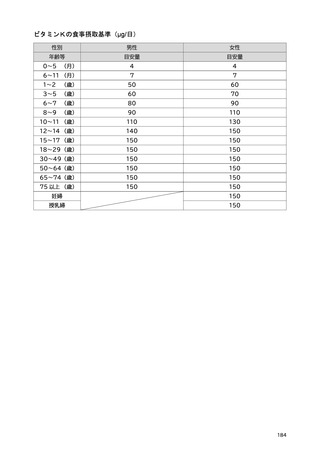
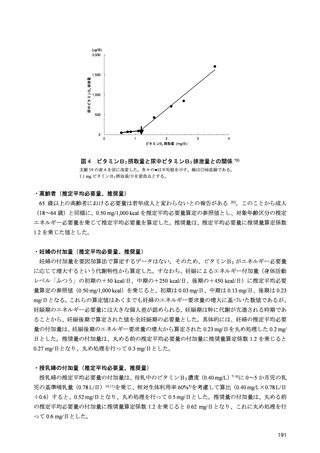
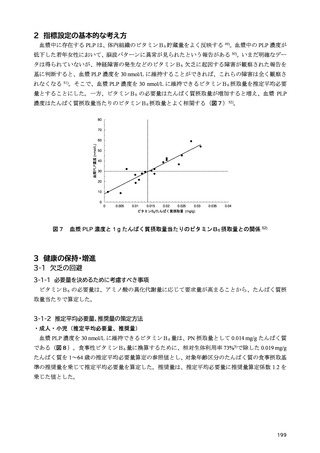
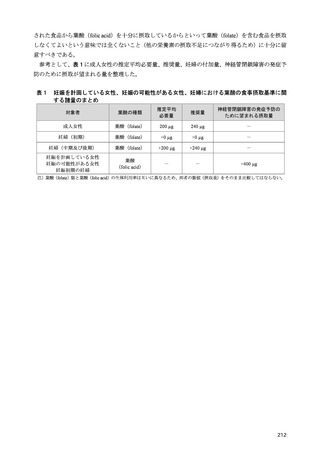
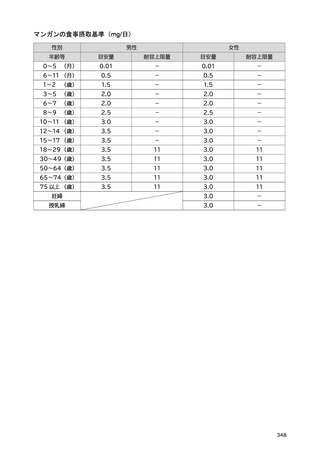
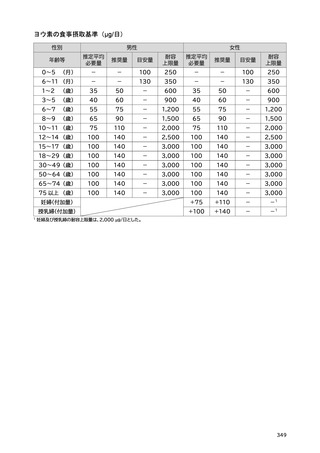
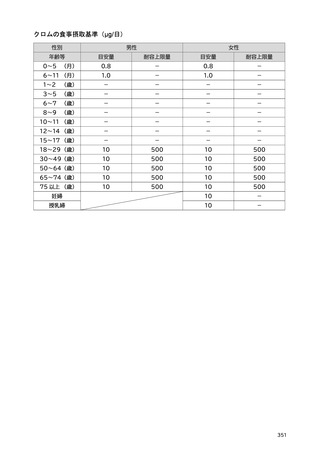
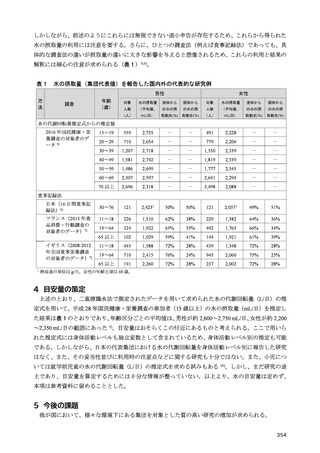
「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書 (427 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_44138.html |
| 出典情報 | 「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
87) Tielemans SMAJ, Altorf-van der Kuil W, Engberink MF, et al. Intake of total protein, plant protein and
animal protein in relation to blood pressure: a meta-analysis of observational and intervention studies. J
Hum Hypertens. 2013;27(9):564-571.
88) Gopinath B, Flood VM, Rochtchina E, et al. Influence of high glycemic index and glycemic load diets on
blood pressure during adolescence. Hypertension. 2012;59(6):1272-1277.
89) Brown IJ, Stamler J, Van Horn L, et al. Sugar-sweetened beverage, sugar intake of individuals, and their
blood pressure: International Study of Macro/Micronutrients and Blood Pressure. Hypertension.
2011;57(4):695-701.
90) Qin P, Li Q, Zhao Y, et al. Sugar and artificially sweetened beverages and risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes
mellitus, hypertension, and all-cause mortality: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.
Eur J Epidemiol. 2020;35(7):655-671.
91) Filippou CD, Tsioufis CP, Thomopoulos CG, et al. Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet
and blood pressure reduction in adults with and without hypertension: A systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. Adv Nutr. 2020;11(5):1150-1160.
92) Estruch R, Ros E, Salas-Salvadó J, et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean
diet supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil or nuts. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(25):e34.
93) Cowell OR, Mistry N, Deighton K, et al. Effects of a Mediterranean diet on blood pressure: a systematic
review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. J Hypertens.
2021;39(4):729-739.
417