よむ、つかう、まなぶ。
資料1-3 ニフェジピン 調査結果報告書及び添付文書 (25 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_29305.html |
| 出典情報 | 薬事・食品衛生審議会 薬事分科会医薬品等安全対策部会安全対策調査会(令和4年度第19回 11/22)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
ダウンロードした画像を利用する際は「出典情報」を明記してください。
低解像度画像をダウンロード
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
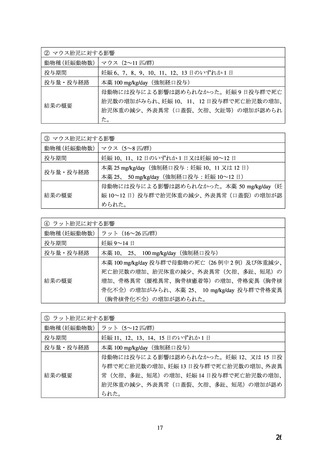
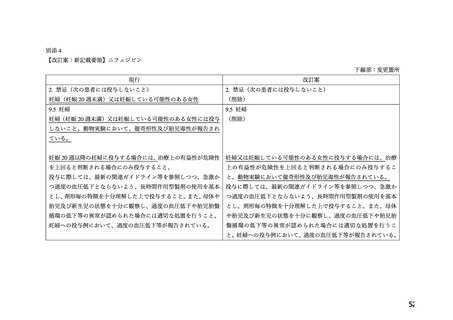
In the rabbit, there was dose-dependent anorexia and weight loss in mothers during the dosing
period. At 30 and 100 mg/kg reduced litter size and weight and increased fetal loss were evident.
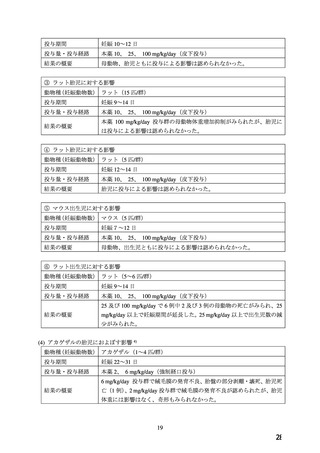
Studies on pregnant Rhesus monkeys with oral doses of 2 (1 animal) or 6 mg/kg/day (4 animals)
revealed no teratogenic effects. The placentas were poorly developed in these animals.
Pre-natal and post-natal studies on rats with daily doses of 3, 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg showed that
nifedipine caused significant prolongation of the gestation period at dosages of 10 mg/kg
upwards and a decrease in litter size. The post-natal development of the newborn animals was
impaired when doses of 30 mg/kg or more had been administered. All offspring in the 100 mg/kg
group died
経口剤(豪州)
(4) 製品名 Adalat OROS/ BAYER AUSTRALIA LTD
効能・効果
INDICATIONS
Adalat OROS is indicated for:
1. the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension
2. the prophylaxis of chronic stable angina pectoris
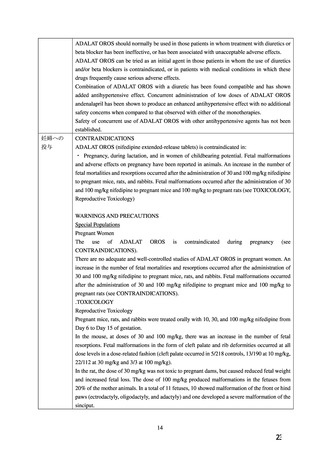
妊婦への
CONTRAINDICATIONS
投与
Adalat OROS is contraindicated in:
-female patients throughout pregnancy
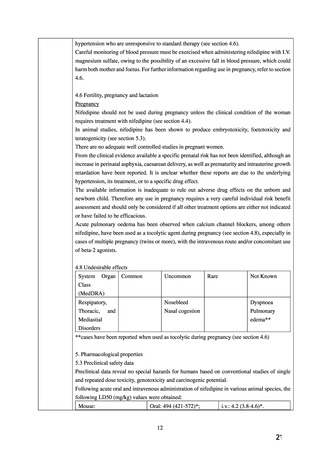
FERTILITY, PREGNANCY AND LACTATION Use in Pregnancy (Category C)
Nifedipine carries the potential for fetal hypoxia, caesarean deliveries, prematurity and
intrauterine growth retardation, which may be associated with maternal hypotension.
