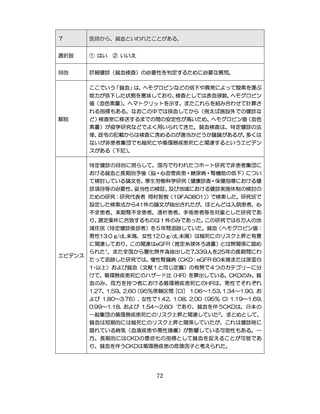
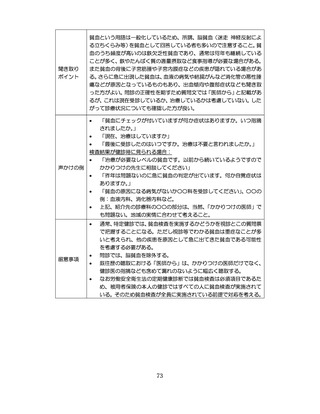
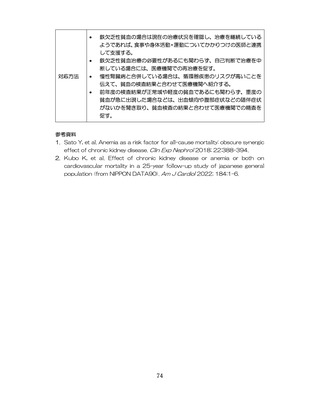
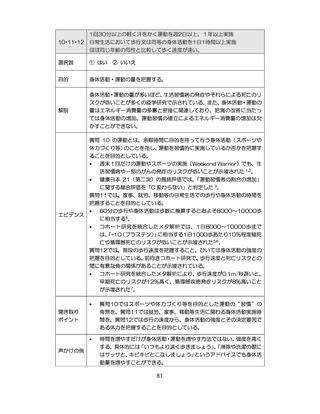
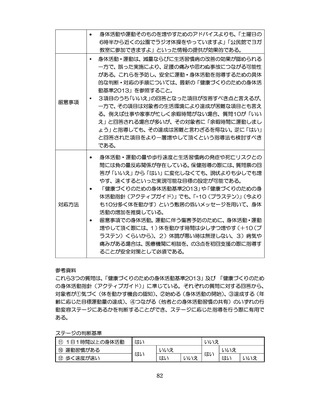
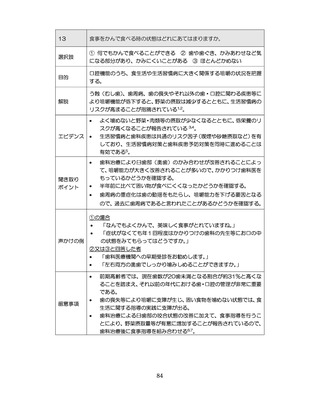
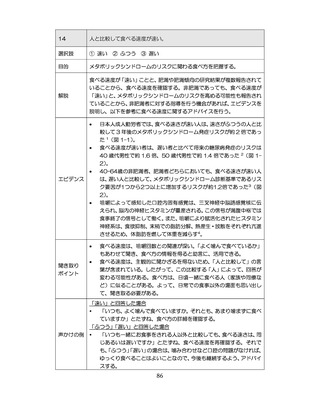
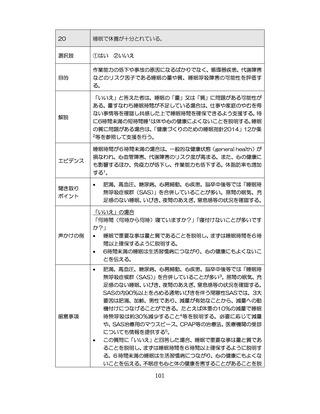
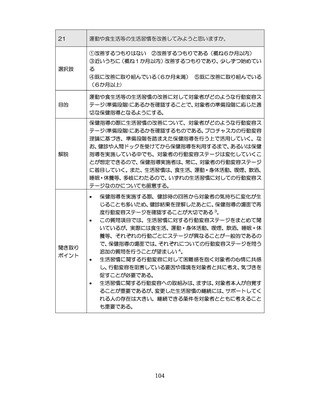
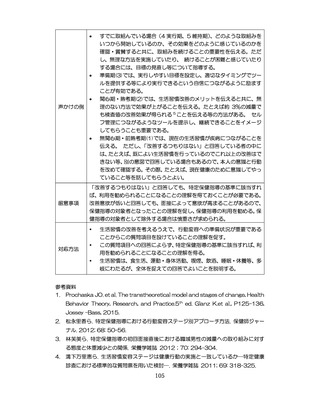
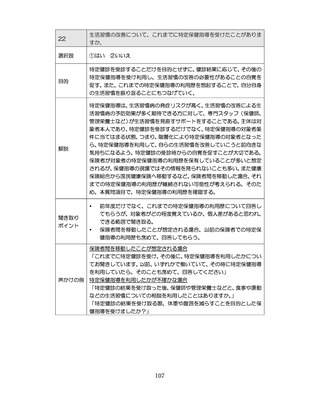
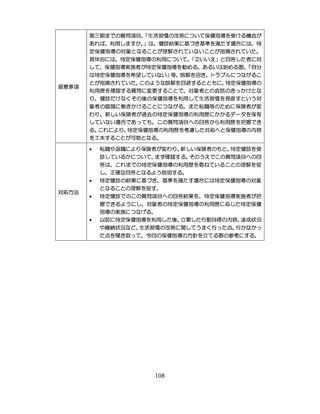
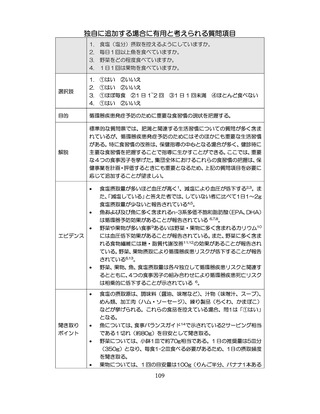
04.【資料2-1】標準的な健診・保健指導プログラム(令和6年度版)(案)1/2 (104 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_31652.html |
| 出典情報 | 標準的な健診・保健指導プログラム改訂に関するワーキンググループ(第2回 3/7)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
