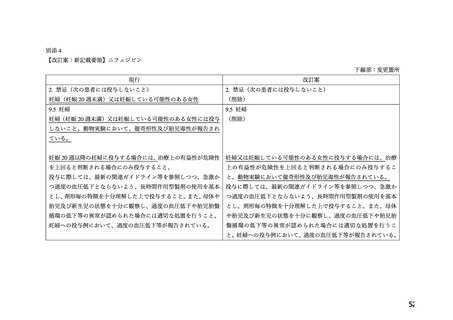
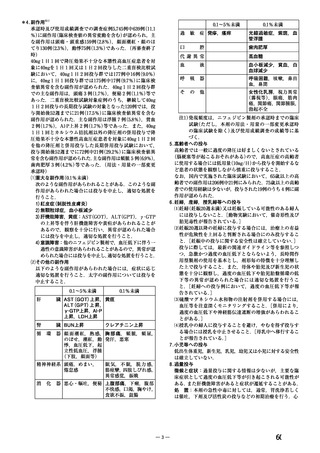
よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料1-3 ニフェジピン 調査結果報告書及び添付文書 (22 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_29305.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事・食品衛生審議会 薬事分科会医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和4年度第19回 11/22)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
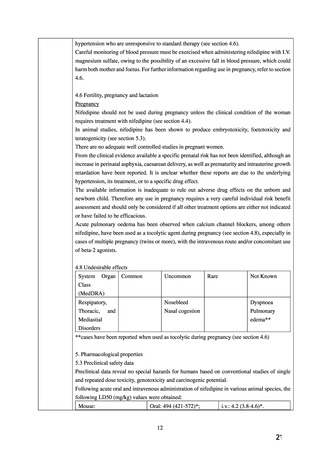
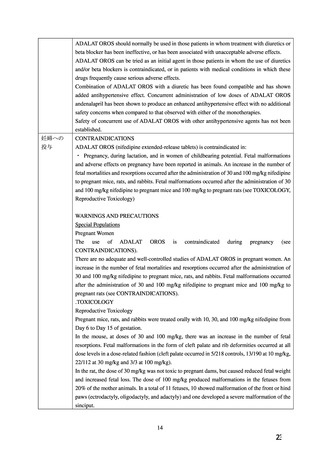
hypertension who are unresponsive to standard therapy (see section 4.6).
Careful monitoring of blood pressure must be exercised when administering nifedipine with I.V.
magnesium sulfate, owing to the possibility of an excessive fall in blood pressure, which could
harm both mother and foetus. For further information regarding use in pregnancy, refer to section
4.6.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
Nifedipine should not be used during pregnancy unless the clinical condition of the woman
requires treatment with nifedipine (see section 4.4).
In animal studies, nifedipine has been shown to produce embryotoxicity, foetotoxicity and
teratogenicity (see section 5.3).
There are no adequate well controlled studies in pregnant women.
From the clinical evidence available a specific prenatal risk has not been identified, although an
increase in perinatal asphyxia, caesarean delivery, as well as prematurity and intrauterine growth
retardation have been reported. It is unclear whether these reports are due to the underlying
hypertension, its treatment, or to a specific drug effect.
The available information is inadequate to rule out adverse drug effects on the unborn and
newborn child. Therefore any use in pregnancy requires a very careful individual risk benefit
assessment and should only be considered if all other treatment options are either not indicated
or have failed to be efficacious.
Acute pulmonary oedema has been observed when calcium channel blockers, among others
nifedipine, have been used as a tocolytic agent during pregnancy (see section 4.8), especially in
cases of multiple pregnancy (twins or more), with the intravenous route and/or concomitant use
of beta-2 agonists.