Accordingly, it is contraindicated throughout pregnancy.
Nifedipine has been shown to produce teratogenic findings in rats, mice and rabbits, including
digital anomalies, malformation of the extremities, cleft palates, cleft sternum and malformation
of the ribs. Digital anomalies are possibly a result of compromised uterine blood flow. Nifedipine
administration was associated with a variety of embryotoxic, placentotoxic and fetotoxic effects,
including stunted fetuses (rats, mice, rabbits), small placentas and underdeveloped chorionic
villi (monkeys), embryonic and fetal deaths (rats, mice, rabbits) and prolonged
pregnancy/decreased neonatal survival (rats; not evaluated in other species).
All of the doses associated with the teratogenic, embryotoxic or fetotoxic effects in animals were
maternally toxic and several times the recommended maximum dose for humans. There are no
adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women.
Acute pulmonary oedema has been observed when calcium channel blockers, among others
nifedipine (primarily in IR formulation), have been used as a tocolytic agent during pregnancy,
especially in cases of multiple pregnancy (twins or more), with the intravenous route and/or
concomitant use of beta-2 agonists.
15
24
period. At 30 and 100 mg/kg reduced litter size and weight and increased fetal loss were evident.
Studies on pregnant Rhesus monkeys with oral doses of 2 (1 animal) or 6 mg/kg/day (4 animals)
revealed no teratogenic effects. The placentas were poorly developed in these animals.
Pre-natal and post-natal studies on rats with daily doses of 3, 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg showed that
nifedipine caused significant prolongation of the gestation period at dosages of 10 mg/kg
upwards and a decrease in litter size. The post-natal development of the newborn animals was
impaired when doses of 30 mg/kg or more had been administered. All offspring in the 100 mg/kg
group died
経口剤(豪州)
(4) 製品名 Adalat OROS/ BAYER AUSTRALIA LTD
効能・効果
INDICATIONS
Adalat OROS is indicated for:
1. the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension
2. the prophylaxis of chronic stable angina pectoris
妊婦への
CONTRAINDICATIONS
投与
Adalat OROS is contraindicated in:
-female patients throughout pregnancy
FERTILITY, PREGNANCY AND LACTATION Use in Pregnancy (Category C)
Nifedipine carries the potential for fetal hypoxia, caesarean deliveries, prematurity and
intrauterine growth retardation, which may be associated with maternal hypotension.
Accordingly, it is contraindicated throughout pregnancy.
Nifedipine has been shown to produce teratogenic findings in rats, mice and rabbits, including
digital anomalies, malformation of the extremities, cleft palates, cleft sternum and malformation
of the ribs. Digital anomalies are possibly a result of compromised uterine blood flow. Nifedipine
administration was associated with a variety of embryotoxic, placentotoxic and fetotoxic effects,
including stunted fetuses (rats, mice, rabbits), small placentas and underdeveloped chorionic
villi (monkeys), embryonic and fetal deaths (rats, mice, rabbits) and prolonged
pregnancy/decreased neonatal survival (rats; not evaluated in other species).
All of the doses associated with the teratogenic, embryotoxic or fetotoxic effects in animals were
maternally toxic and several times the recommended maximum dose for humans. There are no
adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women.
Acute pulmonary oedema has been observed when calcium channel blockers, among others
nifedipine (primarily in IR formulation), have been used as a tocolytic agent during pregnancy,
especially in cases of multiple pregnancy (twins or more), with the intravenous route and/or
concomitant use of beta-2 agonists.
15
24