よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料3-3 メチルプレドニゾロンコハク酸エステルナトリウム (18 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/shingi2/0000198856_00026.html |
| 出典情報 | 医療上の必要性の高い未承認薬・適応外薬検討会議(第54回 2/15)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
の有無について
検討会議は、要望内容に関して不足しているエビデンスはないと判断した。
(2)上記(1)で臨床使用実態が不足している場合は、必要とされる使用実態調査等の内
容について
なし。
(3)その他、製造販売後における留意点について
なし。
10.備考
なし。
11.参考文献一覧
1)
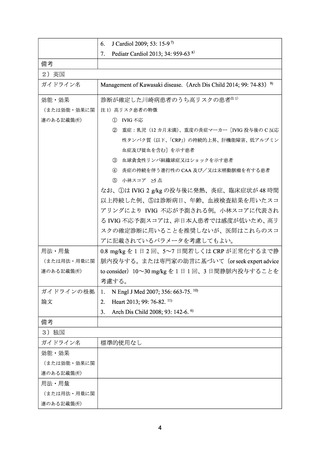
McCrindle BW, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease a
scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation
2017; 135: e1–73.
2)
Wallace CA, et al. Initial intravenous gammaglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease.
Pediatrics 2000; 105: E78.
3)
Wright DA, et al. Treatment of immune globulin-resistant Kawasaki disease with pulsed doses
of corticosteroids. J Pediatr 1996; 128: 146-9.
4)
Lang BA, et al. Corticosteroid treatment of refractory Kawasaki disease. J Rheumatol 2006; 33:
803–9.
5)
Miura M, et al. Steroid pulse therapy for Kawasaki disease unresponsive to additional
immunoglobulin therapy. Paediatr Child Health 2011; 16: 479-84.
6)
Furukawa T, et al. Effects of steroid pulse therapy on immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki
disease. Arch Dis Child 2008; 93: 142–6.
7)
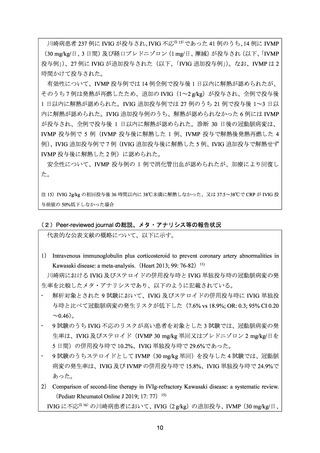
Ogata S, et al. The strategy of immune globulin resistant Kawasaki disease: A comparative study
of additional immune globulin and steroid pulse therapy. J Cardiol 2009; 53: 15–9.
8)
Teraguchi M, et al. Steroid pulse therapy for children with intravenous immunoglobulin therapyresistant Kawasaki disease: A prospective study. Pediatr Cardiol 2013; 34: 959–63.
9)
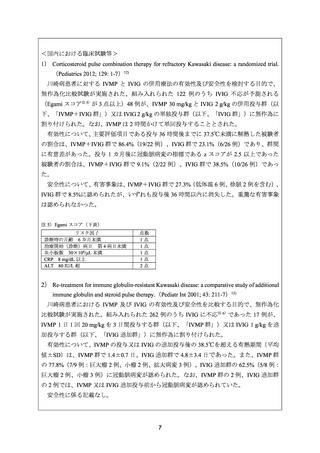
Eleftheriou D, et al. Management of Kawasaki disease. Arch Dis Child 2014; 99:7 4-83.
10) Newburger JW, et al. Randomized trial of pulsed corticosteroid therapy for primary treatment of
Kawasaki disease. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 663-75.
11) Chen S, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin plus corticosteroid to prevent coronary artery
abnormalities in Kawasaki disease: a meta-analysis. Heart 2013; 99: 76-82.
12) Ogata S, et al. Corticosteroid pulse combination therapy for refractory Kawasaki disease: A
18
検討会議は、要望内容に関して不足しているエビデンスはないと判断した。
(2)上記(1)で臨床使用実態が不足している場合は、必要とされる使用実態調査等の内
容について
なし。
(3)その他、製造販売後における留意点について
なし。
10.備考
なし。
11.参考文献一覧
1)
McCrindle BW, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease a
scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation
2017; 135: e1–73.
2)
Wallace CA, et al. Initial intravenous gammaglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease.
Pediatrics 2000; 105: E78.
3)
Wright DA, et al. Treatment of immune globulin-resistant Kawasaki disease with pulsed doses
of corticosteroids. J Pediatr 1996; 128: 146-9.
4)
Lang BA, et al. Corticosteroid treatment of refractory Kawasaki disease. J Rheumatol 2006; 33:
803–9.
5)
Miura M, et al. Steroid pulse therapy for Kawasaki disease unresponsive to additional
immunoglobulin therapy. Paediatr Child Health 2011; 16: 479-84.
6)
Furukawa T, et al. Effects of steroid pulse therapy on immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki
disease. Arch Dis Child 2008; 93: 142–6.
7)
Ogata S, et al. The strategy of immune globulin resistant Kawasaki disease: A comparative study
of additional immune globulin and steroid pulse therapy. J Cardiol 2009; 53: 15–9.
8)
Teraguchi M, et al. Steroid pulse therapy for children with intravenous immunoglobulin therapyresistant Kawasaki disease: A prospective study. Pediatr Cardiol 2013; 34: 959–63.
9)
Eleftheriou D, et al. Management of Kawasaki disease. Arch Dis Child 2014; 99:7 4-83.
10) Newburger JW, et al. Randomized trial of pulsed corticosteroid therapy for primary treatment of
Kawasaki disease. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 663-75.
11) Chen S, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin plus corticosteroid to prevent coronary artery
abnormalities in Kawasaki disease: a meta-analysis. Heart 2013; 99: 76-82.
12) Ogata S, et al. Corticosteroid pulse combination therapy for refractory Kawasaki disease: A
18