よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料3-3 ストラテラカプセル及びストラテラ内用液にて検出された新規ニトロソアミンの限度値について(企業見解)[7.8MB] (19 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_42464.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事審議会 医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和6年度第5回 8/28)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
Chemical Research in Toxicology
pubs.acs.org/crt
Article
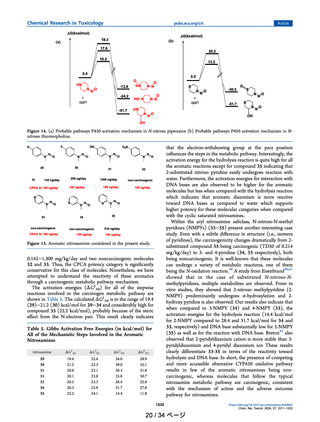
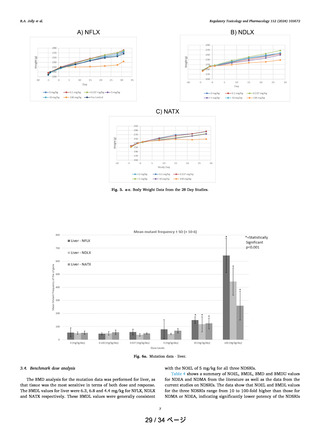
Table 4. Gibbs Activation Free Energies for All the
Mechanistic Steps or the Compounds 25, 26, 27, and 28
nitrosamine
ΔG‡AB
ΔG‡BC
ΔG‡DE
ΔG‡DG
25
26
27
28
19.9
19.3
19.7
20.2
16.0
16.4
16.5
14.9
11.9
11.4
13.5
13.3
12.0
13.1
12.0
12.3
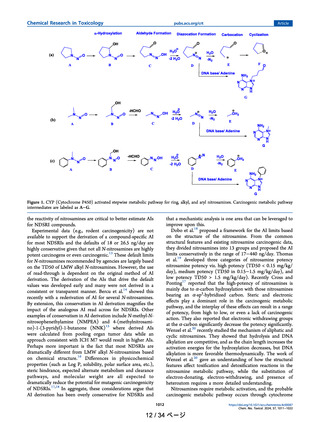
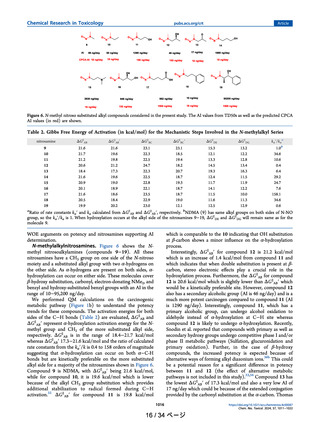
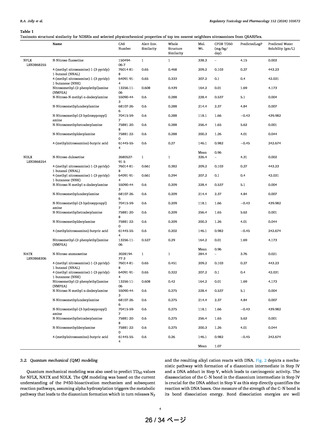
Figure 11. Possible metabolic pathways of NNN. Rate constants (s-1)
predicted from QM calculations are taken from reference Ma et al.28
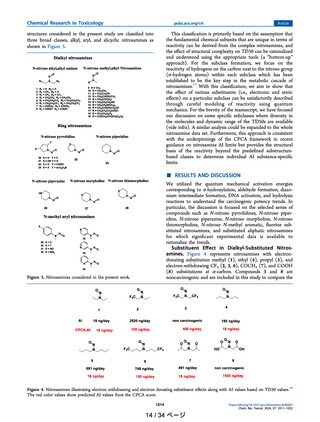
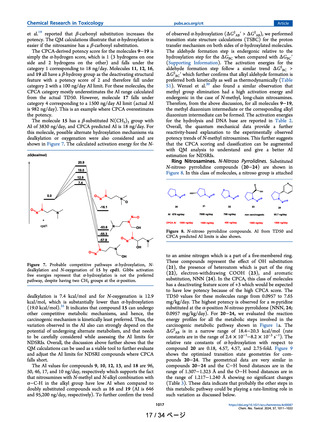
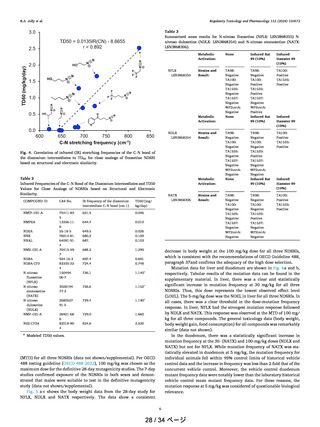
Figure 13. Correlation between Gibbs activation free energies of
reaction with the DNA base.
