よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料1-3 ニフェジピン 調査結果報告書及び添付文書 (45 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_29305.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事・食品衛生審議会 薬事分科会医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和4年度第19回 11/22)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
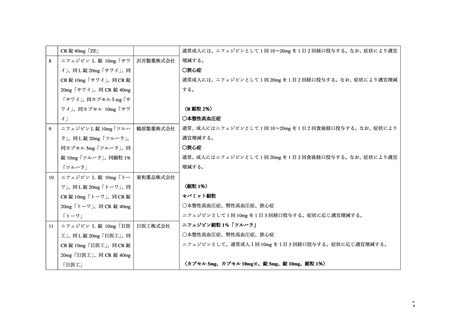
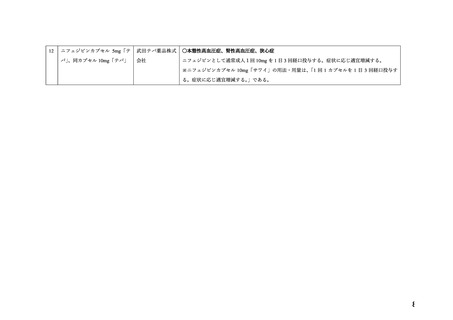
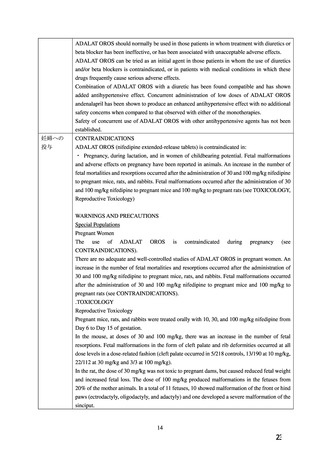
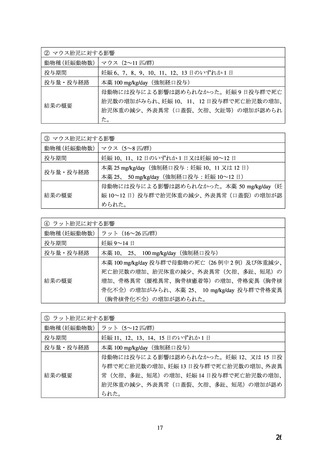
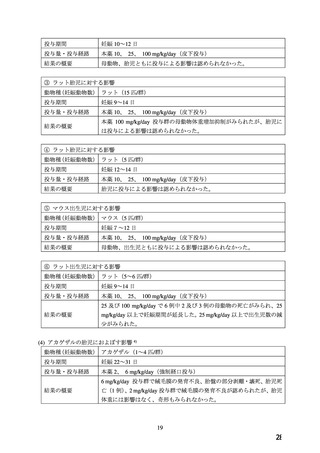
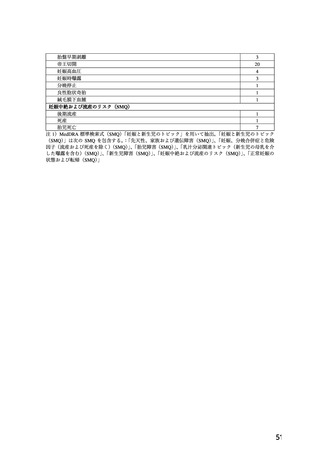
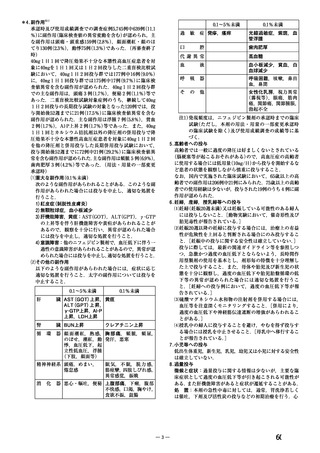
10.1 降圧薬の選択(経口)
経口降圧薬の第一選択薬は、メチルドパ(アルドメット)
、ラベタロール(トランデート)
、ニ
フェジピン(アダラート:妊娠 20 週以降)
、ヒドララジン(アプレゾリンなど)のいずれか
を用いる。
海外ガイドライン 国際妊娠高血圧学会
(6) Brown MA et al. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. ISSHP Classification, Diagnosis, and
Management Recommendations for International Practice. Hypertension. 2018 Jul;72(1):24-43.
doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10803. Review. No abstract available. PMID:
29899139
Section 4. Management Principles for the Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
Chronic Essential Hypertension
Acceptable initial antihypertensives include labetalol, oxprenolol, methyldopa, nifedipine, diltiazem;
prazosin and hydralazine are usually used as second or third line agents.
