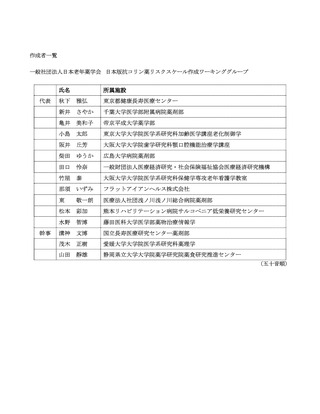
よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
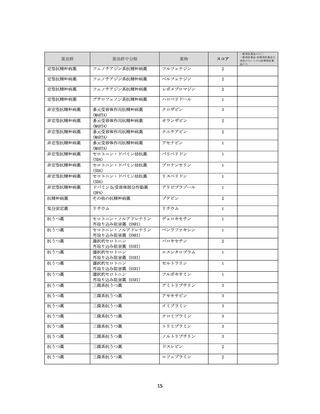
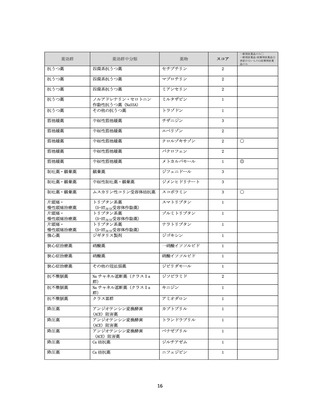
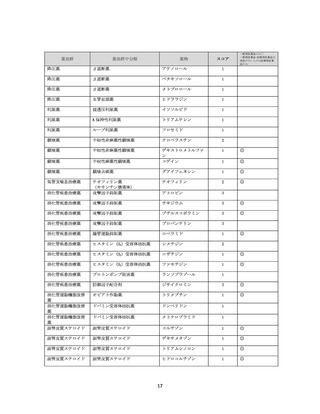
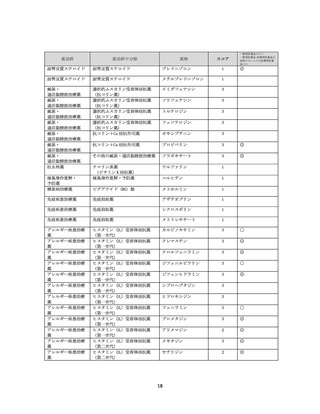
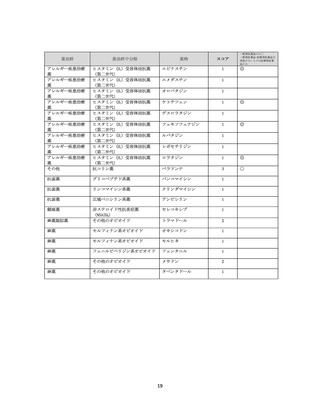
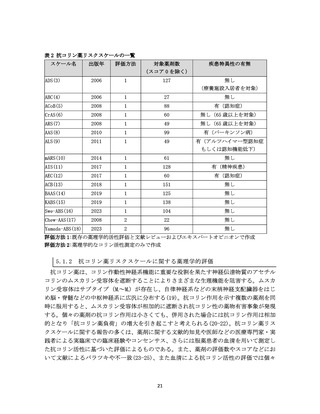
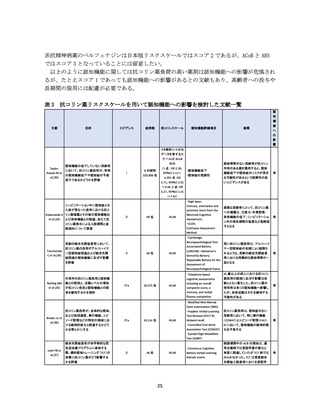
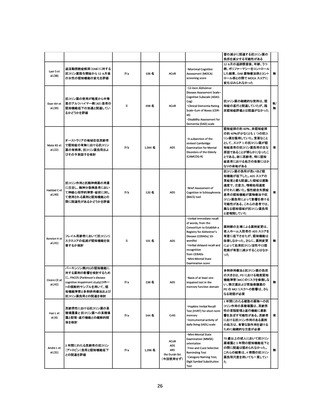
資料4-2 日本版抗コリン薬リスクスケール (39 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_40741.html |
| 出典情報 | 高齢者医薬品適正使用検討会(第18回 6/21)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
19.
