よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (11 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
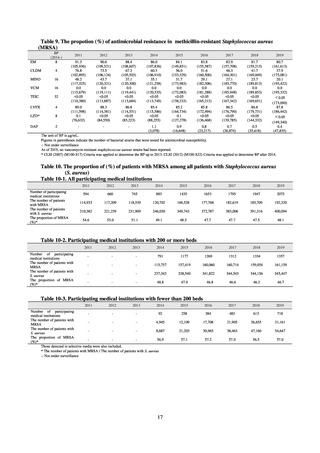
Observations:
Figures for 2019 sales of oral antimicrobials, including oral cephalosporins, oral macrolides, and oral
fluoroquinolones show that usage of these antimicrobials has fallen overall compared with the data for 2013.
However, as the decline is only slight when compared with the 2018 data, better antimicrobial stewardship is
required. In addition, a clear downward trend in antimicrobial resistance rates has emerged among a number of
bacterial species, thereby demonstrating progress toward achieving the numerical targets in the action plan.
However, resistance rates continue to climb, including fluoroquinolone resistance rates among Escherichia coli.
The data in this report demonstrate that further promotion of measures against AMR will be required. There are
reports of a correlation between fluoroquinolone usage and the frequency of occurrence of fluoroquinoloneresistant Escherichia coli. There are also reports of a connection between MRSA and usage of third-generation
cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and macrolides. Accordingly, unnecessary use of third-generation
cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and macrolides must be reduced and the Manual of Antimicrobial Stewardship
employed to promote the proper use of antimicrobials, primarily in respect of acute respiratory tract infections. As
the basic premise underpinning the promotion of antimicrobial stewardship is ensuring that the appropriate
antimicrobials can be used when needed, securing a stable supply of basic antimicrobial agents is crucial. In
addition, information about resistant bacteria in each region and the status of antimicrobial use is being put in
place, as it is desirable to select antimicrobials and promote infection control measures tailored to the situation in
each region. Furthermore, it will be necessary to continue using various techniques for education and awareness
activities targeting the public and medical professionals, to achieve further progress in antimicrobial stewardship.
Among animals, no Enterobacteriaceae resistant to carbapenems, which is one of the most critically important
antimicrobial classes for human medicine, or vancomycin-resistant enterococci, which cause major problems
including nosocomial infections in humans, were isolated. However, rates of resistance to third-generation
cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones in Escherichia coli isolated from diseased companion animals, surveillance
of which began in 2017, were found to be higher than in Escherichia coli isolated from food-producing animals.
This demonstrates the necessity of continuing and enhancing measures to combat antimicrobial resistance not only
via the measures that have been underway for some time in the field of food-producing animals, but also through
the widespread circulation of the guide to prudent use in companion animals launched in 2020.
While rates of resistance to third-generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones in Escherichia coli isolated
from healthy food-producing animals—an outcome index for the Action Plan—have been maintained at a low
level, it will be necessary to continue to raise awareness among veterinarians and producers about their prudent
use as second-line veterinary drugs in food-producing animals. Although the volume of tetracycline sales fell in
2018, rates of resistance to this class of antimicrobial in Escherichia coli isolated from healthy food-producing
animals have not declined. Accordingly, greater efforts are required to promote prudent use of these antimicrobials,
taking into account the actual state of their use among veterinarians and producers.
The existing Action Plan covers the five-year period up to 2020. Although some indices are improving, there
are still many that have seen only scant improvement, added to which a number of new issues have emerged, so it
is necessary to continue addressing them in coordination with international trends. As such, industry, academia,
and government will work together to promote frameworks for collaboration between the organizations tasked
with handling different fields, while also examining the promotion of research that enables cross-cutting evaluation
of the risks to humans, animals, and the environment to be conducted.
10
Figures for 2019 sales of oral antimicrobials, including oral cephalosporins, oral macrolides, and oral
fluoroquinolones show that usage of these antimicrobials has fallen overall compared with the data for 2013.
However, as the decline is only slight when compared with the 2018 data, better antimicrobial stewardship is
required. In addition, a clear downward trend in antimicrobial resistance rates has emerged among a number of
bacterial species, thereby demonstrating progress toward achieving the numerical targets in the action plan.
However, resistance rates continue to climb, including fluoroquinolone resistance rates among Escherichia coli.
The data in this report demonstrate that further promotion of measures against AMR will be required. There are
reports of a correlation between fluoroquinolone usage and the frequency of occurrence of fluoroquinoloneresistant Escherichia coli. There are also reports of a connection between MRSA and usage of third-generation
cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and macrolides. Accordingly, unnecessary use of third-generation
cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and macrolides must be reduced and the Manual of Antimicrobial Stewardship
employed to promote the proper use of antimicrobials, primarily in respect of acute respiratory tract infections. As
the basic premise underpinning the promotion of antimicrobial stewardship is ensuring that the appropriate
antimicrobials can be used when needed, securing a stable supply of basic antimicrobial agents is crucial. In
addition, information about resistant bacteria in each region and the status of antimicrobial use is being put in
place, as it is desirable to select antimicrobials and promote infection control measures tailored to the situation in
each region. Furthermore, it will be necessary to continue using various techniques for education and awareness
activities targeting the public and medical professionals, to achieve further progress in antimicrobial stewardship.
Among animals, no Enterobacteriaceae resistant to carbapenems, which is one of the most critically important
antimicrobial classes for human medicine, or vancomycin-resistant enterococci, which cause major problems
including nosocomial infections in humans, were isolated. However, rates of resistance to third-generation
cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones in Escherichia coli isolated from diseased companion animals, surveillance
of which began in 2017, were found to be higher than in Escherichia coli isolated from food-producing animals.
This demonstrates the necessity of continuing and enhancing measures to combat antimicrobial resistance not only
via the measures that have been underway for some time in the field of food-producing animals, but also through
the widespread circulation of the guide to prudent use in companion animals launched in 2020.
While rates of resistance to third-generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones in Escherichia coli isolated
from healthy food-producing animals—an outcome index for the Action Plan—have been maintained at a low
level, it will be necessary to continue to raise awareness among veterinarians and producers about their prudent
use as second-line veterinary drugs in food-producing animals. Although the volume of tetracycline sales fell in
2018, rates of resistance to this class of antimicrobial in Escherichia coli isolated from healthy food-producing
animals have not declined. Accordingly, greater efforts are required to promote prudent use of these antimicrobials,
taking into account the actual state of their use among veterinarians and producers.
The existing Action Plan covers the five-year period up to 2020. Although some indices are improving, there
are still many that have seen only scant improvement, added to which a number of new issues have emerged, so it
is necessary to continue addressing them in coordination with international trends. As such, industry, academia,
and government will work together to promote frameworks for collaboration between the organizations tasked
with handling different fields, while also examining the promotion of research that enables cross-cutting evaluation
of the risks to humans, animals, and the environment to be conducted.
10