よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料3-3 ストラテラカプセル及びストラテラ内用液にて検出された新規ニトロソアミンの限度値について(企業見解)[7.8MB] (25 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_42464.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事審議会 医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和6年度第5回 8/28)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
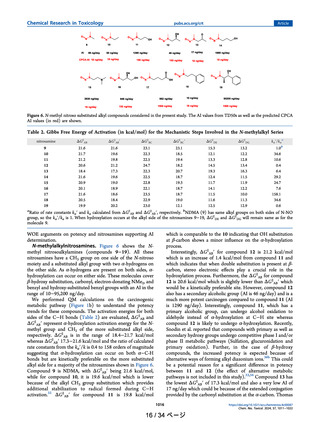
R.A. Jolly et al.
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 152 (2024) 105672
performs well for thermochemistry and reactivity of organic molecules
(Zhao and Truhlar, 2008; López-López and Ayala, 2016; Park and Kang,
2019; Walker et al., 2013; Mardirossian and Head-Gordon, 2016).
Vibrational frequency calculations were performed on the optimized
structures at M062X/6-31+G (d,p) level of theory to verify the optimized geometries are actual minima on the potential energy surface, and
therefore no negative frequencies are observed. Since the stretching
vibrational frequencies are well correlated with bond dissociation energies, which in turn are indicative of relative stability of the bond
(Finkelshtein, 1999), the C─N–
–N infrared stretching frequency of diazo
compounds was considered the QM descriptor and was correlated with
TD50 for all molecules.
v9.3.1. Statistical analyses were conducted on the log10-transformed
mutant frequencies for each tissue type separately. A test article was
considered positive for inducing cII gene mutations if.
2.3. Bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay
For positive test articles, a no-observed effect level (NOEL) for in vivo
mutagenicity was determined. In addition, a benchmark dose (BMD)
analysis of the mutation data was done using EPA software version 2.73.
The response rate was set at 0.5 standard deviations per EPA and EFSA
recommendations for endpoints of concern (Hardy et al., 2017; EPA,
2012). In this way, a Benchmark Dose-Low (Lower 95% confidence
limit; BMDL) was determined for each NDSRI. Tabular results of the
mutation and BMD data can be found in the supplementary material.
• it induced a statistically significant increase in the frequency of cII
gene mutants at any dose level compared with the concurrent
negative control,
• when evaluated for trend, the results were dose-related, and
• the mutant frequency in any treatment group was outside the upper
95% (>2 standard deviations across studies) control limit of the
historical negative control mutant frequency distribution for the
tissue type in this assay
NFLX, NATX, and NDLX were tested in the bacterial reverse mutation
(Ames) assay (BioReliance, Rockville, MD) or LabCorp (Harrogate, UK).
All testing was done per OECD 471 protocol (OECD 471 2022) and under
GLP compliance using five tester strains. Given that nitrosamines are
known to require metabolic activation, a twenty or 30-min preincubation was incorporated into the study design using both rat and
hamster S9 metabolic activation systems (10%) to ensure metabolic
competency of the assay. Acetonitrile was used as a vehicle.
3. Results
3.1. Computational assessments based on structure and physicochemical
properties
2.4. Transgenic rat mutagenicity (TGR) studies
The TGR study used transgenic F344 rats that contain multiple copies
of chromosomally integrated cII gene of the lambda bacteriophage
shuttle vector. The transgenes contain reporter genes for the detection of
various types of mutations induced in vivo by test chemicals (OECD 488
2022). All phases of the TGR studies were compliant with regulatory
guidelines (OECD 488 2022) and GLPs. A concurrent positive control
group treated with N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea was also included to verify the
validity of the assay. The dosing and live phases of the studies were
completed at Charles River Laboratory (Ashland, OH). NDSRIs were
administered to male and female (wild type) F344 rats in seven-day
range finding studies to determine maximally tolerated doses for the
subsequent 28-day mutagenicity studies. In the range finding studies,
rats were dosed at 30, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg, p.o. with the highest
dose being a limit dose according to the OECD 488 guideline. The liver
and duodenum are standard tissues assessed under the OECD 488
guideline which emphasizes the need to consider route of administration
and drug disposition in tissue selection. The liver is considered a relevant target for nitrosamine carcinogenicity as it is the primary site for
metabolic activation for NDSRIs, while the duodenum is relevant for
being a site of first contact following oral administration.
