・1926, 959% CI 87・2-95・0 rs
77・096, 70・3-83・7: p=0・0004), whereas specihcity was signihcantly lower (87・79%6, 87・3-88・0 rs 91・496, 91・1-91・7:
p<0・0001). More cancers were detected in the intervention group than in the control group (184 [0・5026] rs 117 [0 ・3296],
p=0・0003) and were more frequently stage 0 and 1 (144 [71・396] rs 79 [52・0%], p=0・0194). 18 (0・05%) inmterval cancers
were detected in the intervention group compared with 35 (0・10%) in the control group (p=0・034).
O/zc// ん er g/ /g/7ceをた クの7の
⑲ ^
CrossiMark
Published Online
November 4, 2015
http:/dx.doi.orq/10.1016/
SO140-6736(15)00774-6
See Online/Comment
http/dx.doi.orq/10.1016/
S0140-6736(15)00787-4
Department of Surgical
Oncology (Prof N Ohuchi PhD,
A Suzuki PhD, Y-FZheng PhD,
Y N Shiono PhD, T Ishida PhD),
Department of Public Health
(ProflTsuji PhD), and
Department of Biostatistics
(ProfTYamaguchi PhD),
Graduate 5chool of Medicine,
Tohoku University, Sendai
Japan: Department of
Disaster- Related Public
Health, International Research
Institute of Disaster Science,
Tohoku University, Sendai
関連画像
ページ内で利用されている画像ファイルです。
有料会員登録をして頂くことで、このページ内で利用されている画像を個別に閲覧・ダウンロードすることができるようになります。