海外ガイドライン 米国産科婦人科学会
(7) ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 203: Chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy.
Committee on Practice Bulletins- Obstetrics. Obstet and Gynecol. 2019 Jan;133(1):e26-e50. doi:
10.1097/AOG.0000000000003020. PMID: 30575676
Clinical Considerations and Recommendations
▶What treatments should be used for pregnant women with chronic hypertension, and what are the
goals of treatment?
Control of Chronic Hypertension
For chronic maintenance treatment, the oral agents listed in Table 2 can be considered alone or in
combination. The table lists the most commonly used medications in pregnancy and is not meant to
be comprehensive. For the long-term treatment of pregnant women who require pharmacologic
therapy, labetalol or nifedipine are reasonable options and are recommended above all other
antihypertensive drugs.
Clinical Considerations and Recommendations
▶ What considerations are important for pregnancy counsein in patients with chronic
hypertension?
The medication review should place special emphasis on agents to be avoided, in particular
angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers.
Background
Effects of Chronic Hypertension on Pregnancy
Fetal risks
Limited evidence is emerging that patients with chronic hypertension may be at higher risk of fetal
congenital malformations. In a systematic review of 16 observational studies, a higher relative risk of
congenital heart disease of 1.4 (95% CI, 1.221.7) and 2.0 (95% CI, 1.522.7) was found among the
35
44
経口降圧薬の第一選択薬は、メチルドパ(アルドメット)
、ラベタロール(トランデート)
、ニ
フェジピン(アダラート:妊娠 20 週以降)
、ヒドララジン(アプレゾリンなど)のいずれか
を用いる。
海外ガイドライン 国際妊娠高血圧学会
(6) Brown MA et al. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. ISSHP Classification, Diagnosis, and
Management Recommendations for International Practice. Hypertension. 2018 Jul;72(1):24-43.
doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10803. Review. No abstract available. PMID:
29899139
Section 4. Management Principles for the Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
Chronic Essential Hypertension
Acceptable initial antihypertensives include labetalol, oxprenolol, methyldopa, nifedipine, diltiazem;
prazosin and hydralazine are usually used as second or third line agents.
海外ガイドライン 米国産科婦人科学会
(7) ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 203: Chronic Hypertension in Pregnancy.
Committee on Practice Bulletins- Obstetrics. Obstet and Gynecol. 2019 Jan;133(1):e26-e50. doi:
10.1097/AOG.0000000000003020. PMID: 30575676
Clinical Considerations and Recommendations
▶What treatments should be used for pregnant women with chronic hypertension, and what are the
goals of treatment?
Control of Chronic Hypertension
For chronic maintenance treatment, the oral agents listed in Table 2 can be considered alone or in
combination. The table lists the most commonly used medications in pregnancy and is not meant to
be comprehensive. For the long-term treatment of pregnant women who require pharmacologic
therapy, labetalol or nifedipine are reasonable options and are recommended above all other
antihypertensive drugs.
Clinical Considerations and Recommendations
▶ What considerations are important for pregnancy counsein in patients with chronic
hypertension?
The medication review should place special emphasis on agents to be avoided, in particular
angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers.
Background
Effects of Chronic Hypertension on Pregnancy
Fetal risks
Limited evidence is emerging that patients with chronic hypertension may be at higher risk of fetal
congenital malformations. In a systematic review of 16 observational studies, a higher relative risk of
congenital heart disease of 1.4 (95% CI, 1.221.7) and 2.0 (95% CI, 1.522.7) was found among the
35
44