よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料3-3 ストラテラカプセル及びストラテラ内用液にて検出された新規ニトロソアミンの限度値について(企業見解)[7.8MB] (13 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_42464.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事審議会 医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和6年度第5回 8/28)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
Chemical Research in Toxicology
pubs.acs.org/crt
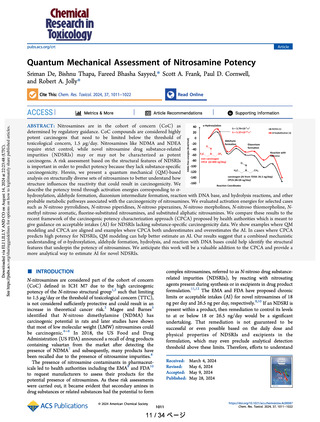
P450 and is shown in Figure 1.17,18,20,21 The mechanism
involves mainly through several steps viz. hydroxylation,
aldehyde formation, diazonium cation formation, hydrolysis,
or reaction with the DNA base. A detailed mechanistic
evaluation of these metabolic steps could help to further
develop and generate better AI estimates, and that is the intent
of the present work.
Health authorities have proposed guidance that read across
and other modeling approaches can be used to determine an
AI for NDSRIs.10 Most recently, agencies have published a
carcinogenic potency categorization approach (CPCA) framework to allow manufacturers to generate an AI for NDSRIs.9,22
The CPCA is fundamentally based on the assumption that
nitrosamines are carcinogenic via the α-hydroxylation mechanism. It may be noted that CPCA is applicable to
nitrosamines with α-carbon while it is not applicable to Nnitrosamides, N-nitrosoureas, N-nitrosoguanidines, or N-nitroso groups, which are part of the aromatic ring.
The CPCA is based on deriving a potency score based on
the α-hydrogen count and then adjusting for activating and
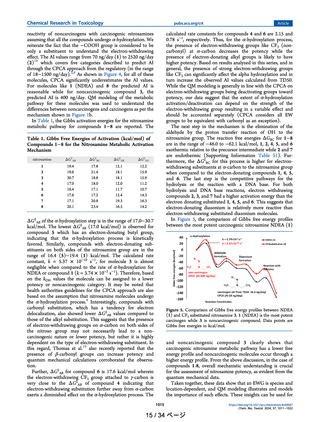
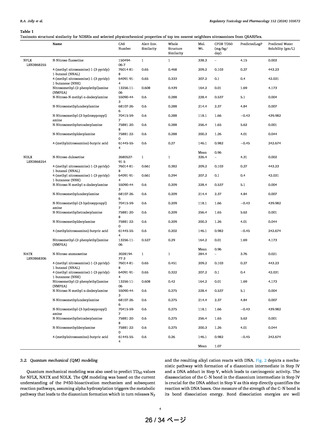
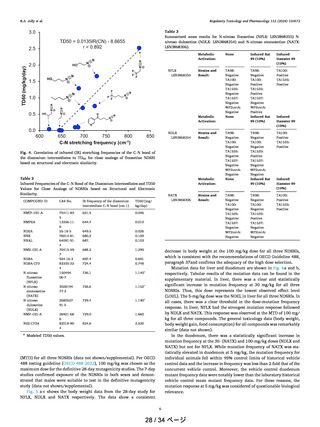
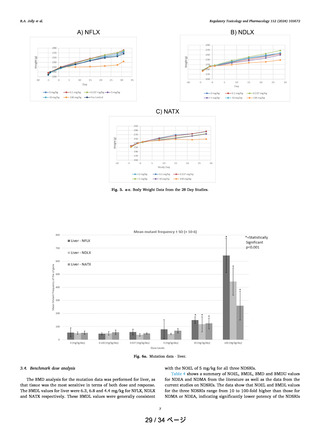
deactivating features. For Category 1, the AI is 18 ng/day, for
Category 2, the AI is 100 ng/day, for Category 3, the AI is 400
ng/day, for Categories 4 and 5, the AI limit is 1500 ng/day.
