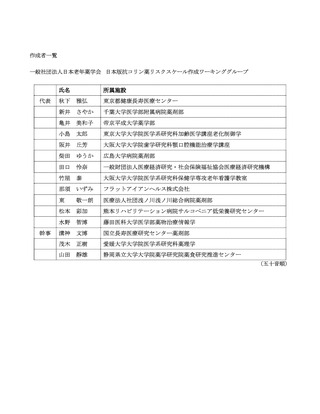
よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
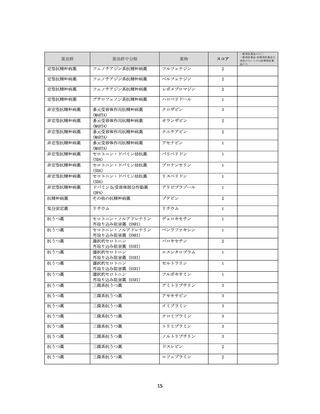
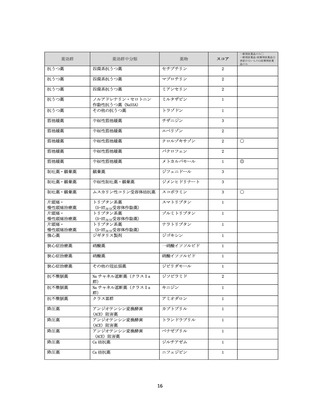
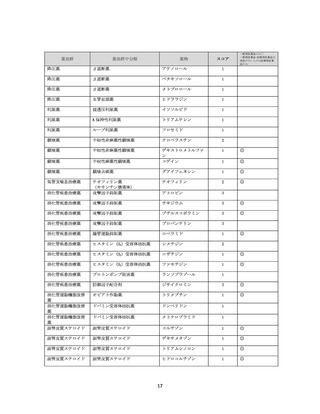
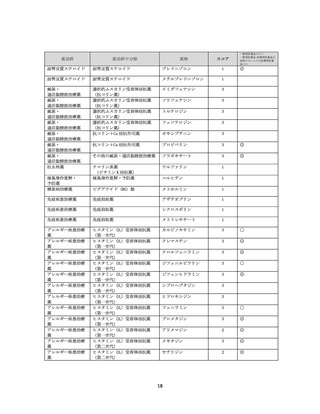
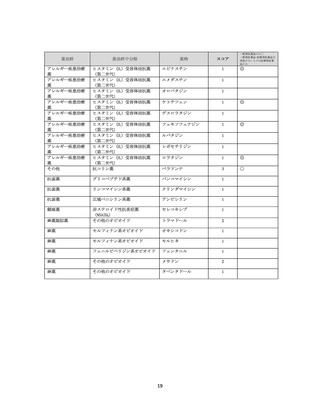
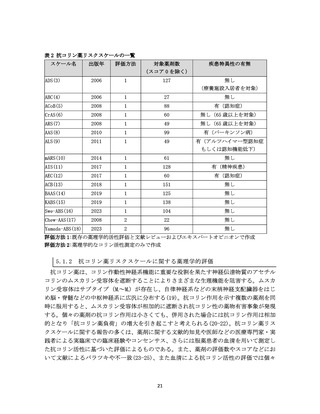
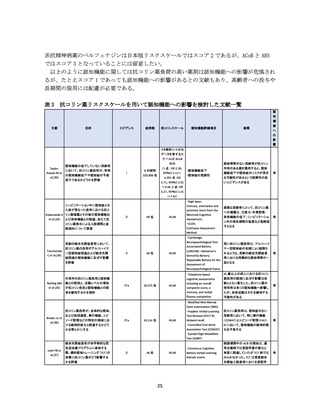
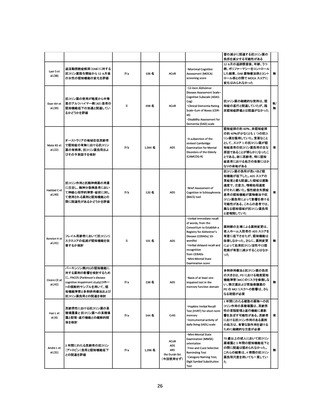
資料4-2 日本版抗コリン薬リスクスケール (38 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_40741.html |
| 出典情報 | 高齢者医薬品適正使用検討会(第18回 6/21)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
7
引用文献
1.
