よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (16 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
ⅴ. Acintobacter spp.
Table 6. Trends in the proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Acinetobacter spp.
BP
128
PIPC
TAZ/
PIPC
SBT/
ABPC
CAZ
4/128
2011
13.2
(19,125)
-
2012
13.2
(19,433)
-
16/32
2013
12.9
(20,183)
7.8
(4,953)
5.8
(4,498)
10.0
(20,856)
9.2
(15,394)
2.3
(16,947)
2.3
(17,027)
9.5
(19,422)
3.5
(20,863)
8.3
(20,040)
2014
12.4
(20,223)
7.8
(5,215)
5.2
(6,462)
9.3
(20,852)
7.6
(17,424)
3.6
(11,147)
2.0
(18,859)
8.9
(18,832)
3.6
(20,851)
8.5
(20,047)
2015
11.5
(27,887)
8.1
(9,058)
4.8
(11,356)
8.0
(28,166)
7.2
(25,412)
3.2
(13,942)
1.8
(28,227)
8.5
(25,689)
3.1
(28,568)
7.7
(27,858)
2016
10.9
(29,776)
8.6
(10,551)
5,4
(12,831)
7.6
(29,844)
7.4
(27,386)
3.1
(15,147)
1.9
(30,489)
8.5
(27,313)
2.3
(30,279)
8.2
(29,702)
6.5
7.2
(2,942)
(3,601)
32
10.3
10.6
(19,672)
(20,067)
CFPM
32
10.4
10.5
(13,013)
(14,093)
IPM
16
2.2
2.0
(18,048)
(18,238)
MEPM
16
2.9
2.4
(15,485)
(15,880)
GM
16
9.6
10.2
(18,276)
(18,842)
AMK
64
4.5
4.5
(19,348)
(19,793)
LVFX
8
9.5
9.8
(18,732)
(19,484)
The unit of BP is μg/mL.
Figures in parentheses indicate the number of bacterial strains that were tested for antimicrobial susceptibility.
-: Not under surveillance
2017
10.9
(27,468)
9.0
(10,983)
4.7
(12,241)
7.9
(27,308)
7.6
(25,631)
2.5
(14,383)
1.3
(28,064)
8.2
(24,887)
2.3
(27,835)
8.0
(27,360)
2018
10.3
(27,905)
9.4
(12,171)
4.4
(13,111)
7.6
(28,077)
6.8
(26,616)
2.0
(16,995)
1.5
(29,024)
7.8
(25,465)
2.0
(28,437)
7.0
(28,209)
2019
10.7
(26,237)
9.0
(12,401)
4.3
(12,769)
8.6
(26,614)
6.8
(25,224)
1.8
(19,645)
1.4
(27,418)
8.0
(23,925)
2.1
(26,917)
7.5
(26,898)
2) Gram-positive bacteria
Source: JANIS
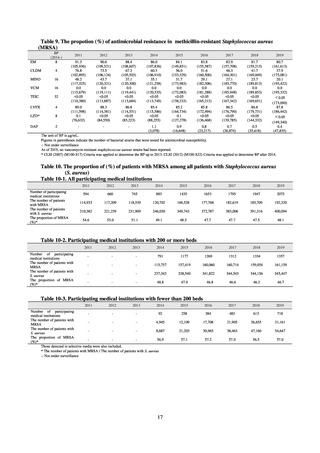
Looking at the recent status of gram-positive bacteria, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
accounted for approximately 50% of all Staphylococcus aureus. Although the proportion has been declining over
the past few years, it remains higher than that seen in other countries. The proportion is higher among medical
institutions with fewer than 200 beds than among those with 200 or more (Table 10). In the case of enterococci,
rising vancomycin (VCM) resistance is a problem in many countries, but as shown in Tables 11 and 12, levels in
Japan are comparatively low, at less than 0.05% in the case of Enterococcus faecalis and 1.5% among
Enterococcus faecium. However, in 2019, the VCM resistance rate among E. faecium rose and widespread
nosocomial outbreaks of VCM-resistant E. faecium have been observed in some regions. Regional changes in
resistance rates will need to be kept under close observation. The proportion of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus
pneumoniae (PRSP) accounted for approximately 40% of all detected pneumococcus in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
samples, though the figure varies from year to year, because only around 100 CSF samples are tested (Table 13).
