よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (29 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
ⅳ. Salmonella Typhi, Salmonella Paratyphi A, Shigella spp.
Source: National Institute of Infectious Diseases
The 28-46 Salmonella Typhi strains that were isolated between 2015 and 2019 were tested for antimicrobial
susceptibility (Table 24). CPFX-non-susceptible strains accounted for 60.7-83.9%, while strains with advanced
resistance (MIC ≥ 4) to ciprofloxacin accounted for 5.9-23.9%. During this period, 11 strains of multidrug-resistant
Salmonella Typhi that indicated resistance to ampicillin (ABPC), CP and ST were isolated, along with two strains
of CTX-resistant Salmonella Typhi.
The 13-30 Salmonella Paratyphi A strains isolated between 2015 and 2019 were tested for antimicrobial
susceptibility. CPFX-non-susceptible strains accounted for 76.9-100% and one strain with advanced CPFX
resistance (MIC ≥ 4) was isolated. No cefotaxime-resistant strains were isolated among the Salmonella Paratyphi
A.
The 73-156 Shigella spp. strains that were isolated between 2015 and 2019 were tested for antimicrobial
susceptibility. ST-resistant strains accounted for 73.6-81.0%; CPFX-non-susceptible strains for 14.3-45.7%; and
cefotaxime-resistant strains for 3.3-16.4%.
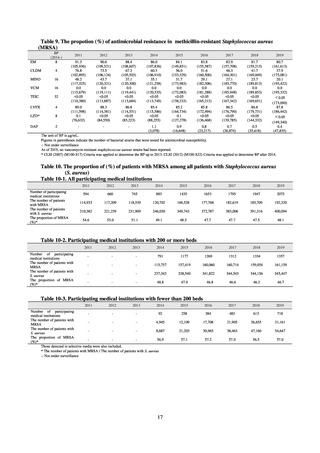
Table 31. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella Typhi
2015
(32 strains)
ABPC
5.7
CP
5.7
ST
5.7
NA
68.8
CPFX
68.8 (12.5*)
CTX
0.0
* Advanced resistance to fluoroquinolone
2016
(46 strains)
2.2
2.2
2.2
63.0
63.0 (23.9*)
0.0
2017
(31 strains)
12.9
12.9
12.9
83.9
83.9 (16.1*)
0.0
2018
(34 strains)
2.9
5.9
5.9
61.7
61.7 (5.9*)
2.9
2019
(28 strains)
10.7
10.7
10.7
57.1
60.7 (10.7*)
3.6
Table 32. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella Paratyphi A
ABPC
CP
ST
NA
CPFX
CTX
2015
(30 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
80.0
83.3
0.0
2016
(20 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
80.0
83.3
0.0
2017
(13 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
76.9
76.9
0.0
2018
(21 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
100
100
0.0
2019
(16 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
87.5
87.5
0.0
2018
(156 strains)
19.2
2019
(91 strains)
14.3
Table 33. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Shigella spp.
ABPC
2015
(105 strains)
21.9
2016
(73 strains)
42.5
2017
(91 strains)
31.9
CP
11.4
24.7
26.4
9.0
6.6
ST
81.0
80.8
73.6
76.9
76.9
NA
63.8
52.1
52.8
45.5
33.0
CPFX
45.7
35.6
35.2
21.2
14.3
CTX
5.7
16.4
13.2
5.1
3.3
28
Source: National Institute of Infectious Diseases
The 28-46 Salmonella Typhi strains that were isolated between 2015 and 2019 were tested for antimicrobial
susceptibility (Table 24). CPFX-non-susceptible strains accounted for 60.7-83.9%, while strains with advanced
resistance (MIC ≥ 4) to ciprofloxacin accounted for 5.9-23.9%. During this period, 11 strains of multidrug-resistant
Salmonella Typhi that indicated resistance to ampicillin (ABPC), CP and ST were isolated, along with two strains
of CTX-resistant Salmonella Typhi.
The 13-30 Salmonella Paratyphi A strains isolated between 2015 and 2019 were tested for antimicrobial
susceptibility. CPFX-non-susceptible strains accounted for 76.9-100% and one strain with advanced CPFX
resistance (MIC ≥ 4) was isolated. No cefotaxime-resistant strains were isolated among the Salmonella Paratyphi
A.
The 73-156 Shigella spp. strains that were isolated between 2015 and 2019 were tested for antimicrobial
susceptibility. ST-resistant strains accounted for 73.6-81.0%; CPFX-non-susceptible strains for 14.3-45.7%; and
cefotaxime-resistant strains for 3.3-16.4%.
Table 31. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella Typhi
2015
(32 strains)
ABPC
5.7
CP
5.7
ST
5.7
NA
68.8
CPFX
68.8 (12.5*)
CTX
0.0
* Advanced resistance to fluoroquinolone
2016
(46 strains)
2.2
2.2
2.2
63.0
63.0 (23.9*)
0.0
2017
(31 strains)
12.9
12.9
12.9
83.9
83.9 (16.1*)
0.0
2018
(34 strains)
2.9
5.9
5.9
61.7
61.7 (5.9*)
2.9
2019
(28 strains)
10.7
10.7
10.7
57.1
60.7 (10.7*)
3.6
Table 32. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella Paratyphi A
ABPC
CP
ST
NA
CPFX
CTX
2015
(30 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
80.0
83.3
0.0
2016
(20 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
80.0
83.3
0.0
2017
(13 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
76.9
76.9
0.0
2018
(21 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
100
100
0.0
2019
(16 strains)
0.0
0.0
0.0
87.5
87.5
0.0
2018
(156 strains)
19.2
2019
(91 strains)
14.3
Table 33. The proportion (%) of antimicrobial-resistant Shigella spp.
ABPC
2015
(105 strains)
21.9
2016
(73 strains)
42.5
2017
(91 strains)
31.9
CP
11.4
24.7
26.4
9.0
6.6
ST
81.0
80.8
73.6
76.9
76.9
NA
63.8
52.1
52.8
45.5
33.0
CPFX
45.7
35.6
35.2
21.2
14.3
CTX
5.7
16.4
13.2
5.1
3.3
28