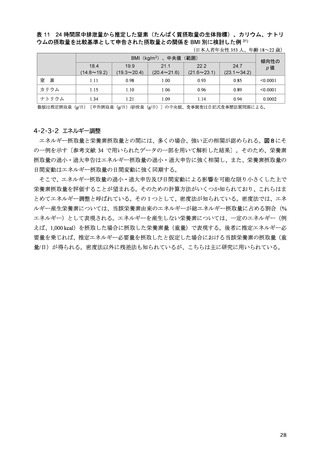
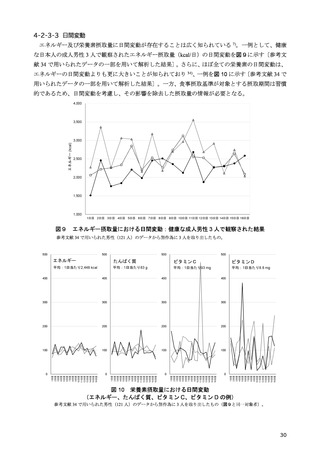
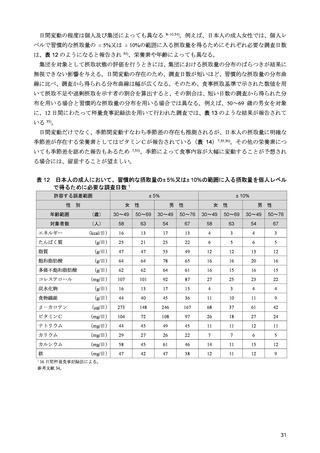
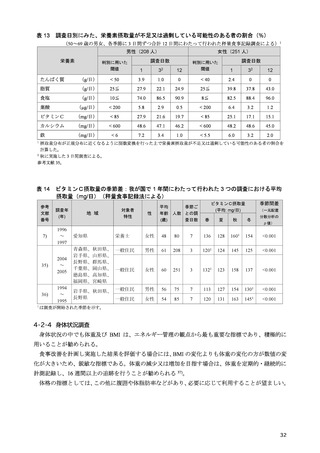
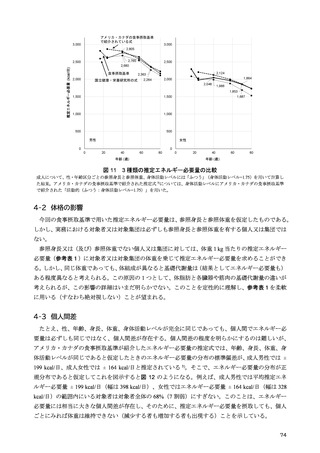
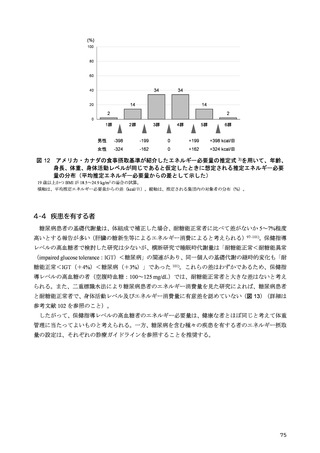
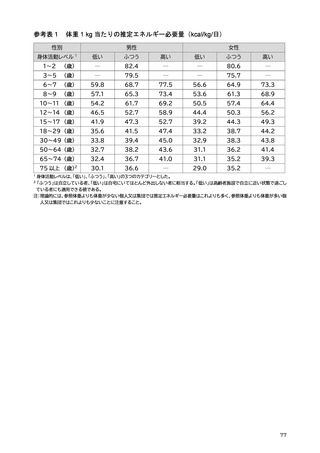
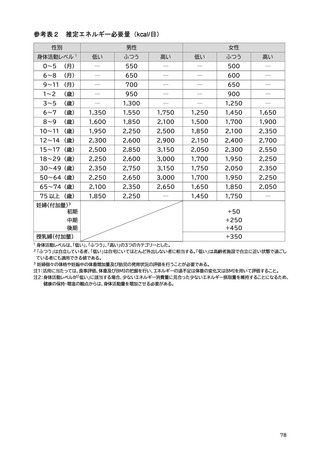
「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書 (90 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_44138.html |
| 出典情報 | 「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
1)
FAO/WHO Ad Hoc Expert Committee. Energy and Protein Requirements: Report of the FAO/WHO Ad
Hoc Expert Committee. World Health Organization Technical Report Series. No. 522, FAO Nutrition
Meetings. Report Series. No. 52. World Health Organization, Geneva; 1973.
2)
田中茂穂. エネルギー消費量とその測定方法. 静脈経腸栄養. 2009;24(5):1013-1019.