Hanlon P, Quinn TJ, Gallacher KI, Myint PK, Jani BD, Nicholl BI, et al. Assessing risks of polypharmacy
involving medications with anticholinergic properties. The Annals of Family Medicine. 2020;18(2):148-55.
2.
Gray SL, Anderson ML, Dublin S, Hanlon JT, Hubbard R, Walker R, et al. Cumulative use of strong
anticholinergics and incident dementia: a prospective cohort study. JAMA internal medicine.
2015;175(3):401-7.
3.
Carnahan RM, Lund BC, Perry PJ, Pollock BG, Culp KR. The anticholinergic drug scale as a measure of
drug‐related anticholinergic burden: associations with serum anticholinergic activity. The Journal of Clinical
Pharmacology. 2006;46(12):1481-6.
4.
Ancelin ML, Artero S, Portet F, Dupuy A-M, Touchon J, Ritchie K. Non-degenerative mild cognitive
impairment in elderly people and use of anticholinergic drugs: longitudinal cohort study. Bmj.
2006;332(7539):455-9.
5.
Boustani M, Campbell N, Munger S, Maidment I, Fox C. Impact of anticholinergics on the aging
brain: a review and practical application. 2008.
6.
Han L, Agostini JV, Allore HG. Cumulative anticholinergic exposure is associated with poor memory
and executive function in older men. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(12):2203-10.
7.
Rudolph JL, Salow MJ, Angelini MC, McGlinchey RE. The anticholinergic risk scale and
anticholinergic adverse effects in older persons. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2008;168(5):508-13.
8.
Ehrt U, Broich K, Larsen JP, Ballard C, Aarsland D. Use of drugs with anticholinergic effect and
impact on cognition in Parkinson's disease: a cohort study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
2010;81(2):160-5.
9.
Sittironnarit G, Ames D, Bush AI, Faux N, Flicker L, Foster J, et al. Effects of anticholinergic drugs on
cognitive function in older Australians: results from the AIBL study. Dementia and geriatric cognitive
disorders. 2011;31(3):173-8.
10.
Sumukadas D, McMurdo ME, Mangoni AA, Guthrie B. Temporal trends in anticholinergic
medication prescription in older people: repeated cross-sectional analysis of population prescribing data.
Age and ageing. 2014;43(4):515-21.
11.
Briet J, Javelot H, Heitzmann E, Weiner L, Lameira C, D'Athis P, et al. The anticholinergic
impregnation scale: Towards the elaboration of a scale adapted to prescriptions in French psychiatric
settings. Therapie. 2017;72(4):427-37.
12.
Bishara D, Harwood D, Sauer J, Taylor DM. Anticholinergic effect on cognition (AEC) of drugs
commonly used in older people. International journal of geriatric psychiatry. 2017;32(6):650-6.
13.
Kiesel EK, Hopf YM, Drey M. An anticholinergic burden score for German prescribers: score
development. BMC Geriatr. 2018;18(1):239.
14.
Nery RT, Reis AMM. Development of a Brazilian anticholinergic activity drug scale. Einstein (Sao
Paulo). 2019;17(2):eAO4435.
15.
Jun K, Hwang S, Ah YM, Suh Y, Lee JY. Development of an Anticholinergic Burden Scale specific for
Korean older adults. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2019;19(7):628-34.
16.
Rube T, Ecorcheville A, Londos E, Modig S, Johansson P. Development of the Swedish
anticholinergic burden scale (Swe-ABS). BMC geriatrics. 2023;23(1):518.
17.
Chew ML, Mulsant BH, Pollock BG, Lehman ME, Greenspan A, Mahmoud RA, et al. Anticholinergic
activity of 107 medications commonly used by older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(7):1333-41.
18.
Yamada S, Mochizuki M, Chimoto J, Futokoro R, Kagota S, Shinozuka K. Development of a
pharmacological evidence‐based anticholinergic burden scale for medications commonly used in older
adults. Geriatrics & Gerontology International. 2023;23(7):558-64.
