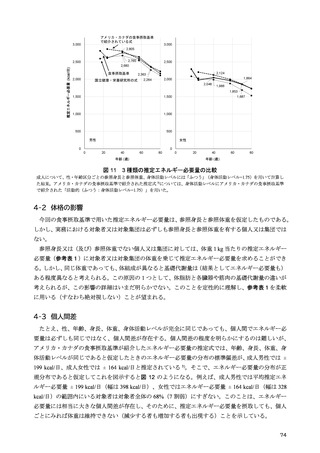
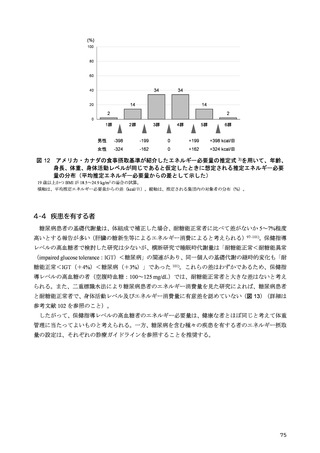
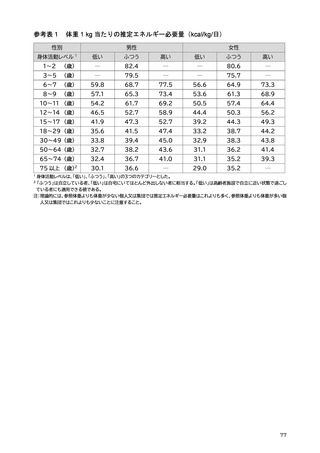
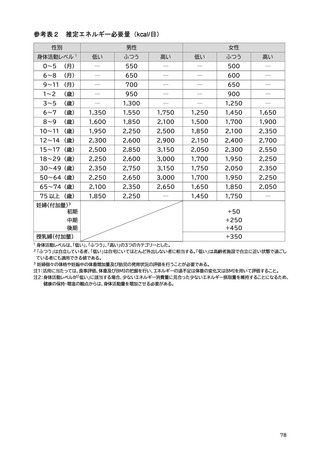
「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書 (412 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_44138.html |
| 出典情報 | 「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
concentration and muscle strength among older women? Results from baseline assessment of the EPIDOS
study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2009;13(2):90-95.
97) Stewart JW, Alekel DL, Ritland LM, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D is related to indicators of overall
physical fitness in healthy postmenopausal women. Menopause. 2009;16(6):1093-1101.
98) Annweiler C, Henni S, Walrand S, et al. Vitamin D and walking speed in older adults: Systematic review
and meta-analysis. Maturitas. 2017;106:8-25.
99) Ensrud KE, Ewing SK, Fredman L, et al. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and frailty status in older
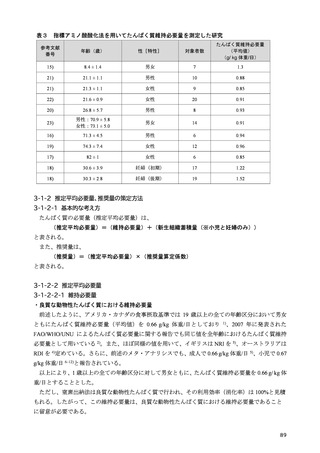
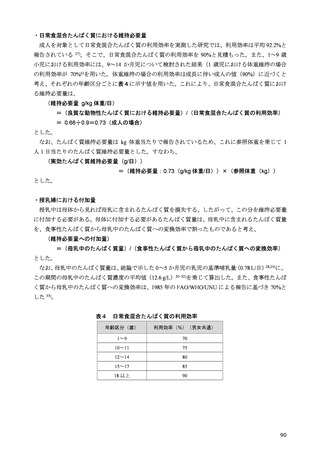
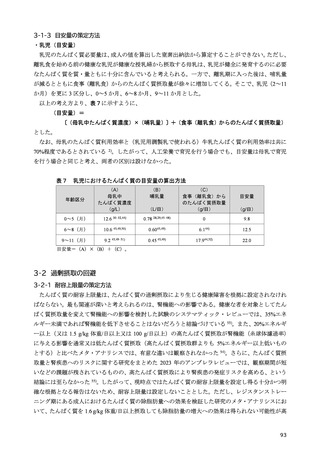
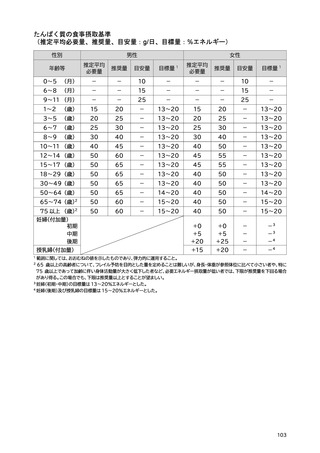
women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(12):5266-5273.
100) Ensrud KE, Blackwell TL, Cauley JA, et al. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and frailty in older
men: the osteoporotic fractures in men study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(1):101-106.
101) Vaes AMM, Brouwer-Brolsma EM, Toussaint N, et al. The association between 25-hydroxyvitamin D
concentration, physical performance and frailty status in older adults. Eur J Nutr. 2019;58(3):1173-1181.
102) Zhou J, Huang P, Liu P, et al. Association of vitamin D deficiency and frailty: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Maturitas. 2016;94:70-76.
103) Uchitomi R, Oyabu M, Kamei Y. Vitamin D and sarcopenia: Potential of vitamin D supplementation in
sarcopenia prevention and treatment. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):3189.
104) Abiri B, Vafa M. Vitamin D and muscle sarcopenia in aging. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2138:29-47.
402