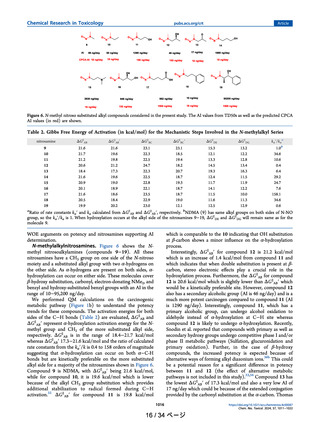
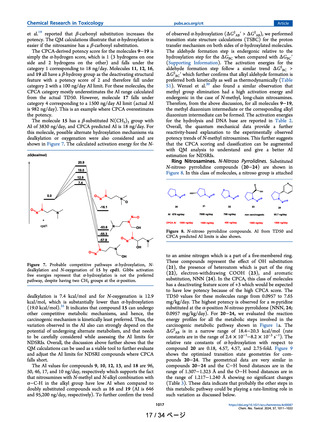
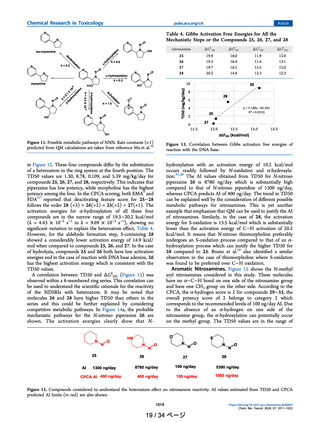
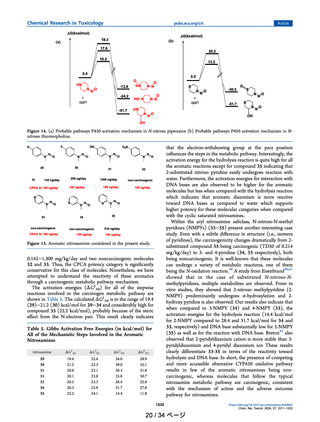
よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料3-3 ストラテラカプセル及びストラテラ内用液にて検出された新規ニトロソアミンの限度値について(企業見解)[7.8MB] (23 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_42464.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事審議会 医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和6年度第5回 8/28)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 152 (2024) 105672
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology
journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yrtph
Estimation of acceptable daily intake values based on modeling and in vivo
mutagenicity of NDSRIs of fluoxetine, duloxetine and atomoxetine
Robert A. Jolly a,* , Paul D. Cornwell a , Jessica Noteboom a , Fareed Bhasha Sayyed b,
Bishnu Thapa a, Lorrene A. Buckley a
a
b
Eli Lilly and Company, Inc. Indianapolis, IN, 46285, USA
Eli Lilly Services India Pvt Ltd, Bengaluru, 560103, India
A R T I C L E I N F O
A B S T R A C T
Handling Editor: Martin Van den berg
Nitrosamine drug substance related impurities or NDSRIs can be formed if an active pharmaceutical ingredient
(API) has an intrinsic secondary amine that can undergo nitrosation. This is a concern as 1) nitrosamines are
potentially highly potent carcinogens, 2) secondary amines in API are common, and 3) NDSRIs that might form
from such secondary amines will be of unknown carcinogenic potency. Approaches for evaluating NDSRIs
include read across, quantum mechanical modeling of reactivity, in vitro mutation data, and transgenic in vivo
mutation data. These approaches were used here to assess NDSRIs that could potentially form from the drugs
fluoxetine, duloxetine and atomoxetine. Based on a read across informed by modeling of physicochemical
properties and mechanistic activation from quantum mechanical modeling, NDSRIs of fluoxetine, duloxetine,
and atomoxetine were 10-100-fold less potent compared with highly potent nitrosamines such as NDMA or
NDEA. While the NDSRIs were all confirmed to be mutagenic in vitro (Ames assay) and in vivo (TGR) studies, the
latter data indicated that the potency of the mutation response was ≥4400 ng/day for all compounds-an order of
magnitude higher than published regulatory limits for these NDSRIs. The approaches described herein can be
used qualitatively to better categorize NDSRIs with respect to potency and inform whether they are in the ICH
M7 (R2) designated Cohort of Concern.
Keywords:
Nitrosamine
NDSRI
Risk assessment
Quantum mechanical modeling
Transgenic rodent assay
Mutagenicity
Acceptable intake
1. Introduction
Nitrosamine drug substance related impurities or NDSRIs, are a
significant issue for pharmaceutical manufacturers, as they can form
whenever an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or intermediate in
its synthetic route has an intrinsic secondary amine that can undergo
nitrosation (Moser et al., 2023; Schlingemann et al., 2022). Control of
NDSRIs is challenging because these impurities can form over the lifetime of a medicine (Nudelman et al., 2023) and are currently regulated
at very low limits. Recently the FDA and EMA have promoted the
carcinogenic potency categorization approach (CPCA; USFDA, 2023;
EMA, 2023) for assessment of NDSRIs. The CPCA is an algorithm
methodology promoted by health authorities for use in AI (Acceptable
Intake) determination using structural features of NDSRIs (Kruhlak
et al., 2024). While many NDSRIs are not potent carcinogens like low
molecular weight (LMW) nitrosamines (Thresher et al., 2020), the CPCA
nevertheless classifies many NDSRIs as being equivalent to or more
potent than NDEA or NDMA (USFDA, 2023; EMA, 2023). This level of
conservatism in setting acceptable limits overestimates the safety
concern and has led to unnecessary market withdrawals, as manufacturers struggle to meet stringent and possibly analytically unfeasible
limits for NDSRIs in their products (Nudelman et al., 2023; Burns et al.,
2023).
