よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料3-3 ストラテラカプセル及びストラテラ内用液にて検出された新規ニトロソアミンの限度値について(企業見解)[7.8MB] (11 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_42464.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事審議会 医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和6年度第5回 8/28)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
pubs.acs.org/crt
Article
Quantum Mechanical Assessment of Nitrosamine Potency
Sriman De, Bishnu Thapa, Fareed Bhasha Sayyed,* Scott A. Frank, Paul D. Cornwell,
and Robert A. Jolly*
Cite This: Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1011−1022
Downloaded via ELI LILLY AND CO on August 14, 2024 at 22:23:48 (UTC).
See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles.
ACCESS
Read Online
Metrics & More
Article Recommendations
sı Supporting Information
*
ABSTRACT: Nitrosamines are in the cohort of concern (CoC) as
determined by regulatory guidance. CoC compounds are considered highly
potent carcinogens that need to be limited below the threshold of
toxicological concern, 1.5 μg/day. Nitrosamines like NDMA and NDEA
require strict control, while novel nitrosamine drug substance-related
impurities (NDSRIs) may or may not be characterized as potent
carcinogens. A risk assessment based on the structural features of NDSRIs
is important in order to predict potency because they lack substance-specific
carcinogenicity. Herein, we present a quantum mechanical (QM)-based
analysis on structurally diverse sets of nitrosamines to better understand how
structure influences the reactivity that could result in carcinogenicity. We
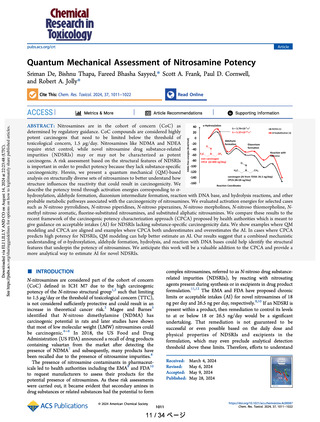
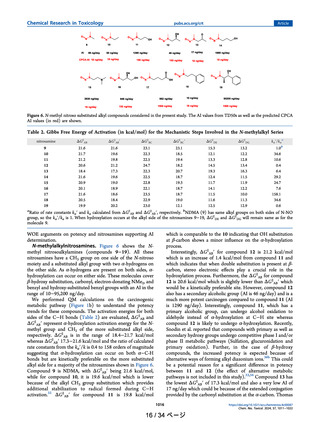
describe the potency trend through activation energies corresponding to αhydroxylation, aldehyde formation, diazonium intermediate formation, reaction with DNA base, and hydrolysis reactions, and other
probable metabolic pathways associated with the carcinogenicity of nitrosamines. We evaluated activation energies for selected cases
such as N-nitroso pyrrolidines, N-nitroso piperidines, N-nitroso piperazines, N-nitroso morpholines, N-nitroso thiomorpholine, Nmethyl nitroso aromatic, fluorine-substituted nitrosamines, and substituted aliphatic nitrosamines. We compare these results to the
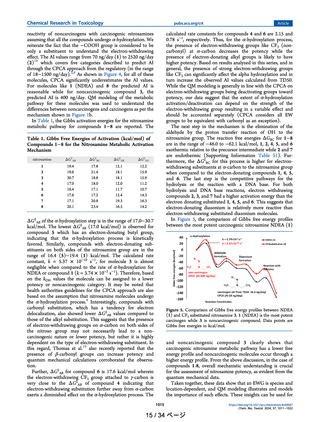
recent framework of the carcinogenic potency characterization approach (CPCA) proposed by health authorities which is meant to
give guidance on acceptable intakes (AI) for NDSRIs lacking substance-specific carcinogenicity data. We show examples where QM
modeling and CPCA are aligned and examples where CPCA both underestimates and overestimates the AI. In cases where CPCA
predicts high potency for NDSRIs, QM modeling can help better estimate an AI. Our results suggest that a combined mechanistic
understanding of α-hydroxylation, aldehyde formation, hydrolysis, and reaction with DNA bases could help identify the structural
features that underpin the potency of nitrosamines. We anticipate this work will be a valuable addition to the CPCA and provide a
more analytical way to estimate AI for novel NDSRIs.
