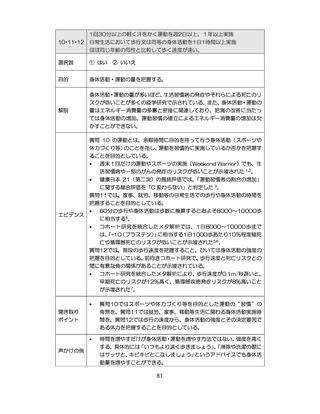
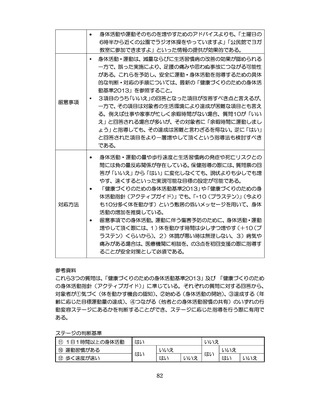
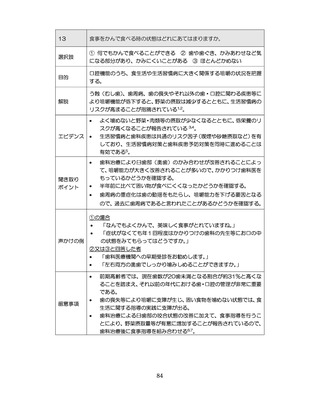
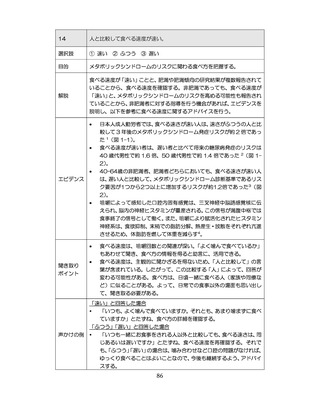
04.【資料2-1】標準的な健診・保健指導プログラム(令和6年度版)(案)1/2 (74 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_31652.html |
| 出典情報 | 標準的な健診・保健指導プログラム改訂に関するワーキンググループ(第2回 3/7)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
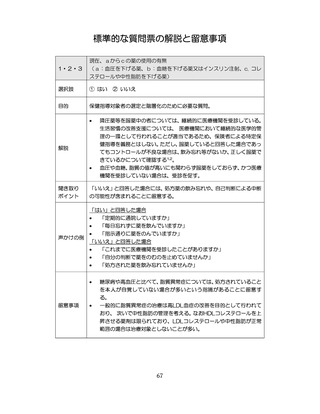
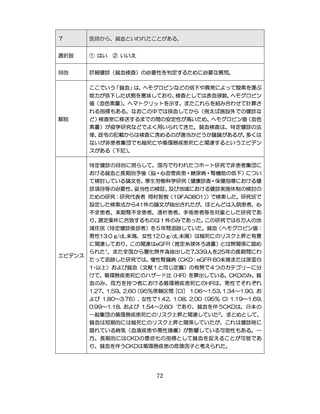
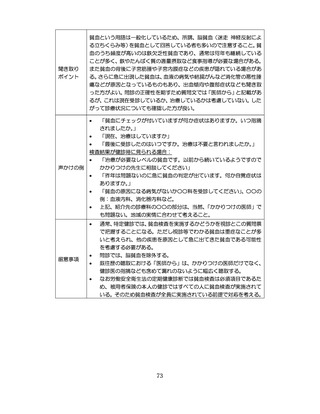
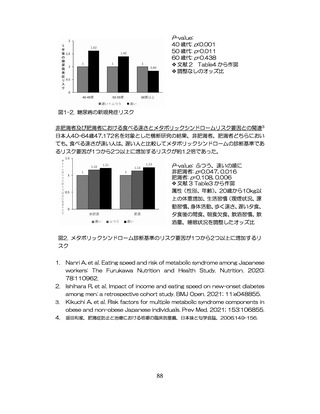
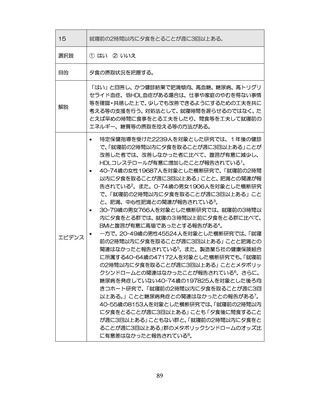
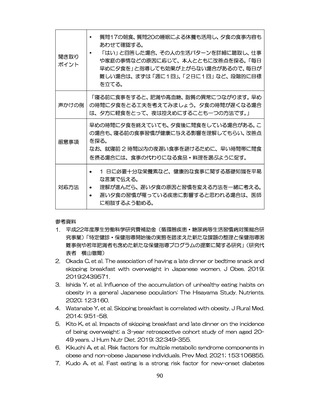
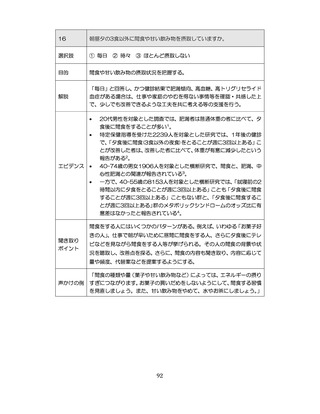
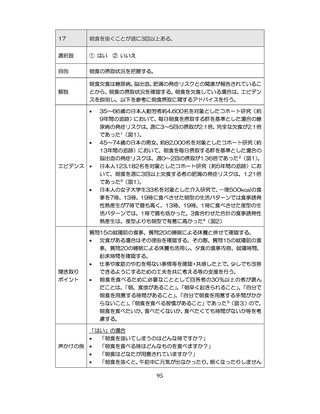
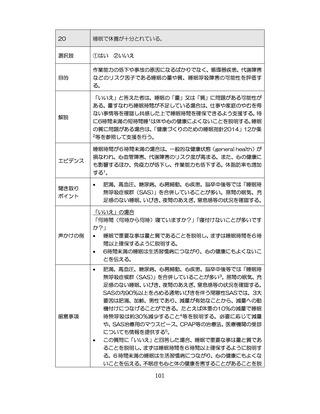
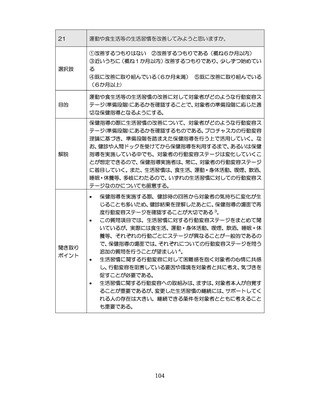