Read across approaches were initially used to estimate AIs for
NDSRIs. Embedded in such approaches are computational methods for
comparing both structure similarity and physicochemical properties.
However, the differences in MW and other properties between NDSRIs
and LMW nitrosamines are significant (Oliveiria et al., 2023), and simple 2-dimensional similarity or considering molecular weight alone may
overestimate the risk (Fine et al., 2023). Nonetheless, this methodology
was used holistically to find the best surrogate nitrosamine to a given
NDSRI to approximate an AI. Understanding of the mecshanism and
adverse outcome pathway for nitrosamines further allowed used of
quantum mechanical (QM) assessments of the steps of nitrosamine
* Corresponding author.
E-mail address: Jollyra@lilly.com (R.A. Jolly).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2024.105672
Received 1 May 2024; Received in revised form 19 June 2024; Accepted 28 June 2024
Available online 4 July 2024
0273-2300/© 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.
23 / 34 ページ
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology
journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yrtph
Estimation of acceptable daily intake values based on modeling and in vivo
mutagenicity of NDSRIs of fluoxetine, duloxetine and atomoxetine
Robert A. Jolly a,* , Paul D. Cornwell a , Jessica Noteboom a , Fareed Bhasha Sayyed b,
Bishnu Thapa a, Lorrene A. Buckley a
a
b
Eli Lilly and Company, Inc. Indianapolis, IN, 46285, USA
Eli Lilly Services India Pvt Ltd, Bengaluru, 560103, India
A R T I C L E I N F O
A B S T R A C T
Handling Editor: Martin Van den berg
Nitrosamine drug substance related impurities or NDSRIs can be formed if an active pharmaceutical ingredient
(API) has an intrinsic secondary amine that can undergo nitrosation. This is a concern as 1) nitrosamines are
potentially highly potent carcinogens, 2) secondary amines in API are common, and 3) NDSRIs that might form
from such secondary amines will be of unknown carcinogenic potency. Approaches for evaluating NDSRIs
include read across, quantum mechanical modeling of reactivity, in vitro mutation data, and transgenic in vivo
mutation data. These approaches were used here to assess NDSRIs that could potentially form from the drugs
fluoxetine, duloxetine and atomoxetine. Based on a read across informed by modeling of physicochemical
properties and mechanistic activation from quantum mechanical modeling, NDSRIs of fluoxetine, duloxetine,
and atomoxetine were 10-100-fold less potent compared with highly potent nitrosamines such as NDMA or
NDEA. While the NDSRIs were all confirmed to be mutagenic in vitro (Ames assay) and in vivo (TGR) studies, the
latter data indicated that the potency of the mutation response was ≥4400 ng/day for all compounds-an order of
magnitude higher than published regulatory limits for these NDSRIs. The approaches described herein can be
used qualitatively to better categorize NDSRIs with respect to potency and inform whether they are in the ICH
M7 (R2) designated Cohort of Concern.
Keywords:
Nitrosamine
NDSRI
Risk assessment
Quantum mechanical modeling
Transgenic rodent assay
Mutagenicity
Acceptable intake
1. Introduction
Nitrosamine drug substance related impurities or NDSRIs, are a
significant issue for pharmaceutical manufacturers, as they can form
whenever an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or intermediate in
its synthetic route has an intrinsic secondary amine that can undergo
nitrosation (Moser et al., 2023; Schlingemann et al., 2022). Control of
NDSRIs is challenging because these impurities can form over the lifetime of a medicine (Nudelman et al., 2023) and are currently regulated
at very low limits. Recently the FDA and EMA have promoted the
carcinogenic potency categorization approach (CPCA; USFDA, 2023;
EMA, 2023) for assessment of NDSRIs. The CPCA is an algorithm
methodology promoted by health authorities for use in AI (Acceptable
Intake) determination using structural features of NDSRIs (Kruhlak
et al., 2024). While many NDSRIs are not potent carcinogens like low
molecular weight (LMW) nitrosamines (Thresher et al., 2020), the CPCA
nevertheless classifies many NDSRIs as being equivalent to or more
potent than NDEA or NDMA (USFDA, 2023; EMA, 2023). This level of
conservatism in setting acceptable limits overestimates the safety
concern and has led to unnecessary market withdrawals, as manufacturers struggle to meet stringent and possibly analytically unfeasible
limits for NDSRIs in their products (Nudelman et al., 2023; Burns et al.,
2023).
Read across approaches were initially used to estimate AIs for
NDSRIs. Embedded in such approaches are computational methods for
comparing both structure similarity and physicochemical properties.
However, the differences in MW and other properties between NDSRIs
and LMW nitrosamines are significant (Oliveiria et al., 2023), and simple 2-dimensional similarity or considering molecular weight alone may
overestimate the risk (Fine et al., 2023). Nonetheless, this methodology
was used holistically to find the best surrogate nitrosamine to a given
NDSRI to approximate an AI. Understanding of the mecshanism and
adverse outcome pathway for nitrosamines further allowed used of
quantum mechanical (QM) assessments of the steps of nitrosamine
* Corresponding author.
E-mail address: Jollyra@lilly.com (R.A. Jolly).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2024.105672
Received 1 May 2024; Received in revised form 19 June 2024; Accepted 28 June 2024
Available online 4 July 2024
0273-2300/© 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.
23 / 34 ページ