While a reasonable starting framework, the CPCA is largely
based on the simple structure read across and the structure−
activity relationships described by Cross and Ponting17 and
Dobo21 and is admittedly overly conservative in its AI
determinations. Some estimates indicate that as much as 30
percent of NDSRIs could default to high potency categories 1
and 2.23 Moreover, when CPCA was used to derive AI
nitrosamines against TD50, we observed a few compounds
where the AI was overestimated with the majority of AI values
being underestimated. In addition, several noncarcinogenic
molecules showed up as categories 2 and 3 in CPCA. This
underscores the inherent conservatism of the CPCA approach
and the need for an additional way to better approximate the
AI for NDSRIs in conjunction with the CPCA.
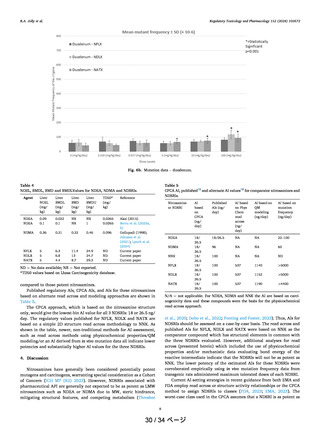
The focus of this work is to determine where clear
observations and trends in the mechanistic data can improve
AI assessments for NDSRIs. We demonstrate that carcinogenic
potency can be rationalized with QM-calculated activation
energies for various mechanistic steps involved in the
carcinogenic metabolic pathway corresponding to α-hydroxylation, aldehyde formation, diazonium intermediate formation, DNA activation, and hydrolysis reactions in N-nitroso
pyrrolidines, N-nitroso piperidine, N-nitroso piperazine, Nnitroso morpholine, N-nitroso thiomorpholine, N-methyl
nitroso aromatic, fluorine substituted nitrosamines and
substituted aliphatic nitrosamines. In the present work, we
consider molecules only with α-sp3 hybridized carbon on at
least one side of the N-nitroso group.
Article
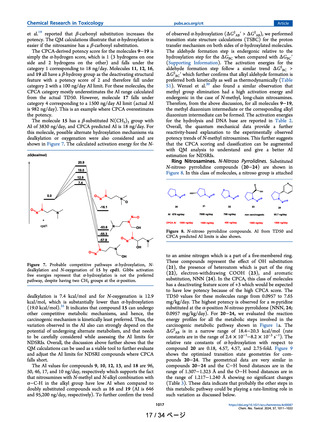
Figure 2. Model compound for P450 oxidation (cpd1).
method (BS1: C, H, N, O, S, F-6-31G(d) and Fe-LANL2DZ)
method with water as solvent employing SMD model.29,30
Further, single-point calculations were performed on the Fecomplexes at the B3LYP-D3BJ/BS-II level (BS-II: C, H, N, O,
S, F-6-31+G(d, p), and Fe-SDD). Based on the literature,28
data for the nitrosamine reactions involved with cpd1, the high
spin state was considered for molecules with alkyl/substituted
alkyl systems, and both low spin as well high spin were
considered for aromatic systems (Supporting Information).
The infrared (IR) frequency calculations were performed on all
the optimized geometries to verify the minima and the firstorder saddle points. Transition state structures were verified
with one imaginary frequency (NIMAG = 1) connecting
reactants and products and no imaginary frequencies for the
reactants, intermediates, and products (NIMAG = 0). The rate
constants are calculated using the below equation where kB is
the Boltzmann constant and h is Planck’s constant.31
k=
kBT
e
h
G‡ / RT
Throughout this article, Gibbs free energies are used for
discussion. In Figure 1, nitrosamine metabolic pathway
intermediates are labeled as A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. The
same notation was adopted to represent the Gibbs free
energies. For instance, ΔG‡AB represents the free energy of
activation for the α-hydroxylation reaction of A with cpd1.
ΔG‡BC represents the activation barrier for the aldehyde
formation step. ΔG‡DE and ΔG‡DG represent the free energy of
activation for hydrolysis and reaction with DNA base,
respectively. We considered adenine as a representative of
the DNA base to understand the reactivity of nitrosamines for
DNA alkylation.
