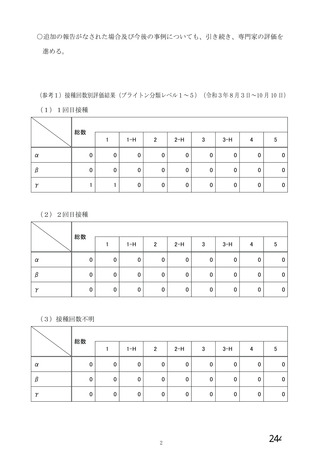
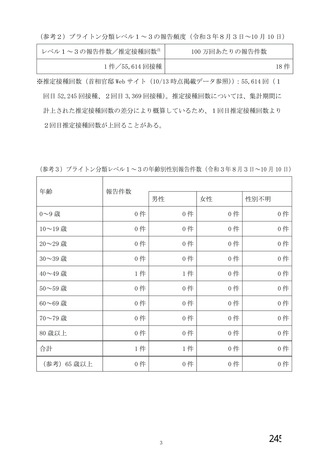
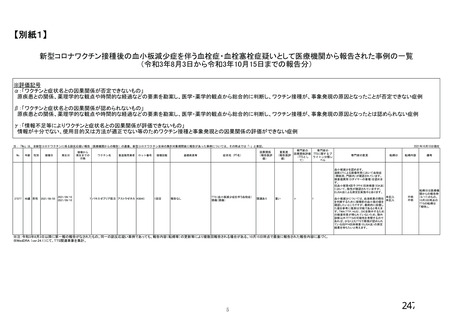
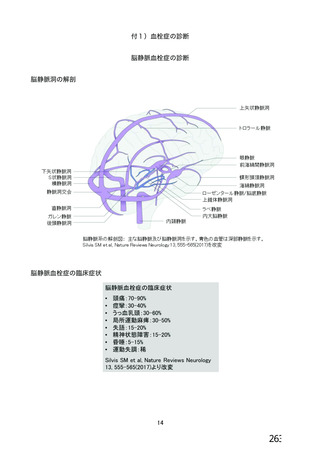
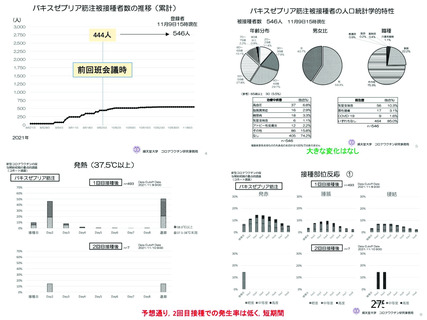
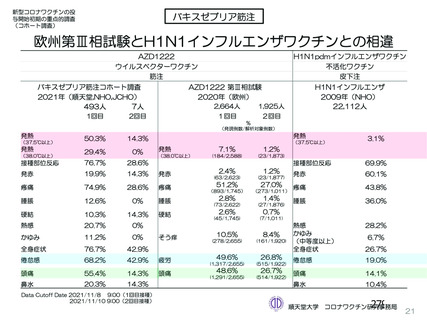
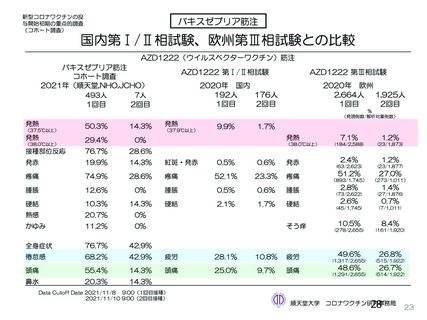
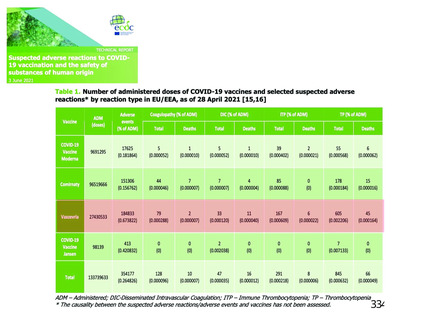
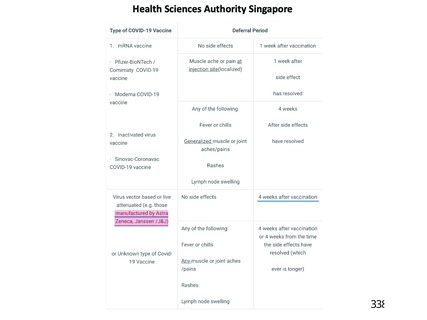
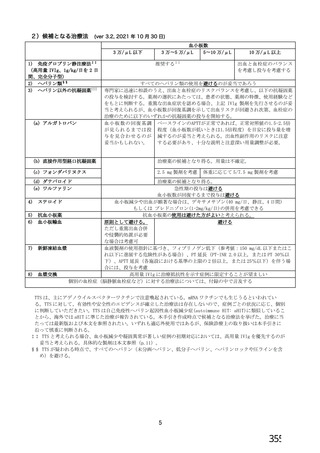
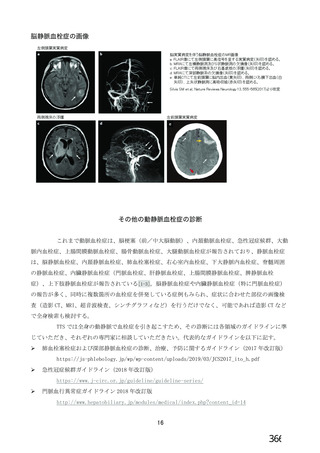
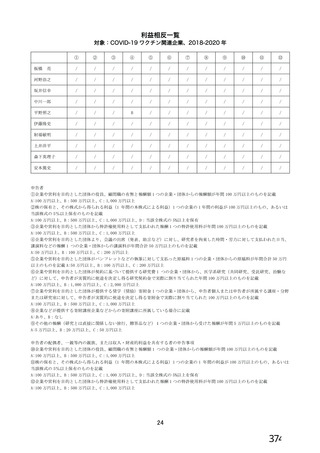
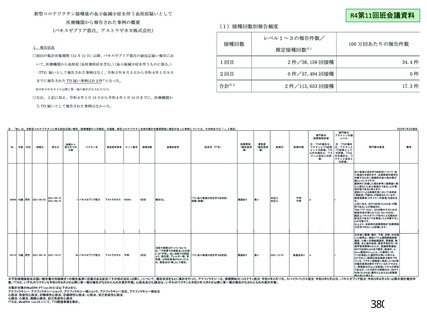
資 料4-2-➁ 令和4年度第2回安全技術調査会の審議結果について➁ (153 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_27906.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事・食品衛生審議会 薬事分科会血液事業部会(令和4年度第2回 9/14)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
10.1182/blood.2021012217.