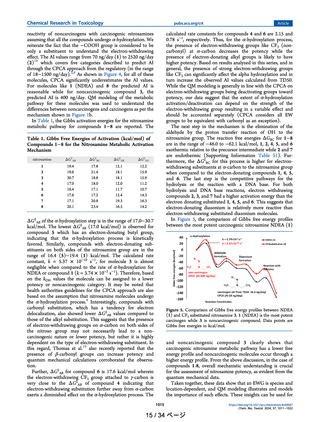
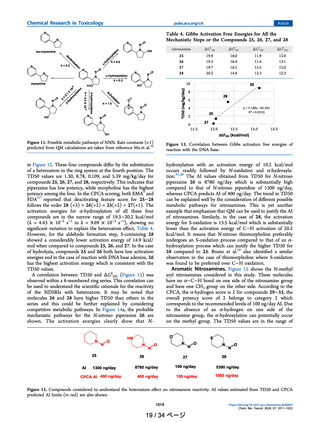
in Figure 12. These four compounds differ by the substitution
of a heteroatom in the ring system at the fourth position. The
TD50 values are 1.30, 8.78, 0.109, and 5.39 mg/kg/day for
compounds 25, 26, 27, and 28, respectively. This indicates that
piperazine has low potency, while morpholine has the highest
potency among the four. In the CPCA scoring, both EMA9 and
FDA22 reported that deactivating feature score for 25−28
follows the order 28 (+3) > 26(+2) = 25(+2) > 27(+1). The
activation energies for α-hydroxylation of all these four
compounds are in the narrow range of 19.3−20.2 kcal/mol
(k = 4.43 × 10−2 s−1 to k = 9.69 × 10−3 s−1), showing no
significant variation to explain the heteroatom effect, Table 4.
However, for the aldehyde formation step, S-containing 28
showed a considerably lower activation energy of 14.9 kcal/
mol when compared to compounds 25, 26, and 27. In the case
of hydrolysis, compounds 25 and 26 both have low activation
energies and in the case of reaction with DNA base adenine, 26
has the highest activation energy which is consistent with the
TD50 values.
A correlation between TD50 and ΔG‡DG (Figure 13) was
observed within a 6-membered ring series. This correlation can
be used to understand the scientific rationale for the reactivity
of the NDSRIs with heteroatom. It may be noted that
molecules 26 and 28 have higher TD50 than others in the
series and this could be further explained by considering
competitive metabolic pathways. In Figure 14a, the probable
mechanistic pathways for the N-nitroso piperazine 26 are
shown. The activation energies clearly show that N-
hydroxylation with an activation energy of 10.2 kcal/mol
occurs readily followed by N-oxidation and α-hydroxylation.37,38 The AI values obtained from TD50 for N-nitroso
piperazine 26 is 8780 ng/day which is substantially high
compared to that of N-nitroso piperidine of 1300 ng/day,
whereas CPCA predicts AI of 400 ng/day. The trend in TD50
can be explained well by the consideration of different possible
metabolic pathways for nitrosamines. This is yet another
example that emphasizes that QM can be used to justify the AI
of nitrosamines. Similarly, in the case of 28, the activation
energy for S-oxidation is 13.5 kcal/mol which is substantially
lower than the activation energy of C−H activation of 20.2
kcal/mol. It means that N-nitroso thiomorpholine preferably
undergoes an S-oxidation process compared to that of an αhydroxylation process which can justify the higher TD50 for
28 compared to 25. Bruno et al.39 also identified a similar
observation in the case of thiomorpholine where S-oxidation
was found to be preferred over C−H oxidation.
Aromatic Nitrosamines. Figure 15 shows the N-methyl
aryl nitrosamines considered in this study. These molecules
have no α−C−H bond on one side of the nitrosamine group
and have one CH3 group on the other side. According to the
CPCA, the α-hydrogen score is 2 for compounds 29−35, the
overall potency score of 2 belongs to category 2 which
corresponds to the recommended levels of 100 ng/day AI. Due
to the absence of an α-hydrogen on one side of the
nitrosamine group, the α-hydroxylation can potentially occur
on the methyl group. The TD50 values are in the range of
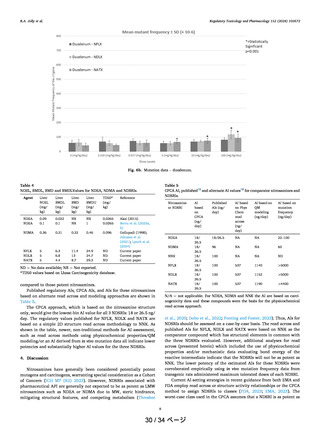
Figure 12. Compounds considered to understand the heteroatom effect on nitrosamine reactivity. AI values estimated from TD50 and CPCA
predicted AI limits (in red) are also shown.
