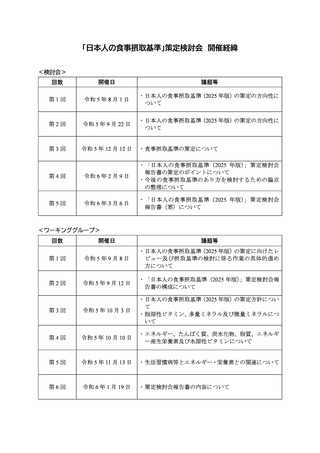
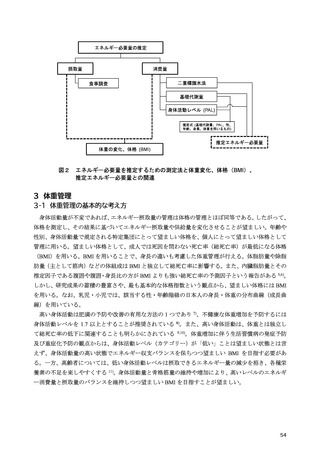
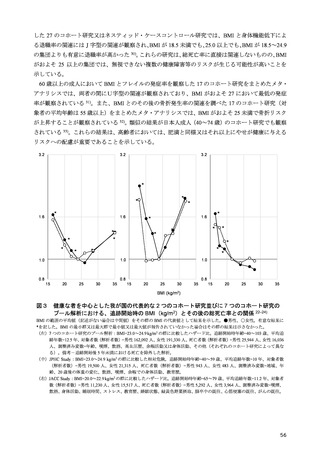
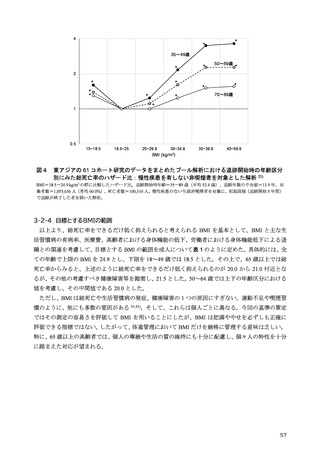
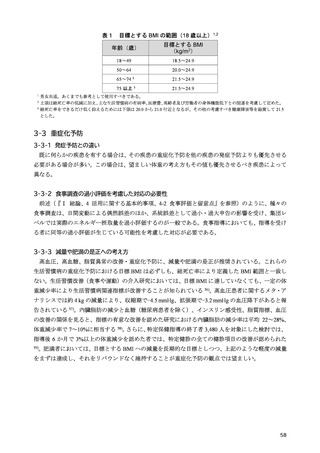
「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書 (469 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_44138.html |
| 出典情報 | 「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
20) Yamamoto T, Nakayama M, Miyazaki M, et al. Impact of lower body mass index on risk of all-cause
mortality and infection-related death in Japanese chronic kidney disease patients. BMC Nephrol.
2020;21(1):244.
21) Ikizler TA, Burrowes JD, Byham-Gray LD, et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for nutrition in CKD:
2020 update. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;76(3 Suppl 1):S1-S107.
22) Cano NJM, Aparicio M, Brunori G, et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: adult renal failure.
Clin Nutr. 2009;28(4):401-414.
23) Wright M, Jones C. Renal association clinical practice guideline on nutrition in CKD. Nephron Clin Pract.
2011;118 Suppl 1(s1):c153-64.
24) Iff S, Wong G, Webster AC, et al. Relative energy balance, CKD, and risk of cardiovascular and all-cause
mortality. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63(3):437-445.
25) Watanabe D, Yoshida T, Nanri H, et al. Association between the prevalence of frailty and doubly labeled
water-calibrated energy intake among community-dwelling older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
2021;76(5):876-884.
26) Hodson EM, Cooper TE. Altered dietary salt intake for preventing diabetic kidney disease and its
progression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023;1(1):CD006763.
27) Lin J, Hu FB, Curhan GC. Associations of diet with albuminuria and kidney function decline. Clin J Am
Soc Nephrol. 2010;5(5):836-843.
28) Vegter S, Perna A, Postma MJ, et al. Sodium intake, ACE inhibition, and progression to ESRD. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 2012;23(1):165-173.
29) Lambers Heerspink HJ, Holtkamp FA, Parving HH, et al. Moderation of dietary sodium potentiates the renal
and cardiovascular protective effects of angiotensin receptor blockers. Kidney Int. 2012;82(3):330-337.
30) Thomas MC, Moran J, Forsblom C, et al. The association between dietary sodium intake, ESRD, and allcause mortality in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(4):861-866.
31) Effects of dietary protein restriction on the progression of moderate renal disease in the Modification of Diet
in Renal Disease Study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996;7(12):2616-2626.
32) Yue H, Zhou P, Xu Z, et al. Effect of low-protein diet on kidney function and nutrition in nephropathy: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr. 2020;39(9):2675-2685.
33) Yan B, Su X, Xu B, et al. Effect of diet protein restriction on progression of chronic kidney disease: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0206134.
34) Jiang S, Fang J, Li W. Protein restriction for diabetic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2023;1(1):CD014906.
35) Rughooputh MS, Zeng R, Yao Y. Protein diet restriction slows chronic kidney disease progression in nondiabetic and in type 1 diabetic patients, but not in type 2 diabetic patients: A meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials using glomerular filtration rate as a surrogate. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0145505.
36) Hahn D, Hodson EM, Fouque D. Low protein diets for non-diabetic adults with chronic kidney disease.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;10(10):CD001892.
37) Fouque D, Laville M. Low protein diets for chronic kidney disease in non diabetic adults. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3):CD001892.
459