よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料3-3 ストラテラカプセル及びストラテラ内用液にて検出された新規ニトロソアミンの限度値について(企業見解)[7.8MB] (26 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_42464.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事審議会 医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和6年度第5回 8/28)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
R.A. Jolly et al.
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 152 (2024) 105672
Table 1
Tanimoto structural similarity for NDSRIs and selected physicochemical properties of top ten nearest neighbors nitrosamines from QSARFlex.
NFLX
LSN3868255
Name
CAS
Number
Alert Env.
Similarity
Whole
Structure
Similarity
Mol.
Wt.
CPDB TD50
(mg/kg/
day)
PredictedLogP
Predicted Water
Solubility (gm/L)
N-Nitroso fluoxetine
15049406-7
76014-818
64091-914
13256-1106
55090-443
68107-266
70415-597
75881-208
75881-220
61445-554
1
1
338.3
–
4.15
0.003
0.65
0.468
209.2
0.103
0.27
443.23
0.65
0.333
207.2
0.1
0.4
42.031
0.608
0.439
164.2
0.01
1.69
4.173
0.6
0.288
228.4
0.537
5.1
0.004
0.6
0.288
214.4
2.37
4.84
0.007
0.6
0.288
118.1
1.66
− 0.43
439.982
0.6
0.288
256.4
1.65
5.63
0.001
0.6
0.288
200.3
1.26
4.01
0.044
0.6
0.27
146.1
0.982
− 0.45
242.674
268052791-5
76014-818
64091-914
55090-443
68107-266
70415-597
75881-208
75881-220
61445-554
13256-1106
1
1
Mean
326.4
0.96
–
4.31
0.002
0.661
0.382
209.2
0.103
0.27
443.23
0.661
0.294
207.2
0.1
0.4
42.031
0.6
0.209
228.4
0.537
5.1
0.004
0.6
0.209
214.4
2.37
4.84
0.007
0.6
0.209
118.1
1.66
− 0.43
439.982
0.6
0.209
256.4
1.65
5.63
0.001
0.6
0.209
200.3
1.26
4.01
0.044
0.6
0.202
146.1
0.982
− 0.45
242.674
0.527
0.29
164.2
0.01
1.69
4.173
302819477-3
76014-818
64091-914
13256-1106
55090-443
68107-266
70415-597
75881-208
75881-220
61445-554
1
1
Mean
284.4
0.96
–
3.76
0.021
0.65
0.451
209.2
0.103
0.27
443.23
0.65
0.322
207.2
0.1
0.4
42.031
0.608
0.42
164.2
0.01
1.69
4.173
0.6
0.275
228.4
0.537
5.1
0.004
0.6
0.275
214.4
2.37
4.84
0.007
0.6
0.275
118.1
1.66
− 0.43
439.982
0.6
0.275
256.4
1.65
5.63
0.001
0.6
0.275
200.3
1.26
4.01
0.044
0.6
0.26
146.1
0.982
− 0.45
242.674
Mean
1.07
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanol (NNAL)
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanone (NNK)
Nitrosomethyl-(2-phenylethyl)amine
(NMPEA)
N-Nitroso-N-methyl-n-dodecylamine
N-Nitrosomethylundecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyl-(3-hydroxypropyl)
amine
N-Nitrosomethyltetradecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyldecylamine
4-(methylnitrosoamino)-butyric acid
NDLX
LSN3868254
N-Nitroso duloxetine
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanol (NNAL)
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanone (NNK)
N-Nitroso-N-methyl-n-dodecylamine
N-Nitrosomethylundecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyl-(3-hydroxypropyl)
amine
N-Nitrosomethyltetradecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyldecylamine
4-(methylnitrosoamino)-butyric acid
Nitrosomethyl-(2-phenylethyl)amine
(NMPEA)
NATX
LSN3868306
N-Nitroso atomoxetine
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanol (NNAL)
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanone (NNK)
Nitrosomethyl-(2-phenylethyl)amine
(NMPEA)
N-Nitroso-N-methyl-n-dodecylamine
N-Nitrosomethylundecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyl-(3-hydroxypropyl)
amine
N-Nitrosomethyltetradecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyldecylamine
4-(methylnitrosoamino)-butyric acid
3.2. Quantum mechanical (QM) modeling
and the resulting alkyl cation reacts with DNA. Fig. 2 depicts a mechanistic pathway with formation of a diazonium intermediate in Step IV
and a DNA adduct in Step V, which leads to carcinogenic activity. The
disassociation of the C–N bond in the diazonium intermediate in Step IV
is crucial for the DNA adduct in Step V as this step directly quantifies the
reaction with DNA bases. One measure of the strength of the C–N bond is
its bond dissociation energy. Bond dissociation energies are well
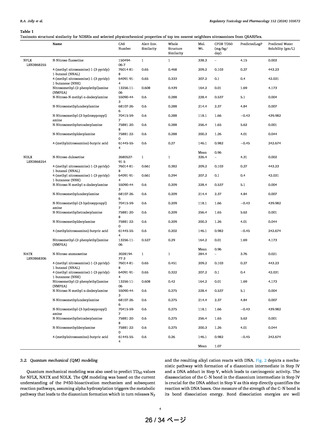
Quantum mechanical modeling was also used to predict TD50 values
for NFLX, NATX and NDLX. The QM modeling was based on the current
understanding of the P450-bioactivation mechanism and subsequent
reaction pathways, assuming alpha hydroxylation triggers the metabolic
pathway that leads to the diazonium formation which in turn releases N2
4
26 / 34 ページ
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 152 (2024) 105672
Table 1
Tanimoto structural similarity for NDSRIs and selected physicochemical properties of top ten nearest neighbors nitrosamines from QSARFlex.