24. Bruyne SD, Degandt, Ghys T, Louagie H. Thrombocytopenia after coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination:
remember
to
put
the
blame
on
others
too.
Crit
Care
Med.
2021
Sep
24.
Doi:
10.1097/CCM.0000000000005327
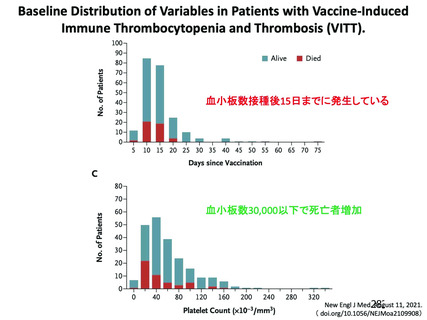
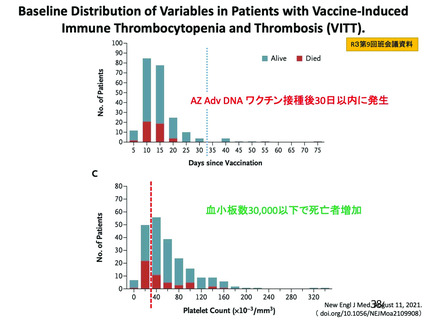
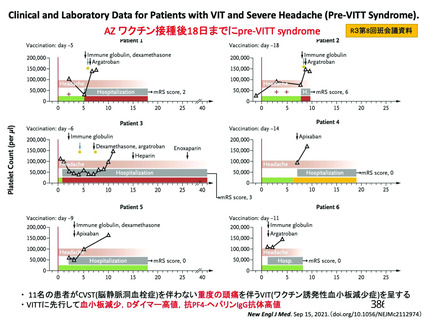
25. Pavord S, Scully M, Hunt BJ, et al.: Clinical Features of Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia and
Thrombosis. N Engl J Med 2021;385:1680-1689. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2109908.
26. Padmanabhan A, Jones CG, Pechauer SM, Curtis BR, Bougie DW, Irani MS, Bryant BJ, Alperin JB,
Deloughery TG, Mulvey KP, Dhakal B, Wen R, Wang D, Aster RH. IVIg for Treatment of Severe Refractory
Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Chest. 2017; 152: 478-485. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.03.050.
27. Warkentin TE, Climans TH, Morin P-A: Intravenous Immune Globulin to Prevent Heparin-Induced
Thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378: 1845-1848. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1801799.
28. Warkentin TE. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment and prevention of heparininduced
thrombocytopenia:
a
review.
Expert
Rev
Hematol.
2019;
12:
685-698.
doi:
10.1080/17474086.2019.1636645.
29. Kang M, Alahmadi M, Sawh S, Kovacs MJ, Lazo-Langner A. Fondaparinux for the treatment of suspected
heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a propensity score-matched study. Blood. 2015; 125:924-929.
30. Warkentin TE, Sheppard JA, Chu FV, Kapoor A, Crowther MA, Gangji A. Plasma exchange to remove HIT
antibodies: dissociation between enzyme-immunoassay and platelet activation test reactivities. Blood.
2015; 125: 195-198. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-07-590844.
31. Ferro JM, Coutinho JM, Dentali F, Kobayashi A, Alasheev A, Canhão P, Karpov D, Nagel S, Posthuma L,
Roriz JM, Caria J, Frässdorf M, Huisman H, Reilly P, Diener HC ; for the RE-SPECT CVT Study Group. Safety
and Efficacy of Dabigatran Etexilate vs Dose-Adjusted Warfarin in Patients With Cerebral Venous
Thrombosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2019; 76: 1457-1465.
32. Lee GKH, Chen VH, Tan CH, Leow AST, Kong WY, Sia CH, Chew NWS, Tu TM, Chan BPL, Yeo LLL, Sharma
VK, TanBYQ. Comparing the efficacy and safety of direct oral anticoagulants with vitamin k antagonist
in cerebral venous thrombosis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020; 50: 724-731. doi: 10.1007/s11239-02002106-7.
33. American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council Leadership. Diagnosis and
Management
of
Cerebral
Venous
Sinus
Thrombosis
with
Vaccine-Induced
Thrombotic
Thrombocytopenia. Stroke. 2021;52:2478-2482. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.035564.
34. Caprio F, Bernstein RA. Duration of Anticoagulation After Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Neurocrit
Care. 2012; 16: 335-342. doi: 10.1007/s12028-011-9661-1.
35. Pavord S, Lester W, Makris M, Scully M, Hunt B. Guidance from the Expert Haematology Panel (EHP) on
Covid-19 Vaccine-induced Immune Thrombocytopenia and Thrombosis (VITT). (Updated Guidance on
21
371