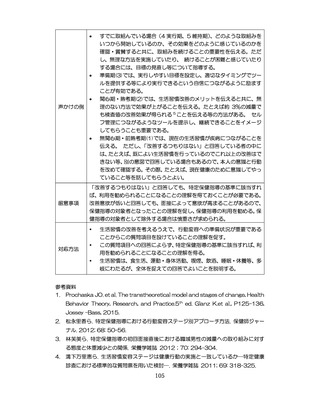
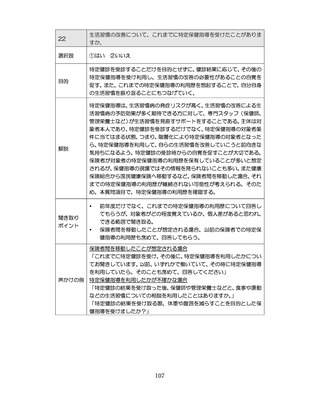
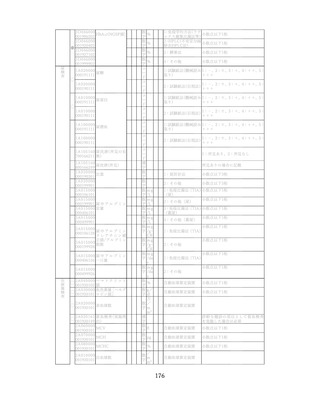
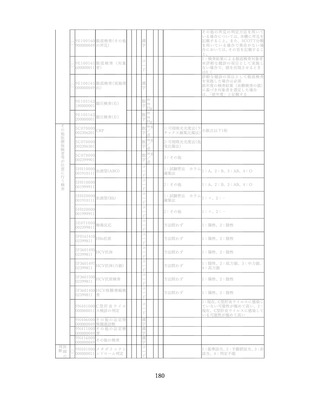
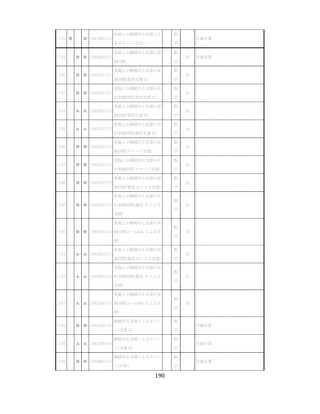
「診断された医療機関はどこですか」
「具体的な病名はわかりますか」
「継続的な受診が必要であるといわれましたか」
「主治医の先生は治療が必要といっていましたか、また投薬を受けた
ことがありますか?」
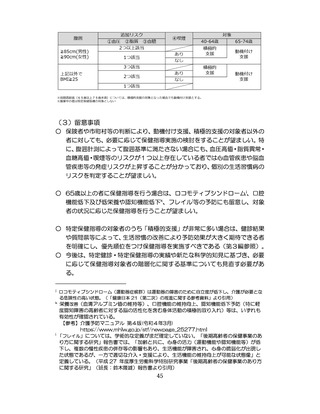
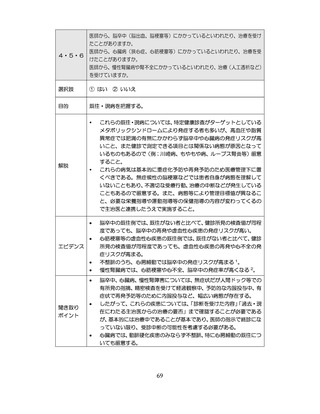
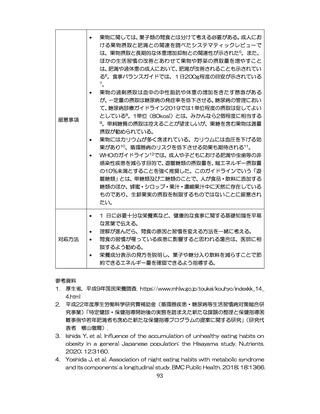
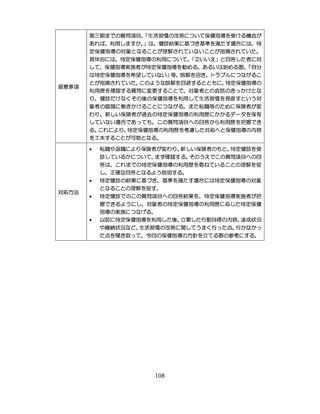
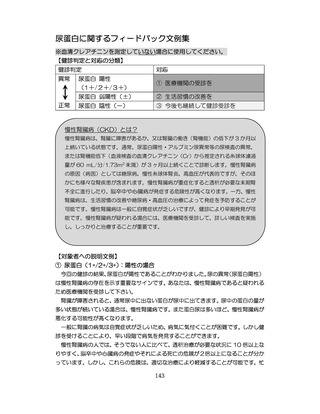
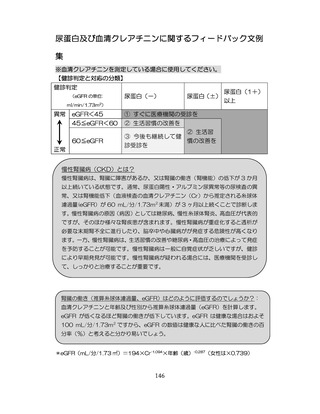
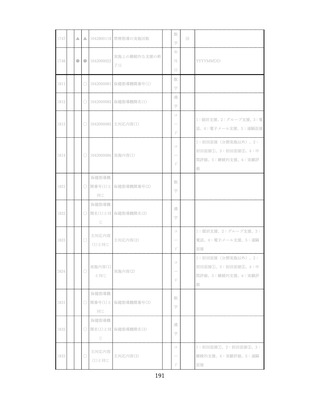
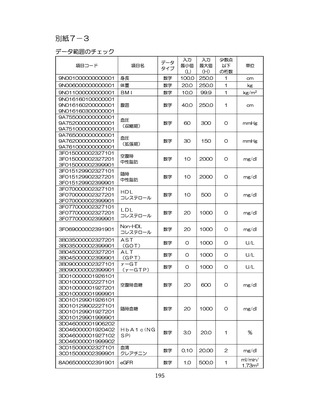
慢性腎臓病(CKD)とは、腎臓の障害(蛋白尿等)
、もしくは糸球体濾
過量(GFR)が60ml/分/1.73m2未満の腎機能低下が一定期間持続し
留意事項
た状態をいう。
推定GFR(eGFR)は、血清クレアチニン値、年齢、性から推算できる
3
。
本来的には主治医によるフォローアップが望ましいので健康診査や保