1019
19 / 34 ページ
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.4c00087
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1011−1022
pubs.acs.org/crt
Article
Table 4. Gibbs Activation Free Energies for All the
Mechanistic Steps or the Compounds 25, 26, 27, and 28
nitrosamine
ΔG‡AB
ΔG‡BC
ΔG‡DE
ΔG‡DG
25
26
27
28
19.9
19.3
19.7
20.2
16.0
16.4
16.5
14.9
11.9
11.4
13.5
13.3
12.0
13.1
12.0
12.3
Figure 11. Possible metabolic pathways of NNN. Rate constants (s-1)
predicted from QM calculations are taken from reference Ma et al.28
Figure 13. Correlation between Gibbs activation free energies of
reaction with the DNA base.
in Figure 12. These four compounds differ by the substitution
of a heteroatom in the ring system at the fourth position. The
TD50 values are 1.30, 8.78, 0.109, and 5.39 mg/kg/day for
compounds 25, 26, 27, and 28, respectively. This indicates that
piperazine has low potency, while morpholine has the highest
potency among the four. In the CPCA scoring, both EMA9 and
FDA22 reported that deactivating feature score for 25−28
follows the order 28 (+3) > 26(+2) = 25(+2) > 27(+1). The
activation energies for α-hydroxylation of all these four
compounds are in the narrow range of 19.3−20.2 kcal/mol
(k = 4.43 × 10−2 s−1 to k = 9.69 × 10−3 s−1), showing no
significant variation to explain the heteroatom effect, Table 4.
However, for the aldehyde formation step, S-containing 28
showed a considerably lower activation energy of 14.9 kcal/
mol when compared to compounds 25, 26, and 27. In the case
of hydrolysis, compounds 25 and 26 both have low activation
energies and in the case of reaction with DNA base adenine, 26
has the highest activation energy which is consistent with the
TD50 values.
A correlation between TD50 and ΔG‡DG (Figure 13) was
observed within a 6-membered ring series. This correlation can
be used to understand the scientific rationale for the reactivity
of the NDSRIs with heteroatom. It may be noted that
molecules 26 and 28 have higher TD50 than others in the
series and this could be further explained by considering
competitive metabolic pathways. In Figure 14a, the probable
mechanistic pathways for the N-nitroso piperazine 26 are
shown. The activation energies clearly show that N-
hydroxylation with an activation energy of 10.2 kcal/mol
occurs readily followed by N-oxidation and α-hydroxylation.37,38 The AI values obtained from TD50 for N-nitroso
piperazine 26 is 8780 ng/day which is substantially high
compared to that of N-nitroso piperidine of 1300 ng/day,
whereas CPCA predicts AI of 400 ng/day. The trend in TD50
can be explained well by the consideration of different possible
metabolic pathways for nitrosamines. This is yet another
example that emphasizes that QM can be used to justify the AI
of nitrosamines. Similarly, in the case of 28, the activation
energy for S-oxidation is 13.5 kcal/mol which is substantially
lower than the activation energy of C−H activation of 20.2
kcal/mol. It means that N-nitroso thiomorpholine preferably
undergoes an S-oxidation process compared to that of an αhydroxylation process which can justify the higher TD50 for
28 compared to 25. Bruno et al.39 also identified a similar
observation in the case of thiomorpholine where S-oxidation
was found to be preferred over C−H oxidation.
Aromatic Nitrosamines. Figure 15 shows the N-methyl
aryl nitrosamines considered in this study. These molecules
have no α−C−H bond on one side of the nitrosamine group
and have one CH3 group on the other side. According to the
CPCA, the α-hydrogen score is 2 for compounds 29−35, the
overall potency score of 2 belongs to category 2 which
corresponds to the recommended levels of 100 ng/day AI. Due
to the absence of an α-hydrogen on one side of the
nitrosamine group, the α-hydroxylation can potentially occur
on the methyl group. The TD50 values are in the range of
Figure 12. Compounds considered to understand the heteroatom effect on nitrosamine reactivity. AI values estimated from TD50 and CPCA
predicted AI limits (in red) are also shown.
1019
19 / 34 ページ
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.4c00087
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1011−1022