よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (99 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
3) Prospects
Clear similarity was observed in the proportion of antimicrobial-resistant strains derived from humans and of those
derived from food. As these data are vital to the One Health approach, which covers the environment, animals, food, and
humans, a system has been established that uses conversion software to integrate the data with JANIS and JVARM data to
facilitate integrated evaluation of all three.
(9) Monitoring on the antimicrobial-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae
1) Overview
In the diagnosis of gonococcal infection, the utilization of nucleic acid testing has been promoted. Isolation culture is
only implemented for some patients. Because antimicrobial susceptibility tests for Neisseria gonorrhoeae cannot be easily
implemented in general laboratories or laboratory companies, it is difficult for JANIS to monitor trends in these bacteria.
Therefore, a monitoring on the antimicrobial-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae has been undertaken as research activities at
AMED since 2015. The collected data are also reported to GLASS, which is operated by WHO.
2) Survey methods
More than 40 cooperating clinics are designated across Japan. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were performed at five
facilities capable of testing across Japan, after collecting specimens from the cooperating clinics, or collecting strains
through laboratory companies. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were performed using an agar plate dilution method,
recommended by CLSI or EUCAST, or using Etest. MIC values were measured for CTRX and spectinomycin (SPCM) as
recommended agents; for AZM, which was used as part of the two-drug combination therapy overseas; and for PCG, CFIX,
and CPFX, which had been used as recommended agents in the past. The EUCAST standards were used for susceptibility
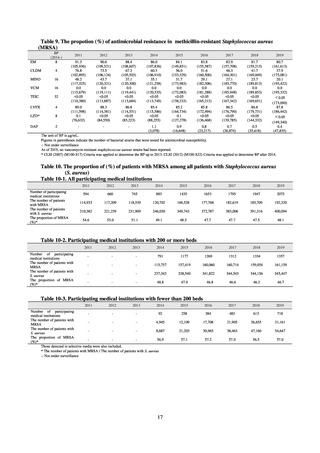
and resistance assessment (Table A). For reference, the proportion of resistant strain based on CLSI Guidelines (M100S25) (Table B) is indicated in Table C. The figures for AZM in the tables are based on the MIC distribution of strains that
have antimicrobial-resistant gene, as indicated by CLSI Guideline (M100-S27).
3) Prospects
Physicians need to empirically choose therapeutic agents for gonococcal infection according to the result of the
monitoring given the difficulty in routinely performing antimicrobial susceptibility tests.
For empiric treatment, it is recommended to use an agent with the potential success rate of 95% or higher. At present,
ceftriaxone and spectinomycin are the only recommendable agents in Japan. Because Neisseria gonorrhoeae that are
present in the pharynx are an important source of infection, Neisseria gonorrhoeae in pharynx should be treated. Due to
its in vivo pharmacokinetics, spectinomycin does not have effect on Neisseria gonorrhoeae present in the pharynx.
Therefore, ceftriaxone is the only practically recommendable agent.
In sporadic cases, strains isolated in Japan indicate the ceftriaxone MIC of 0.5 μg/mL in antimicrobial susceptibility tests.
Ceftriaxone is administered by intramuscular injection overseas, and therefore subject to dose limitation. Therefore, if
strains that indicate the ceftriaxone MIC of 0.5 μg/mL are transmitted to overseas, it is likely that ceftriaxone loses its effect.
Hence, it is required to continue with the careful monitoring of isolated strains in coming years. Reports of the isolation of
strains with the same resistance gene as the resistant strain isolated in Osaka in 2015 [7] have been received from across
the globe since 2017.[8]
Table A. Antimicrobial susceptibility assessment criteria based on EUCAST (μg/mL) for Neisseria gonorrhoeae
PCG
CFIX
CTRX
SPCM
AZM
CPFX
Susceptible
≤ 0.06
≤ 0.125
≤ 0.125
≤ 64
≤ 0.25
≤ 0.03
0.125–1
0.5
0.06
Resistant
>1
> 0.125
> 0.125
> 64
> 0.5
> 0.06
Table B. Antimicrobial susceptibility assessment criteria based on CLSI (μg/mL) for Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Susceptible
Resistant
PCG
≤ 0.06
0.125–1
≧2
CFIX
≤ 0.25
-
-
CTRX
≤ 0.25
-
-
SPCM
≤ 32
64
≧ 128
AZM*
CPFX
≤ 0.06
0.12-0.5
* Epidemiological cutoff value indicated in CLSI Standards (M100-S27): wild type (WT) ≤ 1; non-WT ≥ 2
98
≧1
Clear similarity was observed in the proportion of antimicrobial-resistant strains derived from humans and of those
derived from food. As these data are vital to the One Health approach, which covers the environment, animals, food, and
humans, a system has been established that uses conversion software to integrate the data with JANIS and JVARM data to
facilitate integrated evaluation of all three.