38
引用文献
1.
Hanlon P, Quinn TJ, Gallacher KI, Myint PK, Jani BD, Nicholl BI, et al. Assessing risks of polypharmacy
involving medications with anticholinergic properties. The Annals of Family Medicine. 2020;18(2):148-55.
2.
Gray SL, Anderson ML, Dublin S, Hanlon JT, Hubbard R, Walker R, et al. Cumulative use of strong
anticholinergics and incident dementia: a prospective cohort study. JAMA internal medicine.
2015;175(3):401-7.
3.
Carnahan RM, Lund BC, Perry PJ, Pollock BG, Culp KR. The anticholinergic drug scale as a measure of
drug‐related anticholinergic burden: associations with serum anticholinergic activity. The Journal of Clinical
Pharmacology. 2006;46(12):1481-6.
4.
Ancelin ML, Artero S, Portet F, Dupuy A-M, Touchon J, Ritchie K. Non-degenerative mild cognitive
impairment in elderly people and use of anticholinergic drugs: longitudinal cohort study. Bmj.
2006;332(7539):455-9.
5.
Boustani M, Campbell N, Munger S, Maidment I, Fox C. Impact of anticholinergics on the aging
brain: a review and practical application. 2008.
6.
Han L, Agostini JV, Allore HG. Cumulative anticholinergic exposure is associated with poor memory
and executive function in older men. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(12):2203-10.
7.
Rudolph JL, Salow MJ, Angelini MC, McGlinchey RE. The anticholinergic risk scale and
anticholinergic adverse effects in older persons. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2008;168(5):508-13.
8.
Ehrt U, Broich K, Larsen JP, Ballard C, Aarsland D. Use of drugs with anticholinergic effect and
impact on cognition in Parkinson's disease: a cohort study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
2010;81(2):160-5.
9.
Sittironnarit G, Ames D, Bush AI, Faux N, Flicker L, Foster J, et al. Effects of anticholinergic drugs on
cognitive function in older Australians: results from the AIBL study. Dementia and geriatric cognitive
disorders. 2011;31(3):173-8.
10.
Sumukadas D, McMurdo ME, Mangoni AA, Guthrie B. Temporal trends in anticholinergic
medication prescription in older people: repeated cross-sectional analysis of population prescribing data.
Age and ageing. 2014;43(4):515-21.
11.
Briet J, Javelot H, Heitzmann E, Weiner L, Lameira C, D'Athis P, et al. The anticholinergic
impregnation scale: Towards the elaboration of a scale adapted to prescriptions in French psychiatric
settings. Therapie. 2017;72(4):427-37.
12.
Bishara D, Harwood D, Sauer J, Taylor DM. Anticholinergic effect on cognition (AEC) of drugs
commonly used in older people. International journal of geriatric psychiatry. 2017;32(6):650-6.
13.
Kiesel EK, Hopf YM, Drey M. An anticholinergic burden score for German prescribers: score
development. BMC Geriatr. 2018;18(1):239.
14.
Nery RT, Reis AMM. Development of a Brazilian anticholinergic activity drug scale. Einstein (Sao
Paulo). 2019;17(2):eAO4435.
15.
Jun K, Hwang S, Ah YM, Suh Y, Lee JY. Development of an Anticholinergic Burden Scale specific for
Korean older adults. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2019;19(7):628-34.
16.
Rube T, Ecorcheville A, Londos E, Modig S, Johansson P. Development of the Swedish
anticholinergic burden scale (Swe-ABS). BMC geriatrics. 2023;23(1):518.
17.
Chew ML, Mulsant BH, Pollock BG, Lehman ME, Greenspan A, Mahmoud RA, et al. Anticholinergic
activity of 107 medications commonly used by older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(7):1333-41.
18.
Yamada S, Mochizuki M, Chimoto J, Futokoro R, Kagota S, Shinozuka K. Development of a
pharmacological evidence‐based anticholinergic burden scale for medications commonly used in older
adults. Geriatrics & Gerontology International. 2023;23(7):558-64.
38