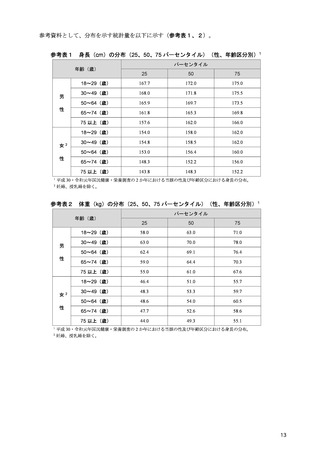
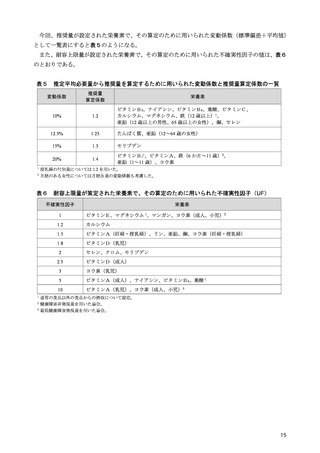
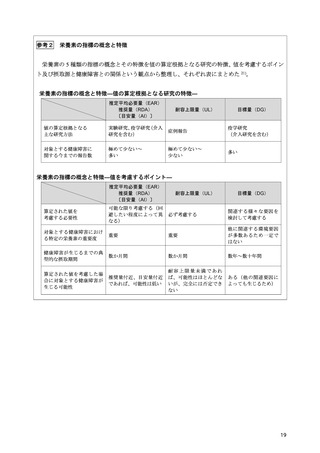
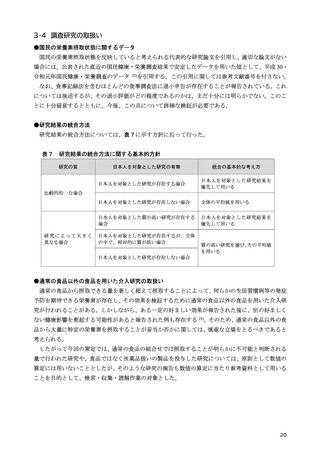
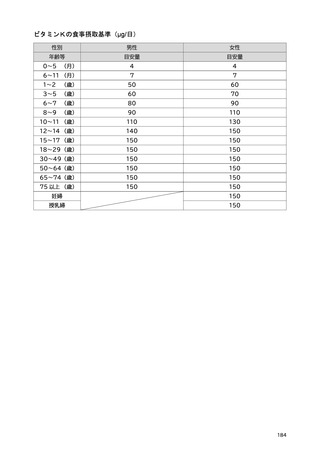
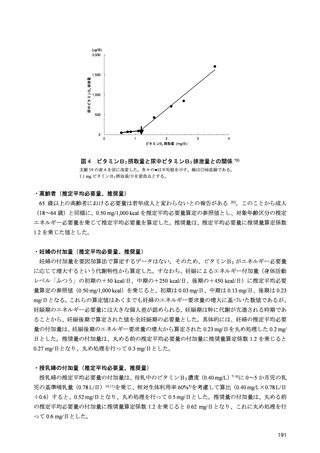
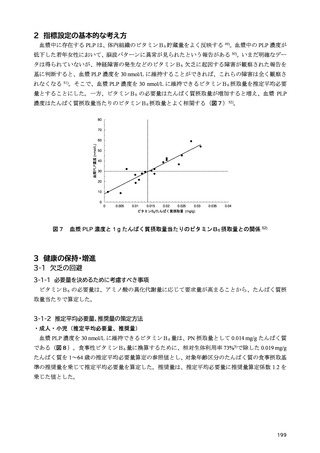
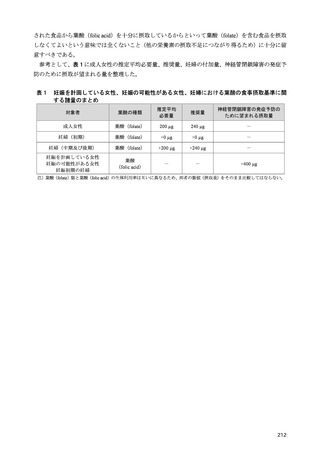
「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書 (450 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_44138.html |
| 出典情報 | 「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
1)
清野裕, 南條輝志男, 田嶼尚子, 他. 糖尿病の分類と診断基準に関する委員会報告 (国際標準化
対応版). 糖尿病. 2012;55(7):485-504.
2)
日本糖尿病学会編. 糖尿病治療ガイド 2022-2023. 文光堂; 2022.
3)
Tokunaga K, Matsuzawa Y, Kotani K, et al. Ideal body weight estimated from the body mass index with the
lowest morbidity. Int J Obes. 1991;15(1):1-5.
4)
Global BMI Mortality Collaboration, Di Angelantonio E, Bhupathiraju S, et al. Body-mass index and allcause mortality: individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents.
Lancet. 2016;388(10046):776-786.
5)
So WY, Yang X, Ma RCW, et al. Risk factors in V-shaped risk associations with all-cause mortality in type
2 diabetes-The Hong Kong Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008;24(3):238-246.
6)
Tanaka S, Tanaka S, Iimuro S, et al. Body mass index and mortality among Japanese patients with type 2
diabetes: pooled analysis of the Japan diabetes complications study and the Japanese elderly diabetes
intervention trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(12):E2692-6.
7)
Kubota Y, Iso H, Tamakoshi A, et al. Association of body mass index and mortality in Japanese diabetic
men and women based on self-reports: The Japan Collaborative Cohort (JACC) study. J Epidemiol.
2015;25(8):553-558.
8)
Edqvist J, Rawshani A, Adiels M, et al. BMI and mortality in patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes: A
comparison with age- and sex-matched control subjects from the general population. Diabetes Care.
2018;41(3):485-493.
9)
Padwal R, Leslie WD, Lix LM, et al. Relationship among body fat percentage, body mass index, and allcause mortality: A cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(8):532-541.
10) Kramer CK, Zinman B, Retnakaran R. Are metabolically healthy overweight and obesity benign
conditions?: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(11):758-769.
11) Stefan N, Schick F, Häring HU. Causes, characteristics, and consequences of metabolically unhealthy
normal weight in humans. Cell Metab. 2017;26(2):292-300.
12) Huang XL, Pan JH, Chen D, et al. Efficacy of lifestyle interventions in patients with type 2 diabetes: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Intern Med. 2016;27:37-47.
13) Terranova CO, Brakenridge CL, Lawler SP, et al. Effectiveness of lifestyle-based weight loss interventions
for adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab.
2015;17(4):371-378.
14) Chen L, Pei JH, Kuang J, et al. Effect of lifestyle intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes: a metaanalysis. Metabolism. 2015;64(2):338-347.
15) Franz MJ, Boucher JL, Rutten-Ramos S, et al. Lifestyle weight-loss intervention outcomes in overweight
and obese adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.
J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015;115(9):1447-1463.
16) Jayedi A, Zeraattalab-Motlagh S, Shahinfar H, et al. Effect of calorie restriction in comparison to usual diet
or usual care on remission of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023;117(5):870-882.
17) Simões Corrêa Galendi J, Leite RGOF, Banzato LR, et al. Effectiveness of strategies for nutritional therapy
440