よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料1-2 調査結果報告書 (20 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_27607.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事・食品衛生審議会 薬事分科会医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和4年度第10回) |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
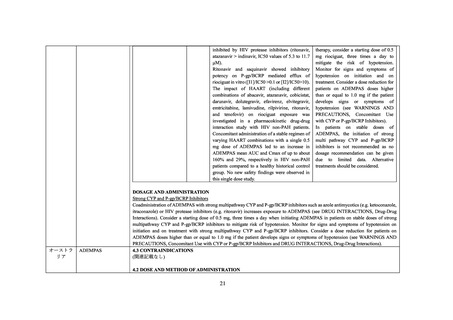
P-gp/BCRP Inhibitors).
Concomitant Use with CYP or P-gp/BCRP Inhibitors
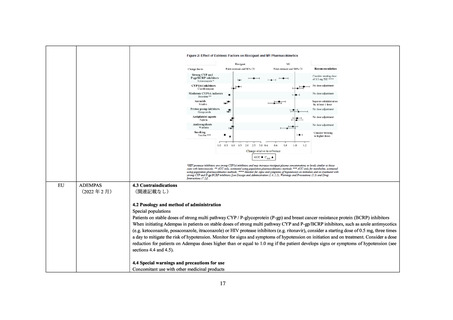
The concomitant use of ADEMPAS with strong multi pathway CYP and P-gp/BCRP inhibitors, such as azole antimycotics (eg,
ketoconazole, itraconazole), or HIV protease inhibitors (eg, ritonavir) results in a pronounced increase in riociguat exposure (see DRUG
INTERACTIONS, Drug-Drug Interactions), and may result in hypotension.
Assess the benefit-risk for each patient individually before prescribing ADEMPAS in patients on stable doses of strong multi pathway
CYP and P-gp/BCRP inhibitors. Consider a starting dose of 0.5 mg ADEMPAS, three times a day to mitigate the risk of hypotension.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of hypotension on initiation and on treatment and consider a dose reduction for patients on ADEMPAS
doses higher than or equal to 1.0 mg if the patient develops signs or symptoms of hypotension (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION,
Strong CYP and P-gp/BCRP Inhibitors and DRUG INTERACTIONS, Drug-Drug Interactions).
In patients on stable doses of ADEMPAS, the initiation of strong multi pathway CYP and P-gp/BCRP inhibitors is not recommended as
no dosage recommendation can be given due to limited data. Alternative treatments should be considered.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Overview
Effects of Riociguat on Other Substances
Effects of Other Substances on Riociguat
ADEMPAS is cleared mainly via biliary/direct fecal excretion of the unchanged drug, and renal excretion of the unchanged drug via
glomerular filtration. ADEMPAS is mainly catalysed to its main metabolite M1 by several CYP isoforms (CYP1A1, CYP2J2, CYP3A4,
CYP3A5). Based on in vitro studies, riociguat was found to be a substrate for the membrane transport proteins P-gp/BCRP. Inhibitors or
inducers of these enzymes or transporters may affect riociguat exposure.
Riociguat exhibits a reduced solubility at neutral pH vs. acidic medium. Co-medication of drugs increasing the upper gastro-intestinal pH
may lead to lower oral bioavailability.
Drug-Drug Interactions
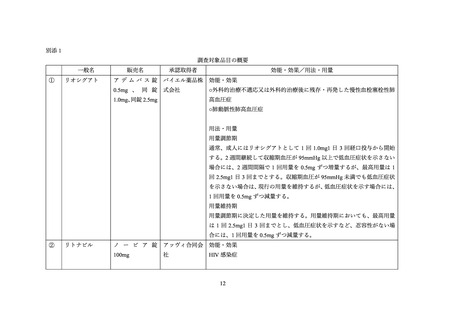
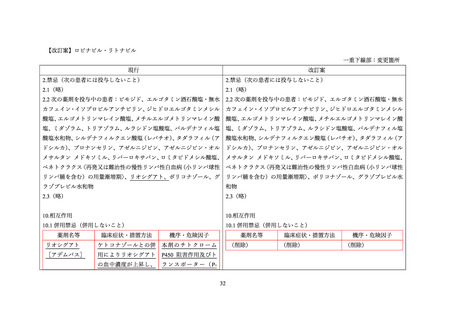
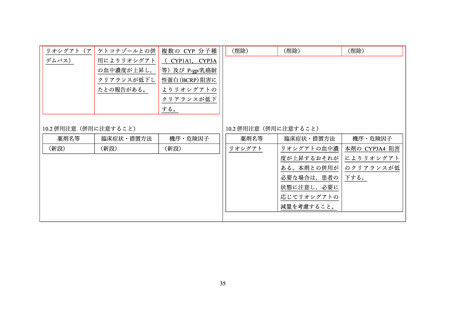
Table 5: Established or Potential Drug-Drug Interactions
Proper Name
Highly
active
antiretroviral
therapy
(HAART)
including
HIV protease inhibitors
Ref
I, CT
Effect
In vitro, abacavir, rilpivirine, efavirenz, ritonavir,
cobicistat and elvitegravir inhibited CYP1A1 and
the metabolism of riociguat in the order listed with
abacavir as the strongest inhibitor. Cobicistat,
ritonavir, atazanavir and darunavir are additionally
classified as CYP3A inhibitors.
