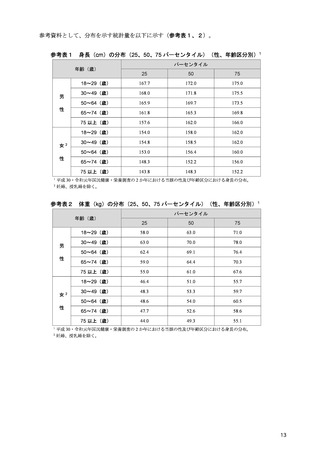
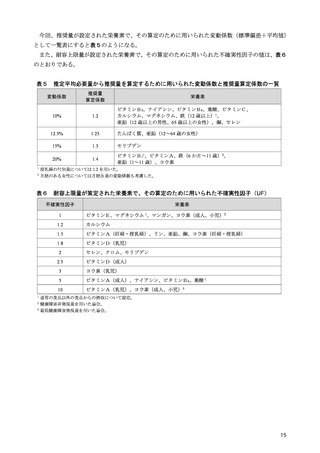
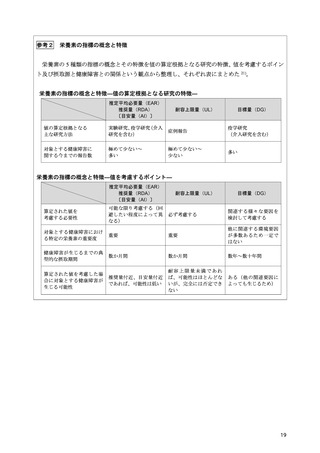
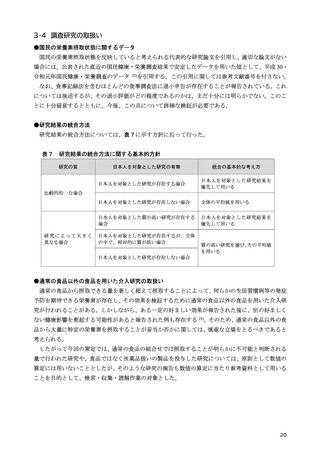
「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書 (111 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_44138.html |
| 出典情報 | 「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
52) 外間登美子, 安里葉子, 仲里幸子. 沖縄県中城村における離乳期の鉄の摂取状況 第 2 報 離乳後
期の栄養調査成績. 小児保健研究. 1998;57(1):45-48.
53) Van Elswyk ME, Weatherford CA, McNeill SH. A systematic review of renal health in healthy individuals
associated with protein intake above the US recommended daily allowance in randomized controlled trials
and observational studies. Adv Nutr. 2018;9(4):404-418.
54) Devries MC, Sithamparapillai A, Brimble KS, et al. Changes in kidney function do not differ between
healthy adults consuming higher- compared with lower- or normal-protein diets: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Nutr. 2018;148(11):1760-1775.
55) Remer T, Kalotai N, Amini AM, et al. Protein intake and risk of urolithiasis and kidney diseases: an umbrella
review of systematic reviews for the evidence-based guideline of the German Nutrition Society. Eur J Nutr.
2023;62(5):1957-1975.
56) Morton RW, Murphy KT, McKellar SR, et al. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression of
the effect of protein supplementation on resistance training-induced gains in muscle mass and strength in
healthy adults. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(6):376-384.
57) Hengeveld LM, de Goede J, Afman LA, et al. Health effects of increasing protein intake above the current
population reference intake in older adults: A systematic review of the Health Council of the Netherlands.
Adv Nutr. 2022;13(4):1083-1117.
58) Coelho-Junior HJ, Calvani R, Picca A, et al. Protein intake and frailty in older adults: A systematic review
and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutrients. 2022;14(13):2767.
59) Coelho-Júnior HJ, Rodrigues B, Uchida M, et al. Low protein intake is associated with frailty in older adults:
A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutrients. 2018;10(9):1334.
60) Coelho-Junior HJ, Calvani R, Azzolino D, et al. Protein intake and sarcopenia in older adults: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8718.
61) Wu SY, Yeh NH, Chang HY, et al. Adequate protein intake in older adults in the context of frailty: crosssectional results of the Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan 2014-2017. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;114(2):649660.
62) Coelho-Júnior HJ, Calvani R, Picca A, et al. Protein-related dietary parameters and frailty status in older
community-dwellers across different frailty instruments. Nutrients. 2020;12(2):508.
63) Mitchell CJ, Milan AM, Mitchell SM, et al. The effects of dietary protein intake on appendicular lean mass
and muscle function in elderly men: a 10-wk randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;106(6):13751383.
64) Wright CS, Zhou J, Sayer RD, et al. Effects of a high-protein diet including whole eggs on muscle
composition and indices of cardiometabolic health and systemic inflammation in older adults with
overweight or obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. 2018;10(7):946.
65) Bray GA, Smith SR, de Jonge L, et al. Effect of dietary protein content on weight gain, energy expenditure,
and body composition during overeating: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012;307(1):47-55.
66) Schulze MB, Haardt J, Amini AM, et al. Protein intake and type 2 diabetes mellitus: an umbrella review of
systematic reviews for the evidence-based guideline for protein intake of the German Nutrition Society. Eur
J Nutr. 2024;63(1):33-50.
101