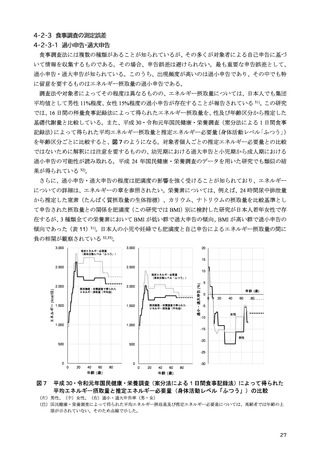
「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書 (408 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_44138.html |
| 出典情報 | 「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
20) De Bandt JP. Leucine and mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent activation of muscle protein synthesis
in aging. J Nutr. 2016;146(12):2616S-2624S.
21) Morton RW, Traylor DA, Weijs PJM, et al. Defining anabolic resistance: implications for delivery of clinical
care nutrition. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2018;24(2):124-130.
22) Volpi E, Mittendorfer B, Rasmussen BB, et al. The response of muscle protein anabolism to combined
hyperaminoacidemia and glucose-induced hyperinsulinemia is impaired in the elderly. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 2000;85(12):4481-4490.
23) Smeuninx B, Greig CA, Breen L. Amount, source and pattern of dietary protein intake across the adult
lifespan: A cross-sectional study. Front Nutr. 2020;7:25.
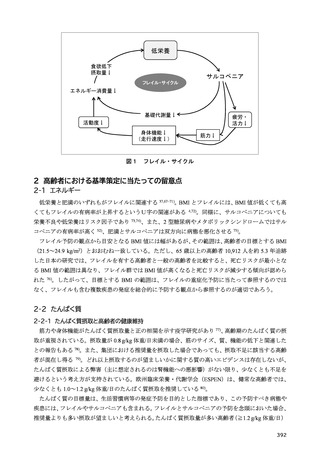
24) 大村卓也, 重本和宏. 基礎研究からの最新知見 メカニズムから解き明かすサルコペニアの病態.
公益財団法人長寿科学振興財団. フレイル予防・対策:基礎研究から臨床、そして地域へ. 2021:177190.
25) Drummond MJ, Dreyer HC, Fry CS, et al. Nutritional and contractile regulation of human skeletal muscle
protein synthesis and mTORC1 signaling. J Appl Physiol. 2009;106(4):1374-1384.
26) Stark M, Lukaszuk J, Prawitz A, et al. Protein timing and its effects on muscular hypertrophy and strength
in individuals engaged in weight-training. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2012;9(1):54.
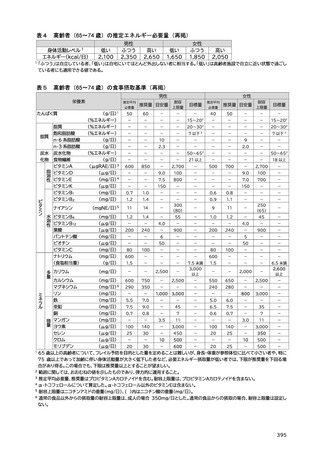
27) 葛谷雅文. 高齢者の栄養評価と低栄養の対策. 日本老年医学会雑誌. 2003;40(3):199-203.
28) Siqueira V de O, Costa BV de L, Lopes ACS, et al. Different equations for determining height among the
elderly: the Bambuí Cohort Study of Aging. Cad Saude Publica. 2012;28(1):125-134.
29) 小宮秀一. BMI と除脂肪量指数(FFMI)及び脂肪量指数(FMI)に関する問題. 健康科学. 2004;26:17.
30) 日本肥満学会編. 肥満症診療ガイドライン 2022. ライフサイエンス出版; 2022.
31) 大内尉義, 秋山弘子, 折茂肇. 新老年学 第 3 版. 東京大学出版会; 2010.
32) 加藤佐千子. 高齢者の低栄養とフレイルティ. 日本家政学会誌. 2018;69(6):462-469.
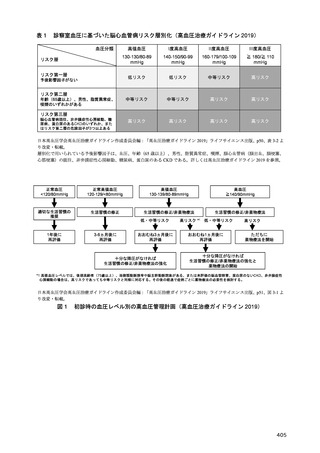
33) Hildrum B, Mykletun A, Dahl AA, et al. Metabolic syndrome and risk of mortality in middle-aged versus
elderly individuals: the Nord-Trøndelag Health Study (HUNT). Diabetologia. 2009;52(4):583-590.
34) Prospective Studies Collaboration, Lewington S, Whitlock G, et al. Blood cholesterol and vascular mortality
by age, sex, and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of individual data from 61 prospective studies with 55,000
vascular deaths. Lancet. 2007;370(9602):1829-1839.
35) Tamakoshi A, Yatsuya H, Lin Y, et al. BMI and all-cause mortality among Japanese older adults: findings
from the Japan collaborative cohort study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010;18(2):362-369.
36) Dramé M, Godaert L. The obesity paradox and mortality in older adults: A systematic review. Nutrients.
2023;15(7):1780.
37) 荒井秀典(編集主幹), 長寿医療研究開発費事業(27-23):要介護高齢者、フレイル高齢者、認
知症高齢者に対する栄養療法、運動療法、薬物療法に関するガイドライン作成に向けた調査研究
班編. フレイル診療ガイド 2018 年版. 一般社団法人日本老年医学会, 国立研究開発法人国立長
寿医療研究センター; 2018.
38) 沓澤智子. サルコペニアとフレイル. 日本呼吸ケア・リハビリテーション学会誌. 2021;29(3):359364.
398