The proportion of PRSP was low for non-CSF samples at below 1% (Table 14), and below 5% even adding
penicillin intermediate resistant bacteria.
15
Table 6. Trends in the proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Acinetobacter spp.
BP
128
PIPC
TAZ/
PIPC
SBT/
ABPC
CAZ
4/128
2011
13.2
(19,125)
-
2012
13.2
(19,433)
-
16/32
2013
12.9
(20,183)
7.8
(4,953)
5.8
(4,498)
10.0
(20,856)
9.2
(15,394)
2.3
(16,947)
2.3
(17,027)
9.5
(19,422)
3.5
(20,863)
8.3
(20,040)
2014
12.4
(20,223)
7.8
(5,215)
5.2
(6,462)
9.3
(20,852)
7.6
(17,424)
3.6
(11,147)
2.0
(18,859)
8.9
(18,832)
3.6
(20,851)
8.5
(20,047)
2015
11.5
(27,887)
8.1
(9,058)
4.8
(11,356)
8.0
(28,166)
7.2
(25,412)
3.2
(13,942)
1.8
(28,227)
8.5
(25,689)
3.1
(28,568)
7.7
(27,858)
2016
10.9
(29,776)
8.6
(10,551)
5,4
(12,831)
7.6
(29,844)
7.4
(27,386)
3.1
(15,147)
1.9
(30,489)
8.5
(27,313)
2.3
(30,279)
8.2
(29,702)
6.5
7.2
(2,942)
(3,601)
32
10.3
10.6
(19,672)
(20,067)
CFPM
32
10.4
10.5
(13,013)
(14,093)
IPM
16
2.2
2.0
(18,048)
(18,238)
MEPM
16
2.9
2.4
(15,485)
(15,880)
GM
16
9.6
10.2
(18,276)
(18,842)
AMK
64
4.5
4.5
(19,348)
(19,793)
LVFX
8
9.5
9.8
(18,732)
(19,484)
The unit of BP is μg/mL.
Figures in parentheses indicate the number of bacterial strains that were tested for antimicrobial susceptibility.
-: Not under surveillance
2017
10.9
(27,468)
9.0
(10,983)
4.7
(12,241)
7.9
(27,308)
7.6
(25,631)
2.5
(14,383)
1.3
(28,064)
8.2
(24,887)
2.3
(27,835)
8.0
(27,360)
2018
10.3
(27,905)
9.4
(12,171)
4.4
(13,111)
7.6
(28,077)
6.8
(26,616)
2.0
(16,995)
1.5
(29,024)
7.8
(25,465)
2.0
(28,437)
7.0
(28,209)
2019
10.7
(26,237)
9.0
(12,401)
4.3
(12,769)
8.6
(26,614)
6.8
(25,224)
1.8
(19,645)
1.4
(27,418)
8.0
(23,925)
2.1
(26,917)
7.5
(26,898)
2) Gram-positive bacteria
Source: JANIS
Looking at the recent status of gram-positive bacteria, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
accounted for approximately 50% of all Staphylococcus aureus. Although the proportion has been declining over
the past few years, it remains higher than that seen in other countries. The proportion is higher among medical
institutions with fewer than 200 beds than among those with 200 or more (Table 10). In the case of enterococci,
rising vancomycin (VCM) resistance is a problem in many countries, but as shown in Tables 11 and 12, levels in
Japan are comparatively low, at less than 0.05% in the case of Enterococcus faecalis and 1.5% among
Enterococcus faecium. However, in 2019, the VCM resistance rate among E. faecium rose and widespread
nosocomial outbreaks of VCM-resistant E. faecium have been observed in some regions. Regional changes in
resistance rates will need to be kept under close observation. The proportion of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus
pneumoniae (PRSP) accounted for approximately 40% of all detected pneumococcus in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
samples, though the figure varies from year to year, because only around 100 CSF samples are tested (Table 13).
The proportion of PRSP was low for non-CSF samples at below 1% (Table 14), and below 5% even adding
penicillin intermediate resistant bacteria.
15