NFLX
LSN3868255
Name
CAS
Number
Alert Env.
Similarity
Whole
Structure
Similarity
Mol.
Wt.
CPDB TD50
(mg/kg/
day)
PredictedLogP
Predicted Water
Solubility (gm/L)
N-Nitroso fluoxetine
15049406-7
76014-818
64091-914
13256-1106
55090-443
68107-266
70415-597
75881-208
75881-220
61445-554
1
1
338.3
–
4.15
0.003
0.65
0.468
209.2
0.103
0.27
443.23
0.65
0.333
207.2
0.1
0.4
42.031
0.608
0.439
164.2
0.01
1.69
4.173
0.6
0.288
228.4
0.537
5.1
0.004
0.6
0.288
214.4
2.37
4.84
0.007
0.6
0.288
118.1
1.66
− 0.43
439.982
0.6
0.288
256.4
1.65
5.63
0.001
0.6
0.288
200.3
1.26
4.01
0.044
0.6
0.27
146.1
0.982
− 0.45
242.674
268052791-5
76014-818
64091-914
55090-443
68107-266
70415-597
75881-208
75881-220
61445-554
13256-1106
1
1
Mean
326.4
0.96
–
4.31
0.002
0.661
0.382
209.2
0.103
0.27
443.23
0.661
0.294
207.2
0.1
0.4
42.031
0.6
0.209
228.4
0.537
5.1
0.004
0.6
0.209
214.4
2.37
4.84
0.007
0.6
0.209
118.1
1.66
− 0.43
439.982
0.6
0.209
256.4
1.65
5.63
0.001
0.6
0.209
200.3
1.26
4.01
0.044
0.6
0.202
146.1
0.982
− 0.45
242.674
0.527
0.29
164.2
0.01
1.69
4.173
302819477-3
76014-818
64091-914
13256-1106
55090-443
68107-266
70415-597
75881-208
75881-220
61445-554
1
1
Mean
284.4
0.96
–
3.76
0.021
0.65
0.451
209.2
0.103
0.27
443.23
0.65
0.322
207.2
0.1
0.4
42.031
0.608
0.42
164.2
0.01
1.69
4.173
0.6
0.275
228.4
0.537
5.1
0.004
0.6
0.275
214.4
2.37
4.84
0.007
0.6
0.275
118.1
1.66
− 0.43
439.982
0.6
0.275
256.4
1.65
5.63
0.001
0.6
0.275
200.3
1.26
4.01
0.044
0.6
0.26
146.1
0.982
− 0.45
242.674
Mean
1.07
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanol (NNAL)
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanone (NNK)
Nitrosomethyl-(2-phenylethyl)amine
(NMPEA)
N-Nitroso-N-methyl-n-dodecylamine
N-Nitrosomethylundecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyl-(3-hydroxypropyl)
amine
N-Nitrosomethyltetradecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyldecylamine
4-(methylnitrosoamino)-butyric acid
NDLX
LSN3868254
N-Nitroso duloxetine
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanol (NNAL)
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanone (NNK)
N-Nitroso-N-methyl-n-dodecylamine
N-Nitrosomethylundecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyl-(3-hydroxypropyl)
amine
N-Nitrosomethyltetradecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyldecylamine
4-(methylnitrosoamino)-butyric acid
Nitrosomethyl-(2-phenylethyl)amine
(NMPEA)
NATX
LSN3868306
N-Nitroso atomoxetine
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanol (NNAL)
4-(methyl nitrosoamine)-1-(3-pyridy)1-butanone (NNK)
Nitrosomethyl-(2-phenylethyl)amine
(NMPEA)
N-Nitroso-N-methyl-n-dodecylamine
N-Nitrosomethylundecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyl-(3-hydroxypropyl)
amine
N-Nitrosomethyltetradecylamine
N-Nitrosomethyldecylamine
4-(methylnitrosoamino)-butyric acid
3.2. Quantum mechanical (QM) modeling
and the resulting alkyl cation reacts with DNA. Fig. 2 depicts a mechanistic pathway with formation of a diazonium intermediate in Step IV
and a DNA adduct in Step V, which leads to carcinogenic activity. The
disassociation of the C–N bond in the diazonium intermediate in Step IV
is crucial for the DNA adduct in Step V as this step directly quantifies the
reaction with DNA bases. One measure of the strength of the C–N bond is
its bond dissociation energy. Bond dissociation energies are well
Quantum mechanical modeling was also used to predict TD50 values
for NFLX, NATX and NDLX. The QM modeling was based on the current
understanding of the P450-bioactivation mechanism and subsequent
reaction pathways, assuming alpha hydroxylation triggers the metabolic
pathway that leads to the diazonium formation which in turn releases N2
4
26 / 34 ページ