Data Set. The data set for this study was curated from the
Lhasa Carcinogenicity Database (LCDB, carcdb.lhasalimited.org).13 From the available nitrosamines, only the secondary
nitrosamines (i.e., C−N(N�O)−C substructure) were
selected for further analysis. We excluded other classes of
compounds containing non-hydrogen heteroatoms at the α
position of the nitrosamine or carbonyl group such as
nitrosamide, nitrosacarbamate, nitrosourea, and other similar
classes that are known to be potentially mutagenic and/or
carcinogenic via different mechanisms. Additionally, compounds containing multiple nitroso groups were excluded from
the analysis. For the quantitative analysis related to the TD50,
the original TD50 values calculated by Gold et al. (herein
referred to as TD50) are used as a primary experimental
reference and the values derived by Lhasa Limited (herein
referred to as Lhasa TD50) are referenced as needed (both
available in LCDB). We selected only the molecules with
rodent in vivo data to avoid the discrepancy in data from
different species (discussed later in the Results and Discussion
section). Note that even within the data sets for rodents, there
is still some discrepancy (male versus female, two-dose range
versus multiple-dose range; tumour type, etc.). We considered
TD50 values from the work of Thomas et al.19 The common
■
COMPUTATIONAL DETAILS AND METHODOLOGY
All the computational calculations have been performed with
Gaussian 16 suite programs.24 All the structures are optimized
with B3LYP method with empirical dispersion correction
(D3BJ)25 and 6-31+G(d,p) level of theory.26,27 As a model
compound for the P450 oxidant, the truncated porphyrin Fecomplex (represented as cpd1) shown in Figure 2 is
considered. Previous reports suggested this model accurately
represents the P450 oxidant mechanism.28 The geometry
optimization as well as the transition state (TS) structures
involved with cpd1 were performed with the B3LYP/BS1
1013
13 / 34 ページ
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.4c00087
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1011−1022
pubs.acs.org/crt
P450 and is shown in Figure 1.17,18,20,21 The mechanism
involves mainly through several steps viz. hydroxylation,
aldehyde formation, diazonium cation formation, hydrolysis,
or reaction with the DNA base. A detailed mechanistic
evaluation of these metabolic steps could help to further
develop and generate better AI estimates, and that is the intent
of the present work.
Health authorities have proposed guidance that read across
and other modeling approaches can be used to determine an
AI for NDSRIs.10 Most recently, agencies have published a
carcinogenic potency categorization approach (CPCA) framework to allow manufacturers to generate an AI for NDSRIs.9,22
The CPCA is fundamentally based on the assumption that
nitrosamines are carcinogenic via the α-hydroxylation mechanism. It may be noted that CPCA is applicable to
nitrosamines with α-carbon while it is not applicable to Nnitrosamides, N-nitrosoureas, N-nitrosoguanidines, or N-nitroso groups, which are part of the aromatic ring.
The CPCA is based on deriving a potency score based on
the α-hydrogen count and then adjusting for activating and
deactivating features. For Category 1, the AI is 18 ng/day, for
Category 2, the AI is 100 ng/day, for Category 3, the AI is 400
ng/day, for Categories 4 and 5, the AI limit is 1500 ng/day.
While a reasonable starting framework, the CPCA is largely
based on the simple structure read across and the structure−
activity relationships described by Cross and Ponting17 and
Dobo21 and is admittedly overly conservative in its AI
determinations. Some estimates indicate that as much as 30
percent of NDSRIs could default to high potency categories 1
and 2.23 Moreover, when CPCA was used to derive AI
nitrosamines against TD50, we observed a few compounds
where the AI was overestimated with the majority of AI values
being underestimated. In addition, several noncarcinogenic
molecules showed up as categories 2 and 3 in CPCA. This
underscores the inherent conservatism of the CPCA approach
and the need for an additional way to better approximate the
AI for NDSRIs in conjunction with the CPCA.
