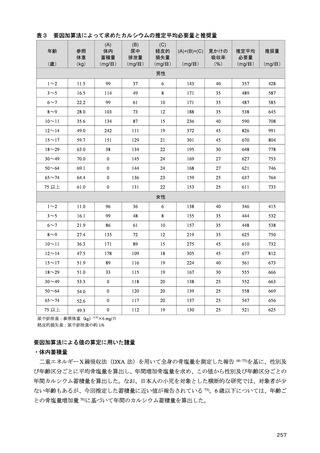
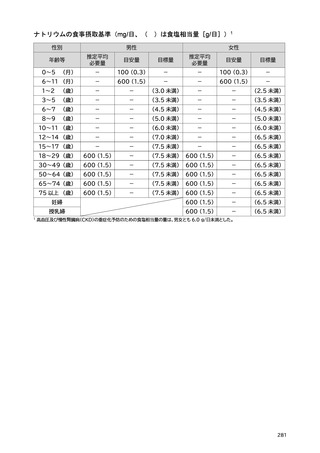
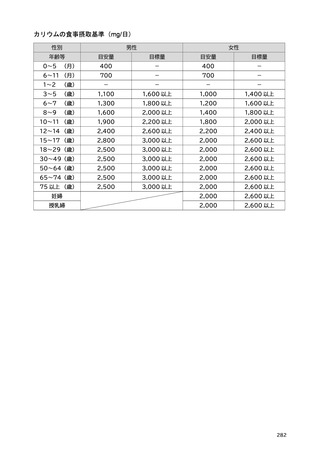
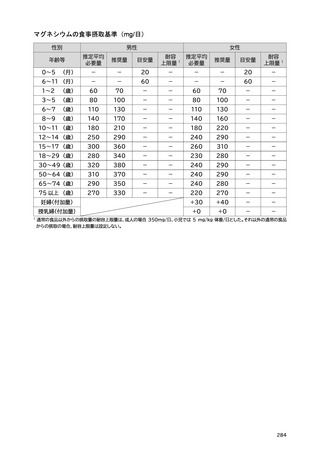
「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書 (287 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_44138.html |
| 出典情報 | 「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
111) Jayedi A, Zargar MS. Dietary calcium intake and hypertension risk: a dose-response meta-analysis of
prospective cohort studies. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019;73(7):969-978.
112) van Mierlo LAJ, Arends LR, Streppel MT, et al. Blood pressure response to calcium supplementation: a
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Hum Hypertens. 2006;20(8):571-580.
113) Dickinson HO, Nicolson DJ, Cook JV, et al. Calcium supplementation for the management of primary
hypertension in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(2):CD004639.
114) Marshall D, Johnell O, Wedel H. Meta-analysis of how well measures of bone mineral density predict
occurrence of osteoporotic fractures. BMJ. 1996;312(7041):1254-1259.
115) Fleet JC, Cashman KD. Magnesium. In: Bowman BA, Russell RM, eds. Present Knowledge in Nutrition.
8th ed. ILSI Press, Washington D.C; 2001:292-301.
116) Institute of Medicine. Magnesium. In: Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium,
Vitamin D, and Fluoride. National Academies Press, Washington, D.C.; 1997:190-249.
117) Rude RK. Magnesium deficiency: a cause of heterogeneous disease in humans. J Bone Miner Res.
1998;13(4):749-758.
118) Schwartz R, Spencer H, Welsh JJ. Magnesium absorption in human subjects from leafy vegetables,
intrinsically labeled with stable 26Mg. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984;39(4):571-576.
119) Abrams SA, Chen Z, Hawthorne KM. Magnesium metabolism in 4-year-old to 8-year-old children. J Bone
Miner Res. 2014;29(1):118-122.
120) Nishimuta M, Kodama N, Shimada M, et al. Estimated equilibrated dietary intakes for nine minerals (Na,
K, Ca, Mg, P, Fe, Zn, Cu, and Mn) adjusted by mineral balance medians in young Japanese females. J Nutr
Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2012;58(2):118-128.
121) Lakshmanan FL, Rao RB, Kim WW, et al. Magnesium intakes, balances, and blood levels of adults
consuming self-selected diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984;40(6 Suppl):1380-1389.
122) Hunt CD, Johnson LK. Magnesium requirements: new estimations for men and women by cross-sectional
statistical analyses of metabolic magnesium balance data. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84(4):843-852.
123) Rosanoff A. Perspective: US adult magnesium requirements need updating: Impacts of rising body weights
and data-derived variance. Adv Nutr. 2021;12(2):298-304.
124) 鈴木和春, 五島孜郎. 日本人小児の微量ミネラル摂取とその出納. 日本栄養・食糧学会誌.
1991;44(2):89-104.
125) Seeling MS. Magnesium Balance in Pregnancy, Magnesium Deficiency in the Pathogenesis of Disease.
Plenum Medical, New York; 1980.
126) Institute of Medicine. Nutrition During Lactation. National Academies Press, Washington, D.C.; 1991.
127) Widdowson EM, Dickerson JWT. Chemical composition of the body. In: Comar CL, Bronner F, eds.
Mineral Metabolism: An Advanced Treatise. Vol. II. The Elements, Part A. Academic Press, New York;
1964:1-247.
128) Klein CJ, Moser-Veillon PB, Douglass LW, et al. A longitudinal study of urinary calcium, magnesium, and
zinc excretion in lactating and nonlactating postpartum women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995;61(4):779-786.
129) Bashir Y, Sneddon JF, Staunton HA, et al. Effects of long-term oral magnesium chloride replacement in
congestive heart failure secondary to coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1993;72(15):1156-1162.
277