■
INTRODUCTION
N-nitrosamines are considered part of the cohort of concern
(CoC) defined in ICH M7 due to the high carcinogenic
potency of the N-nitroso structural group1,2 such that limiting
to 1.5 μg/day or the threshold of toxicological concern (TTC),
is not considered sufficiently protective and could result in an
increase in theoretical cancer risk.2 Magee and Barnes3
identified that N-nitroso dimethylamine (NDMA) has
carcinogenic potential in rats and later studies have shown
that most of low molecular weight (LMW) nitrosamines could
be carcinogenic.4−6 In 2018, the US Food and Drug
Administration (US FDA) announced a recall of drug products
containing valsartan from the market after detecting the
presence of NDMA7 and subsequently, many products have
been recalled due to the presence of nitrosamine impurities.8
The presence of nitrosamine contaminants in pharmaceuticals led to health authorities including the EMA9 and FDA10
to request manufacturers to assess their products for the
potential presence of nitrosamines. As these risk assessments
were carried out, it became evident that secondary amines in
drug substances or related substances had the potential to form
© 2024 American Chemical Society
complex nitrosamines, referred to as N-nitroso drug substancerelated impurities (NDSRIs), by reacting with nitrosating
agents present during synthesis or in excipients in drug product
formulation.11,12 The EMA and FDA have proposed chronic
limits or acceptable intakes (AI) for novel nitrosamines of 18
ng per day and 26.5 ng per day, respectively.9,10 If an NDSRI is
present within a product, then remediation to control its levels
to at or below 18 or 26.5 ng/day would be a significant
undertaking. That remediation is not guaranteed to be
successful or even possible based on the daily dose and
physical properties of NDSRIs and excipients in the
formulation, which may even preclude analytical detection
threshold above these limits. Therefore, efforts to understand
Received: March 4, 2024
Revised: May 6, 2024
Accepted: May 9, 2024
Published: May 28, 2024
1011
11 / 34 ページ
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.4c00087
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1011−1022
Article
Quantum Mechanical Assessment of Nitrosamine Potency
Sriman De, Bishnu Thapa, Fareed Bhasha Sayyed,* Scott A. Frank, Paul D. Cornwell,
and Robert A. Jolly*
Cite This: Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1011−1022
Downloaded via ELI LILLY AND CO on August 14, 2024 at 22:23:48 (UTC).
See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles.
ACCESS
Read Online
Metrics & More
Article Recommendations
sı Supporting Information
*
ABSTRACT: Nitrosamines are in the cohort of concern (CoC) as
determined by regulatory guidance. CoC compounds are considered highly
potent carcinogens that need to be limited below the threshold of
toxicological concern, 1.5 μg/day. Nitrosamines like NDMA and NDEA
require strict control, while novel nitrosamine drug substance-related
impurities (NDSRIs) may or may not be characterized as potent
carcinogens. A risk assessment based on the structural features of NDSRIs
is important in order to predict potency because they lack substance-specific
carcinogenicity. Herein, we present a quantum mechanical (QM)-based
analysis on structurally diverse sets of nitrosamines to better understand how
structure influences the reactivity that could result in carcinogenicity. We
describe the potency trend through activation energies corresponding to αhydroxylation, aldehyde formation, diazonium intermediate formation, reaction with DNA base, and hydrolysis reactions, and other
probable metabolic pathways associated with the carcinogenicity of nitrosamines. We evaluated activation energies for selected cases
such as N-nitroso pyrrolidines, N-nitroso piperidines, N-nitroso piperazines, N-nitroso morpholines, N-nitroso thiomorpholine, Nmethyl nitroso aromatic, fluorine-substituted nitrosamines, and substituted aliphatic nitrosamines. We compare these results to the
recent framework of the carcinogenic potency characterization approach (CPCA) proposed by health authorities which is meant to
give guidance on acceptable intakes (AI) for NDSRIs lacking substance-specific carcinogenicity data. We show examples where QM
modeling and CPCA are aligned and examples where CPCA both underestimates and overestimates the AI. In cases where CPCA
predicts high potency for NDSRIs, QM modeling can help better estimate an AI. Our results suggest that a combined mechanistic
understanding of α-hydroxylation, aldehyde formation, hydrolysis, and reaction with DNA bases could help identify the structural
features that underpin the potency of nitrosamines. We anticipate this work will be a valuable addition to the CPCA and provide a
more analytical way to estimate AI for novel NDSRIs.
■
INTRODUCTION
N-nitrosamines are considered part of the cohort of concern
(CoC) defined in ICH M7 due to the high carcinogenic
potency of the N-nitroso structural group1,2 such that limiting
to 1.5 μg/day or the threshold of toxicological concern (TTC),
is not considered sufficiently protective and could result in an
increase in theoretical cancer risk.2 Magee and Barnes3
identified that N-nitroso dimethylamine (NDMA) has
carcinogenic potential in rats and later studies have shown
that most of low molecular weight (LMW) nitrosamines could
be carcinogenic.4−6 In 2018, the US Food and Drug
Administration (US FDA) announced a recall of drug products
containing valsartan from the market after detecting the
presence of NDMA7 and subsequently, many products have
been recalled due to the presence of nitrosamine impurities.8
The presence of nitrosamine contaminants in pharmaceuticals led to health authorities including the EMA9 and FDA10
to request manufacturers to assess their products for the
potential presence of nitrosamines. As these risk assessments
were carried out, it became evident that secondary amines in
drug substances or related substances had the potential to form
© 2024 American Chemical Society
complex nitrosamines, referred to as N-nitroso drug substancerelated impurities (NDSRIs), by reacting with nitrosating
agents present during synthesis or in excipients in drug product
formulation.11,12 The EMA and FDA have proposed chronic
limits or acceptable intakes (AI) for novel nitrosamines of 18
ng per day and 26.5 ng per day, respectively.9,10 If an NDSRI is
present within a product, then remediation to control its levels
to at or below 18 or 26.5 ng/day would be a significant
undertaking. That remediation is not guaranteed to be
successful or even possible based on the daily dose and
physical properties of NDSRIs and excipients in the
formulation, which may even preclude analytical detection
threshold above these limits. Therefore, efforts to understand
Received: March 4, 2024
Revised: May 6, 2024
Accepted: May 9, 2024
Published: May 28, 2024
1011
11 / 34 ページ
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.4c00087
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1011−1022