In vitro, riociguat main metabolite M1 formation
in human liver microsomes was considerably
20
Clinical Comment
Due to limited clinical experience,
ADEMPAS and multi pathway CYP or
P-gp/BCRP inhibitors should be coadministered with caution.
When initiating ADEMPAS treatment in
patients on stable doses of strong multi
pathway
CYP
and
P-gp/BCRP
inhibitors, e.g. as contained in HAART
Concomitant Use with CYP or P-gp/BCRP Inhibitors
The concomitant use of ADEMPAS with strong multi pathway CYP and P-gp/BCRP inhibitors, such as azole antimycotics (eg,
ketoconazole, itraconazole), or HIV protease inhibitors (eg, ritonavir) results in a pronounced increase in riociguat exposure (see DRUG
INTERACTIONS, Drug-Drug Interactions), and may result in hypotension.
Assess the benefit-risk for each patient individually before prescribing ADEMPAS in patients on stable doses of strong multi pathway
CYP and P-gp/BCRP inhibitors. Consider a starting dose of 0.5 mg ADEMPAS, three times a day to mitigate the risk of hypotension.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of hypotension on initiation and on treatment and consider a dose reduction for patients on ADEMPAS
doses higher than or equal to 1.0 mg if the patient develops signs or symptoms of hypotension (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION,
Strong CYP and P-gp/BCRP Inhibitors and DRUG INTERACTIONS, Drug-Drug Interactions).
In patients on stable doses of ADEMPAS, the initiation of strong multi pathway CYP and P-gp/BCRP inhibitors is not recommended as
no dosage recommendation can be given due to limited data. Alternative treatments should be considered.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Overview
Effects of Riociguat on Other Substances
Effects of Other Substances on Riociguat
ADEMPAS is cleared mainly via biliary/direct fecal excretion of the unchanged drug, and renal excretion of the unchanged drug via
glomerular filtration. ADEMPAS is mainly catalysed to its main metabolite M1 by several CYP isoforms (CYP1A1, CYP2J2, CYP3A4,
CYP3A5). Based on in vitro studies, riociguat was found to be a substrate for the membrane transport proteins P-gp/BCRP. Inhibitors or
inducers of these enzymes or transporters may affect riociguat exposure.
Riociguat exhibits a reduced solubility at neutral pH vs. acidic medium. Co-medication of drugs increasing the upper gastro-intestinal pH
may lead to lower oral bioavailability.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Table 5: Established or Potential Drug-Drug Interactions
Proper Name
Highly
active
antiretroviral
therapy
(HAART)
including
HIV protease inhibitors
Ref
I, CT
Effect
In vitro, abacavir, rilpivirine, efavirenz, ritonavir,
cobicistat and elvitegravir inhibited CYP1A1 and
the metabolism of riociguat in the order listed with
abacavir as the strongest inhibitor. Cobicistat,
ritonavir, atazanavir and darunavir are additionally
classified as CYP3A inhibitors.
In vitro, riociguat main metabolite M1 formation
in human liver microsomes was considerably
20
Clinical Comment
Due to limited clinical experience,
ADEMPAS and multi pathway CYP or
P-gp/BCRP inhibitors should be coadministered with caution.
When initiating ADEMPAS treatment in
patients on stable doses of strong multi
pathway
CYP
and
P-gp/BCRP
inhibitors, e.g. as contained in HAART