Yamada S, Ito Y, Nishijima S, Kadekawa K, Sugaya K. Basic and clinical aspects of antimuscarinic
agents used to treat overactive bladder. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 2018;189:130-48.
20.
Salahudeen Ms DSBNPS. Anticholinergic burden quantified by anticholinergic risk scales and
adverse outcomes in older people: a systematic review.
21.
Fox C, Richardson K, Maidment ID, Savva GM, Matthews FE, Smithard D, et al. Anticholinergic
medication use and cognitive impairment in the older population: the medical research council cognitive
function and ageing study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(8):1477-83.
22.
Mate KE, Kerr KP, Pond D, Williams EJ, Marley J, Disler P, et al. Impact of multiple low-level
anticholinergic medications on anticholinergic load of community-dwelling elderly with and without
dementia. Drugs & aging. 2015;32:159-67.
23.
Durán CE, Azermai M, Vander Stichele RH. Systematic review of anticholinergic risk scales in older
adults. European journal of clinical pharmacology. 2013;69:1485-96.
24.
Lozano-Ortega G, Johnston KM, Cheung A, Wagg A, Campbell NL, Dmochowski RR, et al. A review of
published anticholinergic scales and measures and their applicability in database analyses. Archives of
gerontology and geriatrics. 2020;87:103885.
25.
Al Rihani SB, Deodhar M, Darakjian LI, Dow P, Smith MK, Bikmetov R, et al. Quantifying
anticholinergic burden and sedative load in older adults with polypharmacy: a systematic review of risk
scales and models. Drugs & Aging. 2021:1-18.
26.
Nobrega JN, Raymond RJ, Pollock BG. An improved, high-efficiency assay for assessing serum
anticholinergic activity using cultured cells stably expressing M1 receptors. Journal of Pharmacological and
Toxicological Methods. 2017;86:28-33.
27.
Yamada S, Mochizuki M, Atobe K, Kato Y. Pharmcokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations for
the anticholinergic burden scale of drugs. Geriatrics & Gerontology International. 2024;24:81-7.
28.
Shi S, Klotz U. Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics. Current drug metabolism. 2011;12(7):60110.
29.
Pedigo Jr NW. Neurotransmitter receptor plasticity in aging. Life sciences. 1994;55(25-26):1985-91.
30.
Taylor-Rowan M, Edwards S, Noel-Storr AH, McCleery J, Myint PK, Soiza R, et al. Anticholinergic
burden (prognostic factor) for prediction of dementia or cognitive decline in older adults with no known
cognitive syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021(5).
31.
Andre L, Gallini A, Montastruc F, Coley N, Montastruc JL, Vellas B, et al. Anticholinergic exposure
and cognitive decline in older adults: effect of anticholinergic exposure definitions in a 3‐year analysis of the
multidomain Alzheimer preventive trial (MAPT) study. British journal of clinical pharmacology.
2019;85(1):71-99.
32.
Lavrador M, Cabral AC, Figueiredo IV, Veríssimo MT, Castel-Branco MM, Fernandez-Llimos F. Size of
the associations between anticholinergic burden tool scores and adverse outcomes in older patients.
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy. 2021;43(1):128-36.
33.
Kolanowski A, Mogle J, Fick DM, Campbell N, Hill N, Mulhall P, et al. Anticholinergic exposure during
rehabilitation: cognitive and physical function outcomes in patients with delirium superimposed on
dementia. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2015;23(12):1250-8.
34.
Tsoutsoulas C MBHKSGZVANMMPBGRTK. Anticholinergic Burden and Cognition in Older Patients
With Schizophrenia.
35.
Norling AM, Bennett A, Crowe M, Long DL, Nolin SA, Myers T, et al. Longitudinal associations of
anticholinergic medications on cognition and possible mitigating role of physical activity. J Am Geriatr Soc.
2023;71(6):1937-43.
36.
Broder JC, Ryan J, Shah RC, Lockery JE, Orchard SG, Gilmartin‐Thomas JFM, et al. Anticholinergic
medication burden and cognitive function in participants of the ASPREE study. Pharmacotherapy: The
Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy. 2022;42(2):134-44.
