よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (41 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
ⅱ. Campylobacter jejuni
Monitoring of antimicrobial resistance on 7 agents between 2012 and 2016, and 8 agents adding AZM since
2017 was carried out. In 2018, resistance to NA, CPFX, and TC in cattle-derived strains exceeded 30%, as did
resistance to NA in chicken-derived strains. On the other hand, resistance to SM, EM, and CP was less than 3% in
each case. Resistance to CPFX, which is a critically important antimicrobial for human medicine, was 31.4% in
cattle-derived strains and 29.8% in chicken-derived strains, while AZM resistance rates in both were less than 3%.
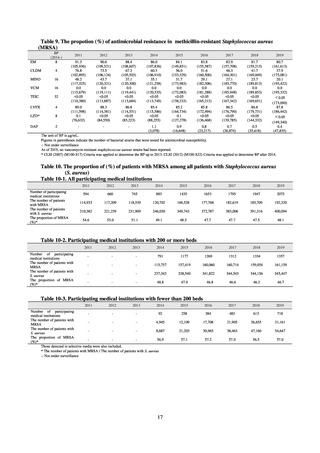
Table 50. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter jejuni derived from animal and
poultry slaughterhouses
Agent*
BP
ABPC
32
SM
32
EM
32†
AZM
4
†
TC
16
CP
16
NA
32
CPFX
4†
Strains tested (n)
Animal
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
2012
0.0
19.7
2.4
1.4
0.0
0.0
-
2013
9.1
19.8
3.5
0.0
0.7
0.0
-
2014
12.9
17.5
3.8
3.5
0.0
0.0
-
2015
8.9
19.1
3.2
2.1
1.3
0.0
-
2016
7.4
16.2
6.2
8.8
0.0
0.0
-
2017
8.2
28.4
4.1
1.5
0.0
1.5
0.0
2018
8.6
14.9
5.7
0.0
2.9
0.0
2.9
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
-
45.1
38.0
0.0
0.0
34.1
39.4
34.1
39.4
82
71
-
52.4
44.4
6.3
0.0
33.6
48.1
29.4
39.5
143
81
-
49.2
38.6
0.0
1.8
50.8
29.8
49.2
29.8
132
57
-
52.2
28.7
1.3
0.0
42.7
27.7
40.8
26.6
157
94
-
63.0
33.8
1.2
2.9
44.4
57.4
44.4
51.5
81
68
1.5
72.2
46.3
6.2
0.0
48.5
46.3
50.5
44.8
97
67
0.0
62.9
23.4
2.9
2.1
31.4
31.9
31.4
29.8
35
47
The unit of BP is μg/mL.
* While GM was also included in the scope of monitoring, the proportion of GM-resistant strains was not listed because BP could not be
established.
†
BP follows CLSI Criteria.
ⅲ. Campylobacter coli
Monitoring of antimicrobial resistance to 7 agents between 2012 and 2016 was carried out, but AZM was added
in 2017, taking the total number to 8. In pig-derived strains in 2018, resistance to SM exceeding 60%, resistance
to TC exceeding 80%, and resistance to NA and CPFX exceeding 50% was observed. On the other hand, CP
resistance was less than 4%. Resistance to CPFX, which is a critically important antimicrobial for human medicine,
was 58.6%, while the AZM resistance rate was 20.7%.
Table 51. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter coli derived from animal
slaughterhouses
Agent*
BP
Animal
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
ABPC
32
Pigs
23.3
25.5
36.6
24.6
15.4
29.5
17.2
SM
32
Pigs
67.4
78.3
69.9
72.3
64.1
68.9
69.0
EM
32†
Pigs
32.6
44.3
43.0
26.2
38.5
31.1
20.7
AZM
4
Pigs
31.1
20.7
-
-
-
-
-
TC
16†
Pigs
84.5
93.4
80.6
87.7
89.7
83.6
86.2
CP
16
Pigs
10.9
3.8
7.5
9.2
15.4
1.6
3.4
NA
32
Pigs
46.5
53.8
52.7
47.7
61.5
50.8
58.6
CPFX
4†
Pigs
46.5
46.2
50.5
47.7
59.0
54.1
58.6
Strains tested (n)
Pigs
129
106
93
65
39
61
29
The unit of BP is μg/mL.
* While GM was also included in the scope of monitoring, the proportion of GM-resistant strains was not listed because BP could not be
established.
†
BP follows CLSI Criteria.
iv. Enterococcus spp.
Monitoring of antimicrobial resistance on 10 agents between 2012 and 2014, and 11 agents adding VCM since
2015 was carried out. Resistance to KM, EM, lincomycin (LCM), and tylosin (TS) in strains isolated from chickens
was observed to exceed 40% in 2017, as was oxytetracycline (OTC) resistance in pig- and chicken-derived strains.