Based on the results of the range finding studies, male transgenic
F344 rats were treated with each NDSRI for 28 days at doses of
0 (vehicle), 0.1. 0.537, 5, 30 and 100 mg/kg p.o followed by a 3-day
washout period (OECD 488 2022). At termination, samples of liver
and duodenum were flash frozen, stored on dry ice and shipped to
Gentronix (Cheshire, UK) for DNA isolation and mutation frequency
analysis. The liver is the primary site of metabolism/bioactivation and
the tumor target tissue for nitrosamines, while duodenum is one of the
initially exposed tissues following the oral route of administration and
has a rapidly dividing cell population. Additionally, the liver is a primary concern for the carcinogenic response of many LMW ntirosamines.
DNA was extracted from frozen liver and duodenum samples based on
methods described for Agilent product RecoverEase™ (Agilent Technologies, 2018). Subsequent cII mutation frequency analysis was based
on the Agilent instruction manual ‘λ Select-cII Mutation Detection System for Big Blue Rodents’ (Agilent Technologies, 2015b), the Agilent
instruction manual ‘Transpack Packaging Extract for Lambda Transgenic Shuttle Vector Recovery’ (Agilent Technoliges, 2015a), and the
OECD 488 transgenic study protocol (OECD 488 2022).
Analysis of mutation data was performed using GraphPad Prism
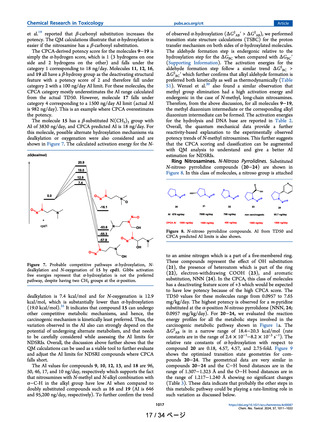
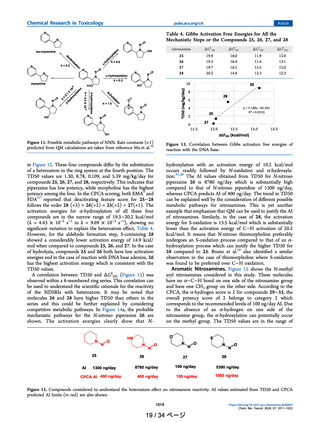
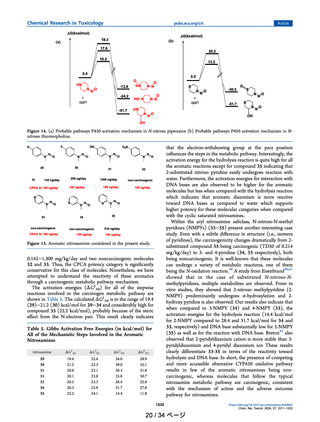
The NDSRIs were compared to other nitrosamine compounds in the
Lhasa database based on structure, substructure similarity, and selected
physiochemical properties. The results of those comparisons are shown
in Table 1. Using both Leadscope and QSARFlex, the closest nitrosamine
analogs in the Lhasa database were NNAL and NNK based purely on 2D
structure. The similarity scores based on local alert environment in
Table 1 (e.g. the alkyl nitrosamine) were higher than whole structure
similarity. NNAL and NNK remained the closest compounds to the
NDSRIs for substructure similarity though by not as wide a margin as for
whole structure similarity. Importantly, and as shown in Table 1, the
predicted LogP and predicted water solubility values were dramatically
different for NNAL and NNK when compared to the NDSRIs being
assessed. For an impurity of a drug given orally, solubility can be
considered especially important in terms of impacting potential exposure. Additionally, other physiochemical properties including molecular
weight, hydrogen bond donors, hydrogen bond acceptors, parent atoms,
molecular weight, polar surface area, and rotatable bonds were assessed
and also suggested that NNK and NNAL were not the best surrogates
(data not shown). Based on physicochemical properties and other similarity metrics, other nitrosamine compounds including alkylamines
such as N-nitroso N-methyl dodecylamine could reasonably be viewed as
better surrogates for potency to the NDSRIs. N-nitroso N-methyl dodecylamine has the lowest TD50 (0.537 mg/kg) among the nitroso alkylamines listed, and that value would result in an AI value of 537 ng per
day for these NDSRIs as described in ICH M7 (R2) (ICH, 2023).