(9) Monitoring on the antimicrobial-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae
1) Overview
In the diagnosis of gonococcal infection, the utilization of nucleic acid testing has been promoted. Isolation culture is
only implemented for some patients. Because antimicrobial susceptibility tests for Neisseria gonorrhoeae cannot be easily
implemented in general laboratories or laboratory companies, it is difficult for JANIS to monitor trends in these bacteria.
Therefore, a monitoring on the antimicrobial-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae has been undertaken as research activities at
AMED since 2015. The collected data are also reported to GLASS, which is operated by WHO.
2) Survey methods
More than 40 cooperating clinics are designated across Japan. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were performed at five
facilities capable of testing across Japan, after collecting specimens from the cooperating clinics, or collecting strains
through laboratory companies. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were performed using an agar plate dilution method,
recommended by CLSI or EUCAST, or using Etest. MIC values were measured for CTRX and spectinomycin (SPCM) as
recommended agents; for AZM, which was used as part of the two-drug combination therapy overseas; and for PCG, CFIX,
and CPFX, which had been used as recommended agents in the past. The EUCAST standards were used for susceptibility
and resistance assessment (Table A). For reference, the proportion of resistant strain based on CLSI Guidelines (M100S25) (Table B) is indicated in Table C. The figures for AZM in the tables are based on the MIC distribution of strains that
have antimicrobial-resistant gene, as indicated by CLSI Guideline (M100-S27).
3) Prospects
Physicians need to empirically choose therapeutic agents for gonococcal infection according to the result of the
monitoring given the difficulty in routinely performing antimicrobial susceptibility tests.
For empiric treatment, it is recommended to use an agent with the potential success rate of 95% or higher. At present,
ceftriaxone and spectinomycin are the only recommendable agents in Japan. Because Neisseria gonorrhoeae that are
present in the pharynx are an important source of infection, Neisseria gonorrhoeae in pharynx should be treated. Due to
its in vivo pharmacokinetics, spectinomycin does not have effect on Neisseria gonorrhoeae present in the pharynx.
Therefore, ceftriaxone is the only practically recommendable agent.
In sporadic cases, strains isolated in Japan indicate the ceftriaxone MIC of 0.5 μg/mL in antimicrobial susceptibility tests.
Ceftriaxone is administered by intramuscular injection overseas, and therefore subject to dose limitation. Therefore, if
strains that indicate the ceftriaxone MIC of 0.5 μg/mL are transmitted to overseas, it is likely that ceftriaxone loses its effect.
Hence, it is required to continue with the careful monitoring of isolated strains in coming years. Reports of the isolation of
strains with the same resistance gene as the resistant strain isolated in Osaka in 2015 [7] have been received from across
the globe since 2017.[8]
Table A. Antimicrobial susceptibility assessment criteria based on EUCAST (μg/mL) for Neisseria gonorrhoeae
PCG
CFIX
CTRX
SPCM
AZM
CPFX
Susceptible
≤ 0.06
≤ 0.125
≤ 0.125
≤ 64
≤ 0.25
≤ 0.03
0.125–1
0.5
0.06
Resistant
>1
> 0.125
> 0.125
> 64
> 0.5
> 0.06
Table B. Antimicrobial susceptibility assessment criteria based on CLSI (μg/mL) for Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Susceptible
Resistant
PCG
≤ 0.06
0.125–1
≧2
CFIX
≤ 0.25
-
-
CTRX
≤ 0.25
-
-
SPCM
≤ 32
64
≧ 128
AZM*
CPFX
≤ 0.06
0.12-0.5
* Epidemiological cutoff value indicated in CLSI Standards (M100-S27): wild type (WT) ≤ 1; non-WT ≥ 2
98
≧1