よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (49 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
ⅲ. Vibrio spp.
Monitoring of agents effective against vibriosis has been carried out since 2017 in respect of strains derived
from diseased fish. In 2018, OTC showed bimodal MIC distribution, with a resistance rate of 15.7%. Although the
MIC distribution of FF was not bimodal and almost all strains showed low MIC values (≤2 μg/ml), one strain did
show a value of 16 μg/ml. Although the MIC distribution of OA was not bimodal, all strains showed low MIC
values (≤1 μg/ml), which suggested that susceptibility to these agents was maintained. Sulfamonomethoxine
(SMMX), however, did not show bimodal MIC distribution, so the resistance rate could not be calculated (Table
61).
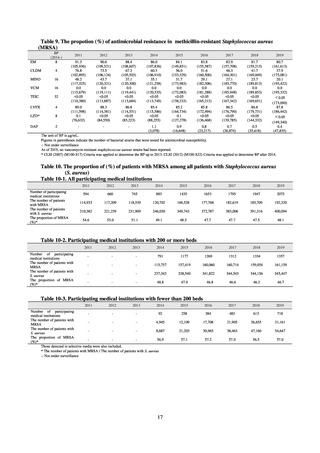
Table 61. Trends in resistance rates among Vibrio spp. (%)
Agent*
OTC
BP
4
Strains tested (n)
2017
2018
12.8
15.7
39
51
The unit of BP is μg/mL.
* While FF, OA and SMMX were also included in the scope of survey, their resistance proportion were not listed because BP cannot be
established.
iv. Vibrio parahaemolyticus derived from aquaculture environment
Monitoring of five agents approved as aquatic drugs (EM, LCM, OTC, OA and FF) was carried out using the
53 and 50 strains derived from aquaculture environments in 2011 and 2012.
Given that no bimodal MIC distribution was observed for any of these agents, the proportion of the strain that
was resistant to those agents was not calculated. MIC values, however, were low (≤ 2 μg/ml for EM, ≤ 1 μg/ml for
OTC and FF, and ≤ 0.5 μg/ml for OA) in all strains, excluding lincomycin (≤ 256 μg/ml for LCM), which
suggested that the susceptibility was maintained to these agents.
48
Monitoring of agents effective against vibriosis has been carried out since 2017 in respect of strains derived
from diseased fish. In 2018, OTC showed bimodal MIC distribution, with a resistance rate of 15.7%. Although the
MIC distribution of FF was not bimodal and almost all strains showed low MIC values (≤2 μg/ml), one strain did
show a value of 16 μg/ml. Although the MIC distribution of OA was not bimodal, all strains showed low MIC
values (≤1 μg/ml), which suggested that susceptibility to these agents was maintained. Sulfamonomethoxine
(SMMX), however, did not show bimodal MIC distribution, so the resistance rate could not be calculated (Table
61).
Table 61. Trends in resistance rates among Vibrio spp. (%)
Agent*
OTC
BP
4
Strains tested (n)
2017
2018
12.8
15.7
39
51
The unit of BP is μg/mL.
* While FF, OA and SMMX were also included in the scope of survey, their resistance proportion were not listed because BP cannot be
established.
iv. Vibrio parahaemolyticus derived from aquaculture environment
Monitoring of five agents approved as aquatic drugs (EM, LCM, OTC, OA and FF) was carried out using the
53 and 50 strains derived from aquaculture environments in 2011 and 2012.
Given that no bimodal MIC distribution was observed for any of these agents, the proportion of the strain that
was resistant to those agents was not calculated. MIC values, however, were low (≤ 2 μg/ml for EM, ≤ 1 μg/ml for
OTC and FF, and ≤ 0.5 μg/ml for OA) in all strains, excluding lincomycin (≤ 256 μg/ml for LCM), which
suggested that the susceptibility was maintained to these agents.
48