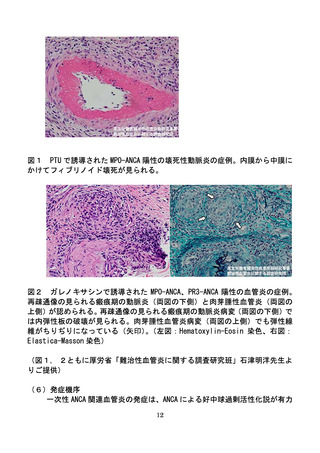
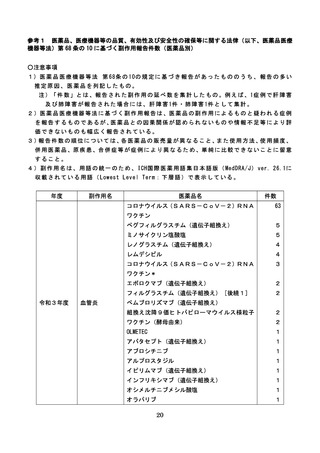
よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料2-4 重篤副作用疾患別対応マニュアル 血管炎による腎障害(ANCA関連含む)(案)[1.2MB] (19 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/shingi2/0000209243_00011.html |
| 出典情報 | 重篤副作用総合対策検討会(第16回 10/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
7.引用文献・参考資料
1) Gao Y, Zhao MH.: Drug-induced anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis.
Nephrology (Carlton). 14:33-41, 2009
2) Merkel PA. Drug-induced vasculitis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 27:849-62, 2001
3) ten Holder SM, Joy MS, Falk RJ.: Cutaneous and systemic manifestations of drug-induced
vasculitis. Ann Pharmacother. 36:130-147.2002.
4) Chen M, et al.: Propylthiouracil-induced antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated
vasculitis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 8:476-83, 2012
5) 古川福美, 池田高治 他:日本皮膚科学会ガイドライン. 血管炎・血管障害診療ガイドライン 2016
年改訂版. 日本皮膚科学会雑誌. 127: 299-415, 2017
6)
Deshayes
S,
et
al.:
A
worldwide
pharmacoepidemiologic
update
on
drud-induced
antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis in the era of targeted therapies.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 74:134-9, 2022
7) Kessenbrock K, et al.: Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat Med.
15:623-5, 2009
8) Gao Y, et al.: Follow-up of avidity and titre of anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies in sera
from patients with propylthiouracil-induced vasculitis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 66:543-7,
2007
9) Nakazawa D, et al.: Abnormal conformation and impaired degradation of propylthiouracilinduced
neutrophil
extracellular
traps:
implications
of
disordered
neutrophil
extracellular traps in a rat model of myeloperoxidase antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodyassociated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 64:3779-87, 2012
10) Gilligan HM, et al.: Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies interact with primary
granule constituents on the surface of apoptotic neutrophils in the absence of neutrophil
priming. J Exp Med. 184:2231-41, 1996
11) Radić M, et al.: Drug-induced vasculitis: a clinical and pathological review. Neth J
Med. 70:12-7, 2012
12) Imaeda AB, et al.: Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice is dependent on Tlr9 and
the Nalp3 inflammasome. J Clin Invest. 119:305-14, 2009
13) Dunphy J, et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and HLA class II alleles in
minocycline-induced lupus-like syndrome. Br J Dermatol.142:461-7, 2000
14) Morita S, et al.: Anti-thyroid drug-induced ANCA-associated vasculitis: a case report
and review of the literature. Endocr J. 47:467-70, 2000
15)
Vogt
BA
et
al.:
Antineutrophil
cytoplasmic
autoantibody-positive
crescentic
glomerulonephritis as a complication of treatment with propylthiouracil in children. J
Pediatr. 124:986-8, 1994
16)
Chen
Y,
et
al.:
Clinico-pathological
features
and
outcomes
of
patients
with
propylthiouracil-associated ANCA vasculitis with renal involvement. J Nephrol. 27:159-64,
18
1) Gao Y, Zhao MH.: Drug-induced anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis.
Nephrology (Carlton). 14:33-41, 2009
2) Merkel PA. Drug-induced vasculitis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 27:849-62, 2001
3) ten Holder SM, Joy MS, Falk RJ.: Cutaneous and systemic manifestations of drug-induced
vasculitis. Ann Pharmacother. 36:130-147.2002.
4) Chen M, et al.: Propylthiouracil-induced antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated
vasculitis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 8:476-83, 2012
5) 古川福美, 池田高治 他:日本皮膚科学会ガイドライン. 血管炎・血管障害診療ガイドライン 2016
年改訂版. 日本皮膚科学会雑誌. 127: 299-415, 2017
6)
Deshayes
S,
et
al.:
A
worldwide
pharmacoepidemiologic
update
on
drud-induced
antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis in the era of targeted therapies.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 74:134-9, 2022
7) Kessenbrock K, et al.: Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat Med.
15:623-5, 2009
8) Gao Y, et al.: Follow-up of avidity and titre of anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies in sera
from patients with propylthiouracil-induced vasculitis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 66:543-7,
2007
9) Nakazawa D, et al.: Abnormal conformation and impaired degradation of propylthiouracilinduced
neutrophil
extracellular
traps:
implications
of
disordered
neutrophil
extracellular traps in a rat model of myeloperoxidase antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodyassociated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 64:3779-87, 2012
10) Gilligan HM, et al.: Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies interact with primary
granule constituents on the surface of apoptotic neutrophils in the absence of neutrophil
priming. J Exp Med. 184:2231-41, 1996
11) Radić M, et al.: Drug-induced vasculitis: a clinical and pathological review. Neth J
Med. 70:12-7, 2012
12) Imaeda AB, et al.: Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice is dependent on Tlr9 and
the Nalp3 inflammasome. J Clin Invest. 119:305-14, 2009
13) Dunphy J, et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and HLA class II alleles in
minocycline-induced lupus-like syndrome. Br J Dermatol.142:461-7, 2000
14) Morita S, et al.: Anti-thyroid drug-induced ANCA-associated vasculitis: a case report
and review of the literature. Endocr J. 47:467-70, 2000
15)
Vogt
BA
et
al.:
Antineutrophil
cytoplasmic
autoantibody-positive
crescentic
glomerulonephritis as a complication of treatment with propylthiouracil in children. J
Pediatr. 124:986-8, 1994
16)
Chen
Y,
et
al.:
Clinico-pathological
features
and
outcomes
of
patients
with
propylthiouracil-associated ANCA vasculitis with renal involvement. J Nephrol. 27:159-64,
18