よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
【参考資料3】【英版R4.1.17】Nippon AMR One Health Report (NAOR) 2020 (34 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_23261.html |
| 出典情報 | 国際的に脅威となる感染症対策関係閣僚会議 薬剤耐性ワンヘルス動向調査検討会(第9回 1/17)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
9) Survey of infections and antimicrobial use at facilities for the elderly
Source: AMRCRC
Funded by a Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant, the AMRCRC conducted a survey of healthcareassociated infections and antimicrobial use at facilities for the elderly.[9]
ⅰ Long-term care facilities for the elderly
The center randomly selected 1,500 facilities from among the members of the Japan Association of Geriatric
Health Services Facilities and conducted a PPS. Responses were received from 134 facilities (a response rate of
8.9%). Geriatric health services facilities are classified into five type according to their performance based on their
function related to home return. In addition, if previous hospital beds are converted to geriatric health services
facility, it is called nursing convalescence type. The majority of responses came from Higher Return-to-home
facilities (32.5%) and Conventional facilities (60.3%).
The median number of oral antimicrobials deployed in the facilities was four, while the median number of
parenteral antimicrobials was two. The main oral antimicrobials used were quinolones and third-generation
cephalosporins, while the main parenteral antimicrobials were third-generation cephalosporins and penicillins.
A total of 10,148 patients were admitted to the facilities on the day the survey was carried out. Of these, 172
(1.7%) were using antimicrobials. The median age of the patients was 86.0 years (IQR: 81-91), while the median
age of male patients was 84.0 years (IQR: 75-89) and that of female patients was 87.0 years (IQR: 83-92). The top
three medical devices being used by patients were peripheral routes and self-inserted or indwelling bladder
catheters, which were both used by 33 people (19.4%), and gastrostomy tubes, which were used by 23 people
(13.5%). A total of 86 people (50.6%) were not using any medical devices. The top focus of infection were urinary
tract infections, affecting 73 people (47.7%); pneumonia, affecting 31 people (20.3%); and upper respiratory tract
infections, affecting 15 people (9.8%). The main antimicrobials used to treat urinary tract infections and
pneumonia were fluoroquinolones and third-generation cephalosporins. It is necessary to continue to ascertain the
status of infections and antimicrobial use at long-term care facilities for the elderly and to promote antimicrobial
stewardship.
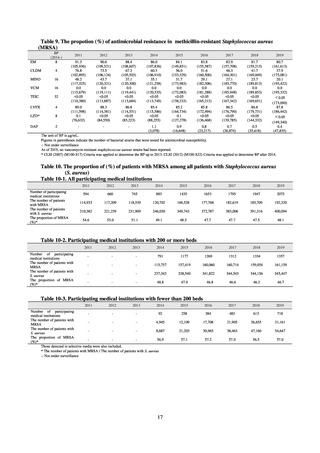
Table 37. Facility Types
Higher Return-to-home
Super return to home
Addition of return-tohome care / home care
support functions II
33 (26.2%)
8 (6.3%)
Conventional
Return-to-home
Addition of return-tohome care / home care
support functions I
40 (31.7%)
Minimum
function
36 (28.6%)
Table 38. Number of antimicrobial agents deployed at facilities: 4 ATC categories
Number of antimicrobial agents based
on the 4 ATC categories
None
1 agent
2 agents
3 agents
4 agents
5 agents
6 agents
7 agents or more
Total
Oral Antimicrobials
Number of Institutions
4
4
21
27
31
23
13
3
126
Parenteral Antimicrobials
Number of Institutions
25
29
27
13
13
6
2
11
126
33
5 (4.0%)
Nursing
Convalescent
4 (3.2%)
Source: AMRCRC
Funded by a Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant, the AMRCRC conducted a survey of healthcareassociated infections and antimicrobial use at facilities for the elderly.[9]
ⅰ Long-term care facilities for the elderly
The center randomly selected 1,500 facilities from among the members of the Japan Association of Geriatric
Health Services Facilities and conducted a PPS. Responses were received from 134 facilities (a response rate of
8.9%). Geriatric health services facilities are classified into five type according to their performance based on their
function related to home return. In addition, if previous hospital beds are converted to geriatric health services
facility, it is called nursing convalescence type. The majority of responses came from Higher Return-to-home
facilities (32.5%) and Conventional facilities (60.3%).
The median number of oral antimicrobials deployed in the facilities was four, while the median number of
parenteral antimicrobials was two. The main oral antimicrobials used were quinolones and third-generation
cephalosporins, while the main parenteral antimicrobials were third-generation cephalosporins and penicillins.
A total of 10,148 patients were admitted to the facilities on the day the survey was carried out. Of these, 172
(1.7%) were using antimicrobials. The median age of the patients was 86.0 years (IQR: 81-91), while the median
age of male patients was 84.0 years (IQR: 75-89) and that of female patients was 87.0 years (IQR: 83-92). The top
three medical devices being used by patients were peripheral routes and self-inserted or indwelling bladder
catheters, which were both used by 33 people (19.4%), and gastrostomy tubes, which were used by 23 people
(13.5%). A total of 86 people (50.6%) were not using any medical devices. The top focus of infection were urinary
tract infections, affecting 73 people (47.7%); pneumonia, affecting 31 people (20.3%); and upper respiratory tract
infections, affecting 15 people (9.8%). The main antimicrobials used to treat urinary tract infections and
pneumonia were fluoroquinolones and third-generation cephalosporins. It is necessary to continue to ascertain the
status of infections and antimicrobial use at long-term care facilities for the elderly and to promote antimicrobial
stewardship.
Table 37. Facility Types
Higher Return-to-home
Super return to home
Addition of return-tohome care / home care
support functions II
33 (26.2%)
8 (6.3%)
Conventional
Return-to-home
Addition of return-tohome care / home care
support functions I
40 (31.7%)
Minimum
function
36 (28.6%)
Table 38. Number of antimicrobial agents deployed at facilities: 4 ATC categories
Number of antimicrobial agents based
on the 4 ATC categories
None
1 agent
2 agents
3 agents
4 agents
5 agents
6 agents
7 agents or more
Total
Oral Antimicrobials
Number of Institutions
4
4
21
27
31
23
13
3
126
Parenteral Antimicrobials
Number of Institutions
25
29
27
13
13
6
2
11
126
33
5 (4.0%)
Nursing
Convalescent
4 (3.2%)