4.8 Undesirable effects
System
Organ
Common
Uncommon
Rare
Not Known
Class
(MedDRA)
Respipatory,
Thoracic,
and
Nosebleed
Dyspnoea
Nasal cogestion
Pulmonary
edema**
Mediastial
Disorders
**cases have been reported when used as tocolytic during pregnancy (see section 4.6)
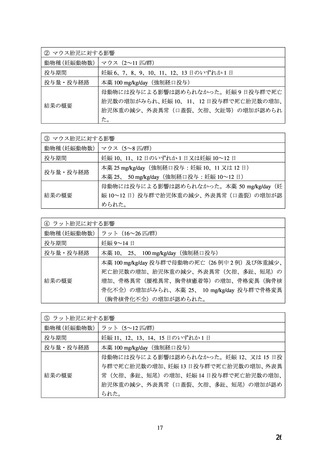
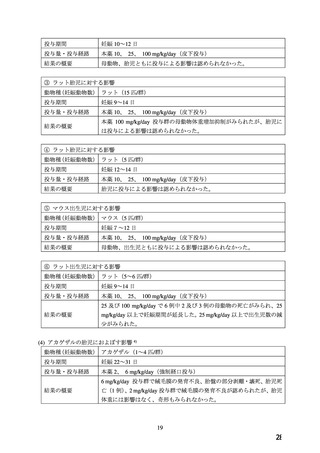
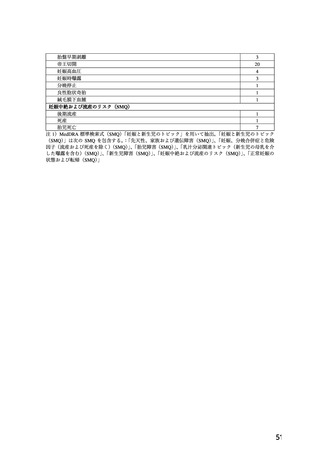
5. Pharmacological properties
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Preclinical data reveal no special hazards for humans based on conventional studies of single
and repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and carcinogenic potential.
Following acute oral and intravenous administration of nifedipine in various animal species, the
following LD50 (mg/kg) values were obtained:
Mouse:
Oral: 494 (421-572)*;
i.v.: 4.2 (3.8-4.6)*.
12
21
Careful monitoring of blood pressure must be exercised when administering nifedipine with I.V.
magnesium sulfate, owing to the possibility of an excessive fall in blood pressure, which could
harm both mother and foetus. For further information regarding use in pregnancy, refer to section
4.6.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
Nifedipine should not be used during pregnancy unless the clinical condition of the woman
requires treatment with nifedipine (see section 4.4).
In animal studies, nifedipine has been shown to produce embryotoxicity, foetotoxicity and
teratogenicity (see section 5.3).
There are no adequate well controlled studies in pregnant women.
From the clinical evidence available a specific prenatal risk has not been identified, although an
increase in perinatal asphyxia, caesarean delivery, as well as prematurity and intrauterine growth
retardation have been reported. It is unclear whether these reports are due to the underlying
hypertension, its treatment, or to a specific drug effect.
The available information is inadequate to rule out adverse drug effects on the unborn and
newborn child. Therefore any use in pregnancy requires a very careful individual risk benefit
assessment and should only be considered if all other treatment options are either not indicated
or have failed to be efficacious.
Acute pulmonary oedema has been observed when calcium channel blockers, among others
nifedipine, have been used as a tocolytic agent during pregnancy (see section 4.8), especially in
cases of multiple pregnancy (twins or more), with the intravenous route and/or concomitant use
of beta-2 agonists.
4.8 Undesirable effects
System
Organ
Common
Uncommon
Rare
Not Known
Class
(MedDRA)
Respipatory,
Thoracic,
and
Nosebleed
Dyspnoea
Nasal cogestion
Pulmonary
edema**
Mediastial
Disorders
**cases have been reported when used as tocolytic during pregnancy (see section 4.6)
5. Pharmacological properties
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Preclinical data reveal no special hazards for humans based on conventional studies of single
and repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and carcinogenic potential.
Following acute oral and intravenous administration of nifedipine in various animal species, the
following LD50 (mg/kg) values were obtained:
Mouse:
Oral: 494 (421-572)*;
i.v.: 4.2 (3.8-4.6)*.
12
21