Another more general approach to AI estimation was done by averaging the TD50 values of the most similar nitrosamines (n = 9) (Table 1).
The tenth compound, N-nitroso ephedrine, was removed, as its TD50 was
much higher than the other nitrosamines, and it was considered an
outlier. This exclusion of the TD50 of N-nitroso ephedrine significantly
decreased the average TD50 and thus provided a more conservative estimate of the average TD50 value. This assessment gave an average TD50
of approximately 1 mg/kg, ten-fold higher than the value for NNK.
While this approach cannot be considered analytical, it does give an
approximate AI for the nearest similar structures and supports a higher
overall AI. This analysis also highlights the challenges for estimating AIs
for NDSRI.
3
25 / 34 ページ
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 152 (2024) 105672
performs well for thermochemistry and reactivity of organic molecules
(Zhao and Truhlar, 2008; López-López and Ayala, 2016; Park and Kang,
2019; Walker et al., 2013; Mardirossian and Head-Gordon, 2016).
Vibrational frequency calculations were performed on the optimized
structures at M062X/6-31+G (d,p) level of theory to verify the optimized geometries are actual minima on the potential energy surface, and
therefore no negative frequencies are observed. Since the stretching
vibrational frequencies are well correlated with bond dissociation energies, which in turn are indicative of relative stability of the bond
(Finkelshtein, 1999), the C─N–
–N infrared stretching frequency of diazo
compounds was considered the QM descriptor and was correlated with
TD50 for all molecules.
v9.3.1. Statistical analyses were conducted on the log10-transformed
mutant frequencies for each tissue type separately. A test article was
considered positive for inducing cII gene mutations if.
2.3. Bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay
For positive test articles, a no-observed effect level (NOEL) for in vivo
mutagenicity was determined. In addition, a benchmark dose (BMD)
analysis of the mutation data was done using EPA software version 2.73.
The response rate was set at 0.5 standard deviations per EPA and EFSA
recommendations for endpoints of concern (Hardy et al., 2017; EPA,
2012). In this way, a Benchmark Dose-Low (Lower 95% confidence
limit; BMDL) was determined for each NDSRI. Tabular results of the
mutation and BMD data can be found in the supplementary material.
• it induced a statistically significant increase in the frequency of cII
gene mutants at any dose level compared with the concurrent
negative control,
• when evaluated for trend, the results were dose-related, and
• the mutant frequency in any treatment group was outside the upper
95% (>2 standard deviations across studies) control limit of the
historical negative control mutant frequency distribution for the
tissue type in this assay
NFLX, NATX, and NDLX were tested in the bacterial reverse mutation
(Ames) assay (BioReliance, Rockville, MD) or LabCorp (Harrogate, UK).
All testing was done per OECD 471 protocol (OECD 471 2022) and under
GLP compliance using five tester strains. Given that nitrosamines are
known to require metabolic activation, a twenty or 30-min preincubation was incorporated into the study design using both rat and
hamster S9 metabolic activation systems (10%) to ensure metabolic
competency of the assay. Acetonitrile was used as a vehicle.
3. Results
3.1. Computational assessments based on structure and physicochemical
properties
2.4. Transgenic rat mutagenicity (TGR) studies
The TGR study used transgenic F344 rats that contain multiple copies
of chromosomally integrated cII gene of the lambda bacteriophage
shuttle vector. The transgenes contain reporter genes for the detection of
various types of mutations induced in vivo by test chemicals (OECD 488
2022). All phases of the TGR studies were compliant with regulatory
guidelines (OECD 488 2022) and GLPs. A concurrent positive control
group treated with N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea was also included to verify the
validity of the assay. The dosing and live phases of the studies were
completed at Charles River Laboratory (Ashland, OH). NDSRIs were
administered to male and female (wild type) F344 rats in seven-day
range finding studies to determine maximally tolerated doses for the
subsequent 28-day mutagenicity studies. In the range finding studies,
rats were dosed at 30, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg, p.o. with the highest
dose being a limit dose according to the OECD 488 guideline. The liver
and duodenum are standard tissues assessed under the OECD 488
guideline which emphasizes the need to consider route of administration
and drug disposition in tissue selection. The liver is considered a relevant target for nitrosamine carcinogenicity as it is the primary site for
metabolic activation for NDSRIs, while the duodenum is relevant for
being a site of first contact following oral administration.
