よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (67 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
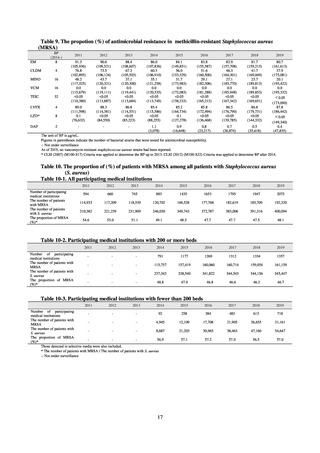
1) Food-producing animals
The estimated volumes of veterinary antimicrobials sold for food-producing animals (cattle, pigs, horses,
chickens, and others) in terms of active ingredients are listed in Table 77. In the period from 2013 to 2018, the
estimated volume of sales ranged between 640.25 t and 694.24 t, with sales in 2018 falling by about 48 t from
the 2017 level. Among the factors that had an impact was a fall in sales of tetracyclines (about 29 t) and
aminoglycosides (about 10 t), with sales of tetracyclines for pigs declining by about 46 t. Tetracyclines (257.36
tons to 286.74 t) took up the largest share in the overall volume of sales of antimicrobials for food-producing
animals, accounting for 39.8 to 44.0%. In contrast, third-generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones, which
are critically important antimicrobials for human medicine, each accounted for less than 1%
Table 77. The estimated volumes of sales of veterinary antimicrobials for food-producing animals (cattle,
pigs, horses, chickens, and others) in terms of active ingredients (unit: metric tons)
2013
Penicillins
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
59.50
61.96
67.25
83.56
84.68
3.12
3.06
3.22
3.34
3.44
3.91
1st generation cephalosporins
(2.45)
(2.34)
(2.52)
(2.52)
(2.51)
(2.73)
2nd generation cephalosporins
(0.19)
(0.20)
(0.12)
(0.16)
(0.18)
(0.22)
3rd generation cephalosporins
(0.49)
(0.51)
(0.58)
(0.65)
(0.74)
(0.96)
Aminoglycosides
37.40
38.66
34.07
47.46
44.37
34.69
Macrolides
56.00
53.30
60.36
72.68
71.96
72.09
Lincosamides
35.88
36.61
23.65
15.62
19.39
16.72
Tetracyclines
286.74
275.83
276.24
280.66
286.01
257.36
Cephalosporins (total)
92.79
Peptides
11.77
9.97
14.54
14.01
19.98
12.34
Other antibioitics
25.71
28.43
32.23
31.55
35.72
36.87
Sulfonamides
95.62
88.43
84.40
78.57
84.10
78.59
0.22
0.20
0.20
0.16
0.31
0.01
Quinolones
Fluoroquinolones
Amphenicols
Furan and derivatives
4.64
4.73
6.41
5.19
5.93
5.80
19.66
25.14
27.39
24.82
25.34
23.28
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
14.98
13.92
13.32
12.07
13.02
11.96
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Total
651.24
640.25
* The figures in parentheses are included in the Cephalosporins (total).
643.28
669.68
694.24
646.40
Other synthetic antibacterials
Antifungal antibiotics
2) Aquatic animals
The estimated volumes of veterinary antimicrobials sold for aquatic animals (seawater fish, freshwater fish,
and ornamental fish) in terms of active ingredients are summarized in Table 78. In the period from 2013 to 2018,
the estimated volume of sales ranged between 100.09 t and 169.88 t, accounting for between 13.4% and 20.4%
of the total volume of veterinary antimicrobial sales. Tetracyclines (ranging between 49.01 t and 57.62 t) took up
the largest share in the overall volume of sales until 2015 but it has changed to a macrolide (erythromycin) since
2016, with sales totaling between 61.44 t and 82.61 t. The approximately 49 t increase in the volume of sales
between 2013 and 2018 was due to a rise in sales of a macrolide (erythromycin), which was attributed to an
outbreak of streptococcosis (Lactococcus garvieae), for which the agent is indicated.
Third-generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones that are important for human health are not approved
for aquatic animal use.
66
The estimated volumes of veterinary antimicrobials sold for food-producing animals (cattle, pigs, horses,
chickens, and others) in terms of active ingredients are listed in Table 77. In the period from 2013 to 2018, the
estimated volume of sales ranged between 640.25 t and 694.24 t, with sales in 2018 falling by about 48 t from
the 2017 level. Among the factors that had an impact was a fall in sales of tetracyclines (about 29 t) and
aminoglycosides (about 10 t), with sales of tetracyclines for pigs declining by about 46 t. Tetracyclines (257.36
tons to 286.74 t) took up the largest share in the overall volume of sales of antimicrobials for food-producing
animals, accounting for 39.8 to 44.0%. In contrast, third-generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones, which
are critically important antimicrobials for human medicine, each accounted for less than 1%
Table 77. The estimated volumes of sales of veterinary antimicrobials for food-producing animals (cattle,
pigs, horses, chickens, and others) in terms of active ingredients (unit: metric tons)
2013
Penicillins
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
59.50
61.96
67.25
83.56
84.68
3.12
3.06
3.22
3.34
3.44
3.91
1st generation cephalosporins
(2.45)
(2.34)
(2.52)
(2.52)
(2.51)
(2.73)
2nd generation cephalosporins
(0.19)
(0.20)
(0.12)
(0.16)
(0.18)
(0.22)
3rd generation cephalosporins
(0.49)
(0.51)
(0.58)
(0.65)
(0.74)
(0.96)
Aminoglycosides
37.40
38.66
34.07
47.46
44.37
34.69
Macrolides
56.00
53.30
60.36
72.68
71.96
72.09
Lincosamides
35.88
36.61
23.65
15.62
19.39
16.72
Tetracyclines
286.74
275.83
276.24
280.66
286.01
257.36
Cephalosporins (total)
92.79
Peptides
11.77
9.97
14.54
14.01
19.98
12.34
Other antibioitics
25.71
28.43
32.23
31.55
35.72
36.87
Sulfonamides
95.62
88.43
84.40
78.57
84.10
78.59
0.22
0.20
0.20
0.16
0.31
0.01
Quinolones
Fluoroquinolones
Amphenicols
Furan and derivatives
4.64
4.73
6.41
5.19
5.93
5.80
19.66
25.14
27.39
24.82
25.34
23.28
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
14.98
13.92
13.32
12.07
13.02
11.96
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Total
651.24
640.25
* The figures in parentheses are included in the Cephalosporins (total).
643.28
669.68
694.24
646.40
Other synthetic antibacterials
Antifungal antibiotics
2) Aquatic animals
The estimated volumes of veterinary antimicrobials sold for aquatic animals (seawater fish, freshwater fish,
and ornamental fish) in terms of active ingredients are summarized in Table 78. In the period from 2013 to 2018,
the estimated volume of sales ranged between 100.09 t and 169.88 t, accounting for between 13.4% and 20.4%
of the total volume of veterinary antimicrobial sales. Tetracyclines (ranging between 49.01 t and 57.62 t) took up
the largest share in the overall volume of sales until 2015 but it has changed to a macrolide (erythromycin) since
2016, with sales totaling between 61.44 t and 82.61 t. The approximately 49 t increase in the volume of sales
between 2013 and 2018 was due to a rise in sales of a macrolide (erythromycin), which was attributed to an
outbreak of streptococcosis (Lactococcus garvieae), for which the agent is indicated.
Third-generation cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones that are important for human health are not approved
for aquatic animal use.
66