よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料3-3 ストラテラカプセル及びストラテラ内用液にて検出された新規ニトロソアミンの限度値について(企業見解)[7.8MB] (30 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_42464.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事審議会 医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和6年度第5回 8/28)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
R.A. Jolly et al.
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 152 (2024) 105672
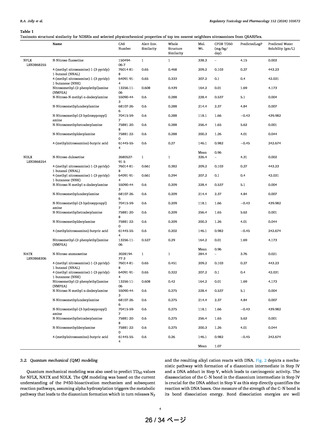
Fig. 6b. Mutation data – duodenum.
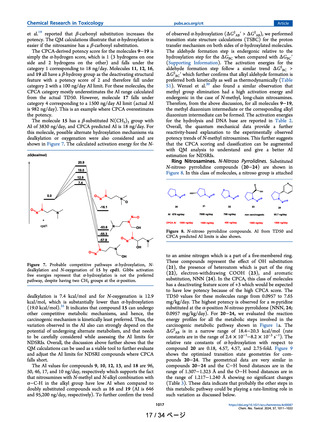
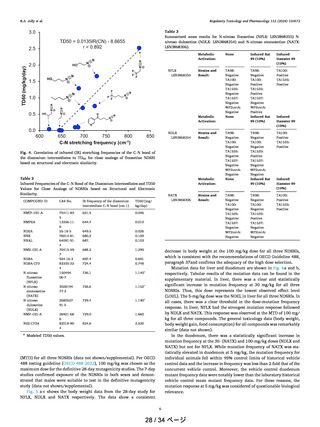
Table 4
NOEL, BMDL, BMD and BMDLValues for NDEA, NDMA and NDSRIs.
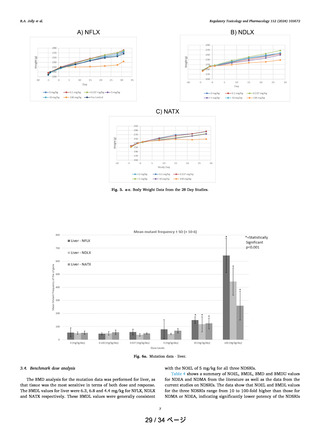
Table 5
CPCA AI, published21 and alternate AI values32 for comparator nitrosamines and
NDSRIs.
Agent
Liver
NOEL
(mg/
kg)
Liver
BMDL
(mg/
kg)
Liver
BMD
(mg/
kg)
Liver
BMDU
(mg/
kg)
TD50*
(mg/
kg)
Reference
NDEA
NDEA
0.09
0.1
0.022
0.1
NR
NR
NR
1
0.0265
0.0265
NDMA
0.36
0.21
0.32
0.46
0.096
NFLX
NDLX
NATX
5
5
5
6.3
6.8
4.4
11.4
13
8.7
24.9
24.7
29.3
ND
ND
ND
Akai (2015)
Bercu et al. (2023a,
b)
Gollupadi (1998);
Johnson et al.
(2021); Lynch et al.
(2024)
Current paper
Current paper
Current paper
Nitrosamine
or NDSRI
AI
based
on
CPCA
(ng/
day)
Published
AIs (ng/
day)
AI based
on Phys
Chem
read
across
(ng/
day)
AI based on
QM
modeling
(ng/day)
AI based on
mutation
frequency
(ng/day)
NDEA
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/26.5
NA
NA
22–100
96
NA
NA
60
100
NA
NA
ND
100
537
1140
>5000
100
537
1152
>5000
100
537
1190
>4400
NDMA
NNK
NFLX
ND = No data available; NR = Not reported.
*TD50 values based on Lhasa Carcinogenicity database.
NDLX
NATX
compared to those potent nitrosamines.
Published regulatory AIs, CPCA AIs, and AIs for these nitrosamines
based on alternate read across and modeling approaches are shown in
Table 5.
The CPCA approach, which is based on the nitrosamine structure
only, would give the lowest-bin AI value for all 3 NDSRIs: 18 or 26.5 ng/
day. The regulatory values published for NFLX, NDLX and NATX are
based on a simple 2D structure read across methodology to NNK. As
shown in the table, newer, non-traditional methods for AI assessment,
such as read across methods using physicochemical properties/QM
modeling/or an AI derived from in vivo mutation data all indicate lower
potencies and substantially higher AI values for the three NDSRIs.
N/A = not applicable. For NDEA, NDMA and NNK the AI are based on carcinogenicity data and these compounds were the basis for the physicochemical
read across approach.
et al., 2020; Dobo et al., 2022; Ponting and Foster, 2023). Thus, AIs for
NDSRIs should be assessed on a case-by-case basis. The read across and
published AIs for NFLX, NDLX and NATX were based on NNK as the
comparator compound which has structural elements in common with
the three NDSRIs evaluated. However, additional analyses for read
across (presented herein) which included the use of physicochemical
properties and/or mechanistic data evaluating bond energy of the
reactive intermediate indicate that the NDSRIs will not be as potent as
NNK. The lower potency of the estimated AIs for these NDSRIs were
corroborated empirically using in vivo mutation frequency data from
transgenic rats administered maximum tolerated doses of each NDSRI.