On the other hand, gentamicin (GM) resistance was less than 10% and no resistance to ampicillin (ABPC) was
observed. Resistance to enrofloxacin (ERFX)—one of the fluoroquinolones, which are critically important
40
Monitoring of antimicrobial resistance on 7 agents between 2012 and 2016, and 8 agents adding AZM since
2017 was carried out. In 2018, resistance to NA, CPFX, and TC in cattle-derived strains exceeded 30%, as did
resistance to NA in chicken-derived strains. On the other hand, resistance to SM, EM, and CP was less than 3% in
each case. Resistance to CPFX, which is a critically important antimicrobial for human medicine, was 31.4% in
cattle-derived strains and 29.8% in chicken-derived strains, while AZM resistance rates in both were less than 3%.
Table 50. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter jejuni derived from animal and
poultry slaughterhouses
Agent*
BP
ABPC
32
SM
32
EM
32†
AZM
4
†
TC
16
CP
16
NA
32
CPFX
4†
Strains tested (n)
Animal
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
2012
0.0
19.7
2.4
1.4
0.0
0.0
-
2013
9.1
19.8
3.5
0.0
0.7
0.0
-
2014
12.9
17.5
3.8
3.5
0.0
0.0
-
2015
8.9
19.1
3.2
2.1
1.3
0.0
-
2016
7.4
16.2
6.2
8.8
0.0
0.0
-
2017
8.2
28.4
4.1
1.5
0.0
1.5
0.0
2018
8.6
14.9
5.7
0.0
2.9
0.0
2.9
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
Cattle
Chickens
-
45.1
38.0
0.0
0.0
34.1
39.4
34.1
39.4
82
71
-
52.4
44.4
6.3
0.0
33.6
48.1
29.4
39.5
143
81
-
49.2
38.6
0.0
1.8
50.8
29.8
49.2
29.8
132
57
-
52.2
28.7
1.3
0.0
42.7
27.7
40.8
26.6
157
94
-
63.0
33.8
1.2
2.9
44.4
57.4
44.4
51.5
81
68
1.5
72.2
46.3
6.2
0.0
48.5
46.3
50.5
44.8
97
67
0.0
62.9
23.4
2.9
2.1
31.4
31.9
31.4
29.8
35
47
The unit of BP is μg/mL.
* While GM was also included in the scope of monitoring, the proportion of GM-resistant strains was not listed because BP could not be
established.
†
BP follows CLSI Criteria.
ⅲ. Campylobacter coli
Monitoring of antimicrobial resistance to 7 agents between 2012 and 2016 was carried out, but AZM was added
in 2017, taking the total number to 8. In pig-derived strains in 2018, resistance to SM exceeding 60%, resistance
to TC exceeding 80%, and resistance to NA and CPFX exceeding 50% was observed. On the other hand, CP
resistance was less than 4%. Resistance to CPFX, which is a critically important antimicrobial for human medicine,
was 58.6%, while the AZM resistance rate was 20.7%.
Table 51. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter coli derived from animal
slaughterhouses
Agent*
BP
Animal
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
ABPC
32
Pigs
23.3
25.5
36.6
24.6
15.4
29.5
17.2
SM
32
Pigs
67.4
78.3
69.9
72.3
64.1
68.9
69.0
EM
32†
Pigs
32.6
44.3
43.0
26.2
38.5
31.1
20.7
AZM
4
Pigs
31.1
20.7
-
-
-
-
-
TC
16†
Pigs
84.5
93.4
80.6
87.7
89.7
83.6
86.2
CP
16
Pigs
10.9
3.8
7.5
9.2
15.4
1.6
3.4
NA
32
Pigs
46.5
53.8
52.7
47.7
61.5
50.8
58.6
CPFX
4†
Pigs
46.5
46.2
50.5
47.7
59.0
54.1
58.6
Strains tested (n)
Pigs
129
106
93
65
39
61
29
The unit of BP is μg/mL.
* While GM was also included in the scope of monitoring, the proportion of GM-resistant strains was not listed because BP could not be
established.
†
BP follows CLSI Criteria.
iv. Enterococcus spp.
Monitoring of antimicrobial resistance on 10 agents between 2012 and 2014, and 11 agents adding VCM since
2015 was carried out. Resistance to KM, EM, lincomycin (LCM), and tylosin (TS) in strains isolated from chickens
was observed to exceed 40% in 2017, as was oxytetracycline (OTC) resistance in pig- and chicken-derived strains.
On the other hand, gentamicin (GM) resistance was less than 10% and no resistance to ampicillin (ABPC) was
observed. Resistance to enrofloxacin (ERFX)—one of the fluoroquinolones, which are critically important
40