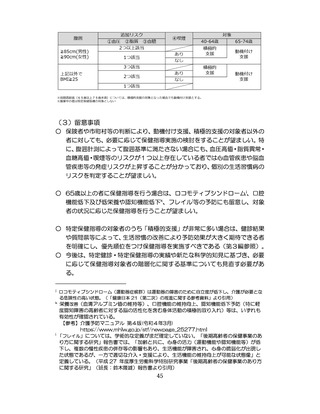
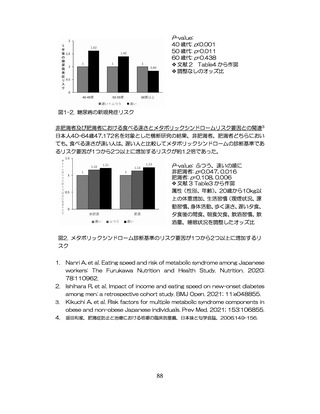
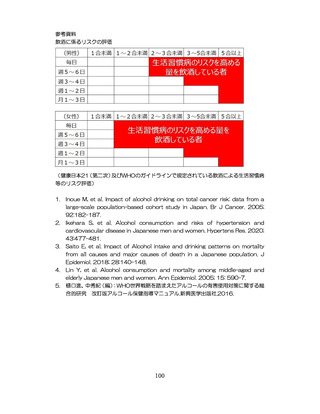
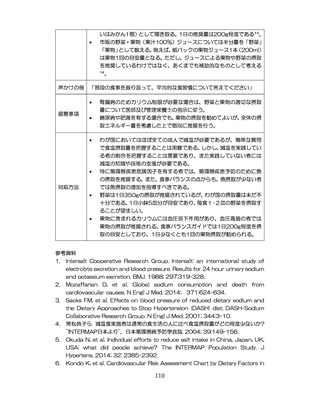
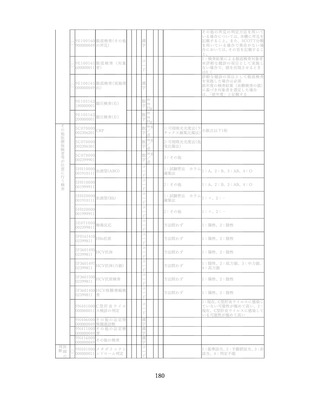
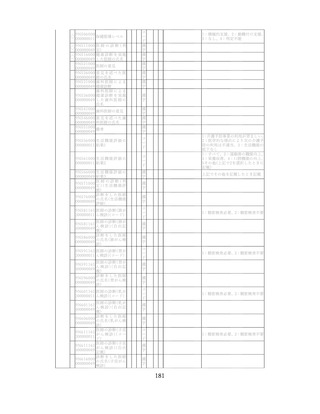
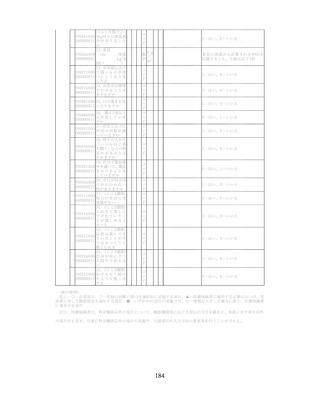
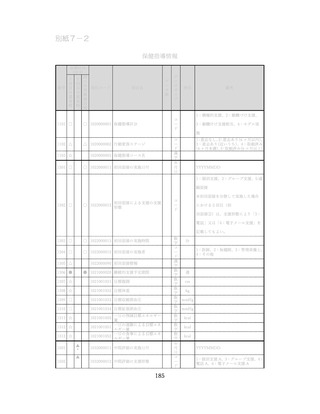
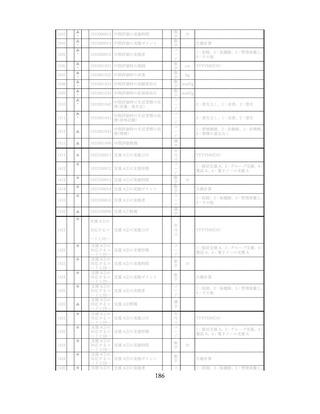
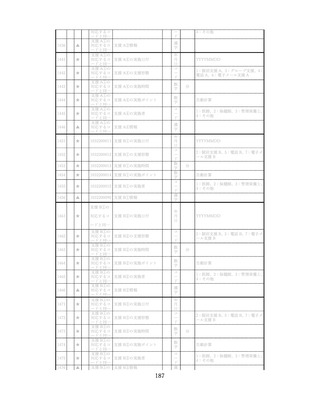
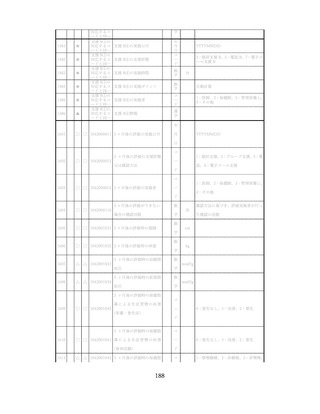
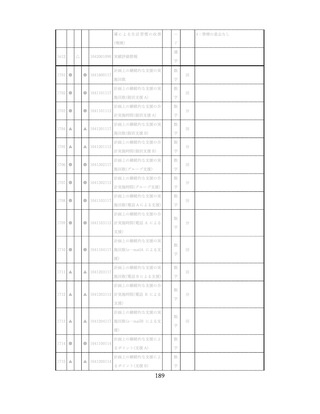
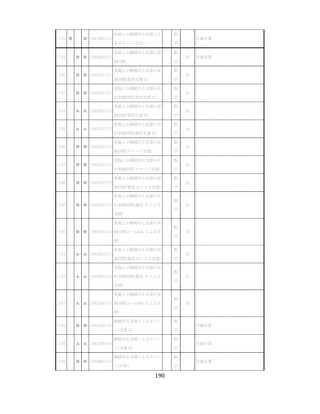
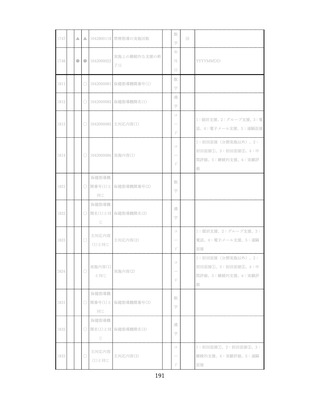
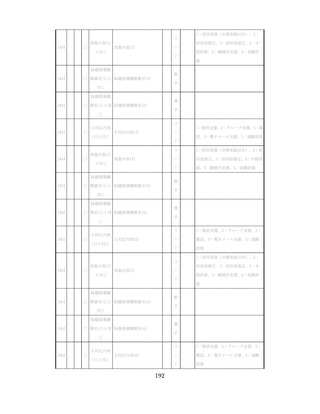
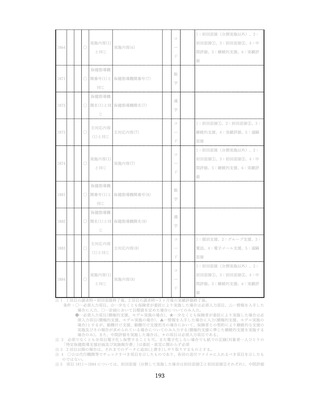
飲酒に係るリスクの評価
(健康日本21(第二次)及びWHOのガイドラインで規定されている飲酒による生活習慣病
等のリスク評価)
1.
Inoue M, et al. Impact of alcohol drinking on total cancer risk: data from a
large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Br J Cancer. 2005;
92:182-187.
2.
Ikehara S, et al. Alcohol consumption and risks of hypertension and
cardiovascular disease in Japanese men and women. Hypertens Res. 2020;
43:477-481.
3.
Saito E, et al. Impact of Alcohol intake and drinking patterns on mortality
from all causes and major causes of death in a Japanese population. J
Epidemiol. 2018; 28:140-148.
4.
Lin Y, et al. Alcohol consumption and mortality among middle-aged and
elderly Japanese men and women. Ann Epidemiol. 2005; 15: 590-7.
5.
樋口進、中秀紀(編)
:WHO世界戦略を踏まえたアルコールの有害使用対策に関する総
合的研究
改訂版アルコール保健指導マニュアル.新興医学出版社.2016.
100