39
Yamada S, Ito Y, Nishijima S, Kadekawa K, Sugaya K. Basic and clinical aspects of antimuscarinic
agents used to treat overactive bladder. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 2018;189:130-48.
20.
Salahudeen Ms DSBNPS. Anticholinergic burden quantified by anticholinergic risk scales and
adverse outcomes in older people: a systematic review.
21.
Fox C, Richardson K, Maidment ID, Savva GM, Matthews FE, Smithard D, et al. Anticholinergic
medication use and cognitive impairment in the older population: the medical research council cognitive
function and ageing study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(8):1477-83.
22.
Mate KE, Kerr KP, Pond D, Williams EJ, Marley J, Disler P, et al. Impact of multiple low-level
anticholinergic medications on anticholinergic load of community-dwelling elderly with and without
dementia. Drugs & aging. 2015;32:159-67.
23.
Durán CE, Azermai M, Vander Stichele RH. Systematic review of anticholinergic risk scales in older
adults. European journal of clinical pharmacology. 2013;69:1485-96.
24.
Lozano-Ortega G, Johnston KM, Cheung A, Wagg A, Campbell NL, Dmochowski RR, et al. A review of
published anticholinergic scales and measures and their applicability in database analyses. Archives of
gerontology and geriatrics. 2020;87:103885.
25.
Al Rihani SB, Deodhar M, Darakjian LI, Dow P, Smith MK, Bikmetov R, et al. Quantifying
anticholinergic burden and sedative load in older adults with polypharmacy: a systematic review of risk
scales and models. Drugs & Aging. 2021:1-18.
26.
Nobrega JN, Raymond RJ, Pollock BG. An improved, high-efficiency assay for assessing serum
anticholinergic activity using cultured cells stably expressing M1 receptors. Journal of Pharmacological and
Toxicological Methods. 2017;86:28-33.
27.
Yamada S, Mochizuki M, Atobe K, Kato Y. Pharmcokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations for
the anticholinergic burden scale of drugs. Geriatrics & Gerontology International. 2024;24:81-7.
28.
Shi S, Klotz U. Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics. Current drug metabolism. 2011;12(7):60110.
29.
Pedigo Jr NW. Neurotransmitter receptor plasticity in aging. Life sciences. 1994;55(25-26):1985-91.
30.
Taylor-Rowan M, Edwards S, Noel-Storr AH, McCleery J, Myint PK, Soiza R, et al. Anticholinergic
burden (prognostic factor) for prediction of dementia or cognitive decline in older adults with no known
cognitive syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021(5).
31.
Andre L, Gallini A, Montastruc F, Coley N, Montastruc JL, Vellas B, et al. Anticholinergic exposure
and cognitive decline in older adults: effect of anticholinergic exposure definitions in a 3‐year analysis of the
multidomain Alzheimer preventive trial (MAPT) study. British journal of clinical pharmacology.
2019;85(1):71-99.
32.
Lavrador M, Cabral AC, Figueiredo IV, Veríssimo MT, Castel-Branco MM, Fernandez-Llimos F. Size of
the associations between anticholinergic burden tool scores and adverse outcomes in older patients.
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy. 2021;43(1):128-36.
33.
Kolanowski A, Mogle J, Fick DM, Campbell N, Hill N, Mulhall P, et al. Anticholinergic exposure during
rehabilitation: cognitive and physical function outcomes in patients with delirium superimposed on
dementia. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2015;23(12):1250-8.
34.
Tsoutsoulas C MBHKSGZVANMMPBGRTK. Anticholinergic Burden and Cognition in Older Patients
With Schizophrenia.
35.
Norling AM, Bennett A, Crowe M, Long DL, Nolin SA, Myers T, et al. Longitudinal associations of
anticholinergic medications on cognition and possible mitigating role of physical activity. J Am Geriatr Soc.
2023;71(6):1937-43.
36.
Broder JC, Ryan J, Shah RC, Lockery JE, Orchard SG, Gilmartin‐Thomas JFM, et al. Anticholinergic
medication burden and cognitive function in participants of the ASPREE study. Pharmacotherapy: The
Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy. 2022;42(2):134-44.
39