The focus of this work is to determine where clear
observations and trends in the mechanistic data can improve
AI assessments for NDSRIs. We demonstrate that carcinogenic
potency can be rationalized with QM-calculated activation
energies for various mechanistic steps involved in the
carcinogenic metabolic pathway corresponding to α-hydroxylation, aldehyde formation, diazonium intermediate formation, DNA activation, and hydrolysis reactions in N-nitroso
pyrrolidines, N-nitroso piperidine, N-nitroso piperazine, Nnitroso morpholine, N-nitroso thiomorpholine, N-methyl
nitroso aromatic, fluorine substituted nitrosamines and
substituted aliphatic nitrosamines. In the present work, we
consider molecules only with α-sp3 hybridized carbon on at
least one side of the N-nitroso group.
Article
Figure 2. Model compound for P450 oxidation (cpd1).
method (BS1: C, H, N, O, S, F-6-31G(d) and Fe-LANL2DZ)
method with water as solvent employing SMD model.29,30
Further, single-point calculations were performed on the Fecomplexes at the B3LYP-D3BJ/BS-II level (BS-II: C, H, N, O,
S, F-6-31+G(d, p), and Fe-SDD). Based on the literature,28
data for the nitrosamine reactions involved with cpd1, the high
spin state was considered for molecules with alkyl/substituted
alkyl systems, and both low spin as well high spin were
considered for aromatic systems (Supporting Information).
The infrared (IR) frequency calculations were performed on all
the optimized geometries to verify the minima and the firstorder saddle points. Transition state structures were verified
with one imaginary frequency (NIMAG = 1) connecting
reactants and products and no imaginary frequencies for the
reactants, intermediates, and products (NIMAG = 0). The rate
constants are calculated using the below equation where kB is
the Boltzmann constant and h is Planck’s constant.31
k=
kBT
e
h
G‡ / RT
Throughout this article, Gibbs free energies are used for
discussion. In Figure 1, nitrosamine metabolic pathway
intermediates are labeled as A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. The
same notation was adopted to represent the Gibbs free
energies. For instance, ΔG‡AB represents the free energy of
activation for the α-hydroxylation reaction of A with cpd1.
ΔG‡BC represents the activation barrier for the aldehyde
formation step. ΔG‡DE and ΔG‡DG represent the free energy of
activation for hydrolysis and reaction with DNA base,
respectively. We considered adenine as a representative of
the DNA base to understand the reactivity of nitrosamines for
DNA alkylation.
Data Set. The data set for this study was curated from the
Lhasa Carcinogenicity Database (LCDB, carcdb.lhasalimited.org).13 From the available nitrosamines, only the secondary
nitrosamines (i.e., C−N(N�O)−C substructure) were
selected for further analysis. We excluded other classes of
compounds containing non-hydrogen heteroatoms at the α
position of the nitrosamine or carbonyl group such as
nitrosamide, nitrosacarbamate, nitrosourea, and other similar
classes that are known to be potentially mutagenic and/or
carcinogenic via different mechanisms. Additionally, compounds containing multiple nitroso groups were excluded from
the analysis. For the quantitative analysis related to the TD50,
the original TD50 values calculated by Gold et al. (herein
referred to as TD50) are used as a primary experimental
reference and the values derived by Lhasa Limited (herein
referred to as Lhasa TD50) are referenced as needed (both
available in LCDB). We selected only the molecules with
rodent in vivo data to avoid the discrepancy in data from
different species (discussed later in the Results and Discussion
section). Note that even within the data sets for rodents, there
is still some discrepancy (male versus female, two-dose range
versus multiple-dose range; tumour type, etc.). We considered
TD50 values from the work of Thomas et al.19 The common
■
COMPUTATIONAL DETAILS AND METHODOLOGY
All the computational calculations have been performed with
Gaussian 16 suite programs.24 All the structures are optimized
with B3LYP method with empirical dispersion correction
(D3BJ)25 and 6-31+G(d,p) level of theory.26,27 As a model
compound for the P450 oxidant, the truncated porphyrin Fecomplex (represented as cpd1) shown in Figure 2 is
considered. Previous reports suggested this model accurately
represents the P450 oxidant mechanism.28 The geometry
optimization as well as the transition state (TS) structures
involved with cpd1 were performed with the B3LYP/BS1
1013
13 / 34 ページ
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.4c00087
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1011−1022