Current AI-setting strategies in recent guidance from both EMA and
FDA employ read across or structure activity relationships or the CPCA
method to assign NDSRIs to classes (FDA, 2023; EMA, 2023). The
worst-case class used in the CPCA assumes that a NDSRI is as potent as
4. Discussion
Nitrosamines have generally been considered potentially potent
mutagens and carcinogens, warranting special consideration as a Cohort
of Concern (ICH M7 (R2) 2023). However, NDSRIs associated with
pharmaceutical API are generally not expected to be as potent as LMW
nitrosamines such as NDEA or NDMA due to MW, steric hindrance,
mitigating structural features, and competing metabolism (Thresher
8
30 / 34 ページ
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 152 (2024) 105672
Fig. 6b. Mutation data – duodenum.
Table 4
NOEL, BMDL, BMD and BMDLValues for NDEA, NDMA and NDSRIs.
Table 5
CPCA AI, published21 and alternate AI values32 for comparator nitrosamines and
NDSRIs.
Agent
Liver
NOEL
(mg/
kg)
Liver
BMDL
(mg/
kg)
Liver
BMD
(mg/
kg)
Liver
BMDU
(mg/
kg)
TD50*
(mg/
kg)
Reference
NDEA
NDEA
0.09
0.1
0.022
0.1
NR
NR
NR
1
0.0265
0.0265
NDMA
0.36
0.21
0.32
0.46
0.096
NFLX
NDLX
NATX
5
5
5
6.3
6.8
4.4
11.4
13
8.7
24.9
24.7
29.3
ND
ND
ND
Akai (2015)
Bercu et al. (2023a,
b)
Gollupadi (1998);
Johnson et al.
(2021); Lynch et al.
(2024)
Current paper
Current paper
Current paper
Nitrosamine
or NDSRI
AI
based
on
CPCA
(ng/
day)
Published
AIs (ng/
day)
AI based
on Phys
Chem
read
across
(ng/
day)
AI based on
QM
modeling
(ng/day)
AI based on
mutation
frequency
(ng/day)
NDEA
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/
26.5
18/26.5
NA
NA
22–100
96
NA
NA
60
100
NA
NA
ND
100
537
1140
>5000
100
537
1152
>5000
100
537
1190
>4400
NDMA
NNK
NFLX
ND = No data available; NR = Not reported.
*TD50 values based on Lhasa Carcinogenicity database.
NDLX
NATX
compared to those potent nitrosamines.
Published regulatory AIs, CPCA AIs, and AIs for these nitrosamines
based on alternate read across and modeling approaches are shown in
Table 5.
The CPCA approach, which is based on the nitrosamine structure
only, would give the lowest-bin AI value for all 3 NDSRIs: 18 or 26.5 ng/
day. The regulatory values published for NFLX, NDLX and NATX are
based on a simple 2D structure read across methodology to NNK. As
shown in the table, newer, non-traditional methods for AI assessment,
such as read across methods using physicochemical properties/QM
modeling/or an AI derived from in vivo mutation data all indicate lower
potencies and substantially higher AI values for the three NDSRIs.
N/A = not applicable. For NDEA, NDMA and NNK the AI are based on carcinogenicity data and these compounds were the basis for the physicochemical
read across approach.
et al., 2020; Dobo et al., 2022; Ponting and Foster, 2023). Thus, AIs for
NDSRIs should be assessed on a case-by-case basis. The read across and
published AIs for NFLX, NDLX and NATX were based on NNK as the
comparator compound which has structural elements in common with
the three NDSRIs evaluated. However, additional analyses for read
across (presented herein) which included the use of physicochemical
properties and/or mechanistic data evaluating bond energy of the
reactive intermediate indicate that the NDSRIs will not be as potent as
NNK. The lower potency of the estimated AIs for these NDSRIs were
corroborated empirically using in vivo mutation frequency data from
transgenic rats administered maximum tolerated doses of each NDSRI.
Current AI-setting strategies in recent guidance from both EMA and
FDA employ read across or structure activity relationships or the CPCA
method to assign NDSRIs to classes (FDA, 2023; EMA, 2023). The
worst-case class used in the CPCA assumes that a NDSRI is as potent as
4. Discussion
Nitrosamines have generally been considered potentially potent
mutagens and carcinogens, warranting special consideration as a Cohort
of Concern (ICH M7 (R2) 2023). However, NDSRIs associated with
pharmaceutical API are generally not expected to be as potent as LMW
nitrosamines such as NDEA or NDMA due to MW, steric hindrance,
mitigating structural features, and competing metabolism (Thresher
8
30 / 34 ページ