Based on the results of the range finding studies, male transgenic
F344 rats were treated with each NDSRI for 28 days at doses of
0 (vehicle), 0.1. 0.537, 5, 30 and 100 mg/kg p.o followed by a 3-day
washout period (OECD 488 2022). At termination, samples of liver
and duodenum were flash frozen, stored on dry ice and shipped to
Gentronix (Cheshire, UK) for DNA isolation and mutation frequency
analysis. The liver is the primary site of metabolism/bioactivation and
the tumor target tissue for nitrosamines, while duodenum is one of the
initially exposed tissues following the oral route of administration and
has a rapidly dividing cell population. Additionally, the liver is a primary concern for the carcinogenic response of many LMW ntirosamines.
DNA was extracted from frozen liver and duodenum samples based on
methods described for Agilent product RecoverEase™ (Agilent Technologies, 2018). Subsequent cII mutation frequency analysis was based
on the Agilent instruction manual ‘λ Select-cII Mutation Detection System for Big Blue Rodents’ (Agilent Technologies, 2015b), the Agilent
instruction manual ‘Transpack Packaging Extract for Lambda Transgenic Shuttle Vector Recovery’ (Agilent Technoliges, 2015a), and the
OECD 488 transgenic study protocol (OECD 488 2022).
Analysis of mutation data was performed using GraphPad Prism
The NDSRIs were compared to other nitrosamine compounds in the
Lhasa database based on structure, substructure similarity, and selected
physiochemical properties. The results of those comparisons are shown
in Table 1. Using both Leadscope and QSARFlex, the closest nitrosamine
analogs in the Lhasa database were NNAL and NNK based purely on 2D
structure. The similarity scores based on local alert environment in
Table 1 (e.g. the alkyl nitrosamine) were higher than whole structure
similarity. NNAL and NNK remained the closest compounds to the
NDSRIs for substructure similarity though by not as wide a margin as for
whole structure similarity. Importantly, and as shown in Table 1, the
predicted LogP and predicted water solubility values were dramatically
different for NNAL and NNK when compared to the NDSRIs being
assessed. For an impurity of a drug given orally, solubility can be
considered especially important in terms of impacting potential exposure. Additionally, other physiochemical properties including molecular
weight, hydrogen bond donors, hydrogen bond acceptors, parent atoms,
molecular weight, polar surface area, and rotatable bonds were assessed
and also suggested that NNK and NNAL were not the best surrogates
(data not shown). Based on physicochemical properties and other similarity metrics, other nitrosamine compounds including alkylamines
such as N-nitroso N-methyl dodecylamine could reasonably be viewed as
better surrogates for potency to the NDSRIs. N-nitroso N-methyl dodecylamine has the lowest TD50 (0.537 mg/kg) among the nitroso alkylamines listed, and that value would result in an AI value of 537 ng per
day for these NDSRIs as described in ICH M7 (R2) (ICH, 2023).
Another more general approach to AI estimation was done by averaging the TD50 values of the most similar nitrosamines (n = 9) (Table 1).
The tenth compound, N-nitroso ephedrine, was removed, as its TD50 was
much higher than the other nitrosamines, and it was considered an
outlier. This exclusion of the TD50 of N-nitroso ephedrine significantly
decreased the average TD50 and thus provided a more conservative estimate of the average TD50 value. This assessment gave an average TD50
of approximately 1 mg/kg, ten-fold higher than the value for NNK.
While this approach cannot be considered analytical, it does give an
approximate AI for the nearest similar structures and supports a higher
overall AI. This analysis also highlights the challenges for estimating AIs
for NDSRI.
3
25 / 34 ページ