健指導で完結しようとしすぎないようにすることが重要である
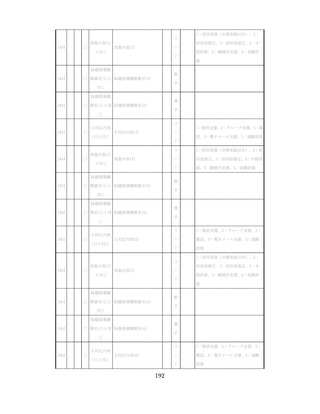
脳卒中、心臓病、慢性腎障害がある場合には単独で保健指導を行わず、
主治医と連携の上実施する、虚血性心疾患では食事・運動療法によるメ
タボリックシンドロームの管理が十分であれば、再発等を予防する効
果がある 4,5。
対応方法
例えば慢性腎不全者は蛋白制限が必要な場合があるなど、健常者と同
じ指導をすることでむしろ病態が悪化する可能性があることを留意す
る。
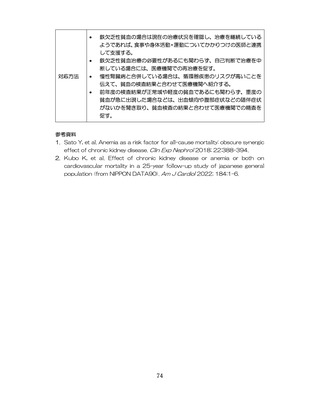
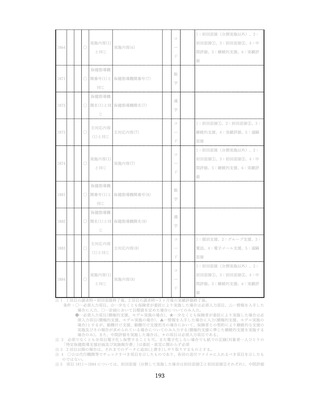
治療が必要であるにもかかわらず未治療になっている受診者には健診
時に確実な受診継続をするよう勧める。
喫煙により脳卒中・心筋梗塞の発症リスクが増大するため禁煙をすす
める 6,7。
参考資料
1.
Goldstein LB, et al. Primary prevention of ischemic stroke: a guideline from
the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke
Council: cosponsored by the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease
Interdisciplinary Working Group; Cardiovascular Nursing Council; Clinical
Cardiology Council; Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism Council; and
the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group:
the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline.
Stroke. 2006; 37:1583–1633.
2.
Go AS, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular
events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:1296–1305.
3.
腎機能測定ツール. 一般社団法人日本腎臓学会. https://jsn.or.jp/general/check/
4.
Bittner V, et al. Comprehensive cardiovascular risk factor control improves
survival: The BARI 2D Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66:765–773.
5.
Pagidipati NJ, et al. Secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: international insights from the TECOS
Trial (Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes With Sitagliptin). Circulation.
2017; 136:1193–1203.
70