3)
Brooks GA, Butte NF, Rand WM, et al. Chronicle of the Institute of Medicine physical activity
recommendation: how a physical activity recommendation came to be among dietary recommendations. Am
J Clin Nutr. 2004;79(5):921S-930S.
4)
Miyake R, Tanaka S, Ohkawara K, et al. Validity of predictive equations for basal metabolic rate in Japanese
adults. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2011;57(3):224-232.
5)
Kodama S, Horikawa C, Fujihara K, et al. Comparisons of the strength of associations with future type 2
diabetes risk among anthropometric obesity indicators, including waist-to-height ratio: a meta-analysis. Am
J Epidemiol. 2012;176(11):959-969.
6)
Savva SC, Lamnisos D, Kafatos AG. Predicting cardiometabolic risk: waist-to-height ratio or BMI. A metaanalysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2013;6:403-419.
7)
Donnelly JE, Blair SN, Jakicic JM, et al. American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Appropriate
physical activity intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Med Sci
Sports Exerc. 2009;41(2):459-471.
8)
Saris WHM, Blair SN, van Baak MA, et al. How much physical activity is enough to prevent unhealthy
weight gain? Outcome of the IASO 1st Stock Conference and consensus statement. Obes
Rev. 2003;4(2):101-114.
9)
Samitz G, Egger M, Zwahlen M. Domains of physical activity and all-cause mortality: systematic review
and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(5):1382-1400.
10) Inoue M, Iso H, Yamamoto S, et al. Daily total physical activity level and premature death in men and
women: results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan (JPHC study). Ann
Epidemiol. 2008;18(7):522-530.
11) U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines
for Americans, 2020–2025. 9th ed. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington, D.C.; 2020.
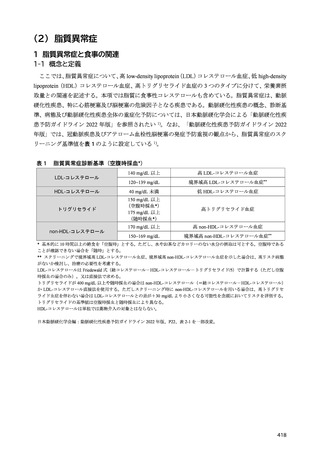
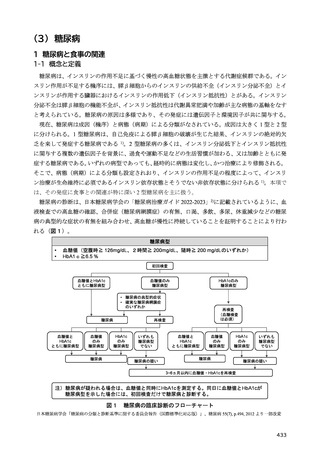
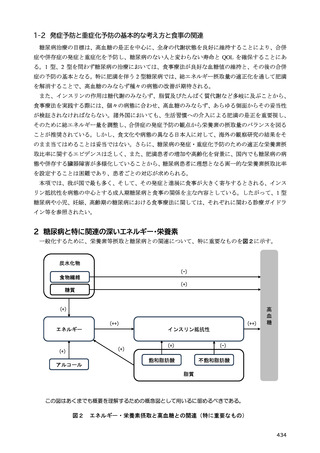
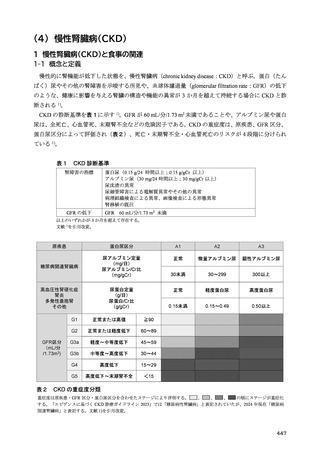
12) 日本腎臓学会. 慢性腎臓病に対する食事療法基準 2014 年. CKD における適正な体重に関する検
討報告. 日本腎臟学会誌. 2014;56(5):586-599.
13) Simopoulos AP. Body weight reference standards. In: Simopoulos AP, Van Itallie T, eds. Obesity: New
Directions in Assessment and Management. Charles Press Pubs, Philadelphia; 1995.
14) Metropolitan Life Insurance Company. Ideal weights for women. Stat Bull Metrop Insur Co. 1942;23:6-8.
15) Metropolitan Life Insurance Company. Ideal weights for men. Stat Bull Metrop Insur Co. 1943;24:6-8.
16) Walker WJ. Relationship of adiposity to serum cholesterol and lipoprotein levels and their modification by
dietary means. Ann Intern Med. 1953;39(4):705-716.
17) 松木駿. 肥満の判定基準. 日本医師会雑誌. 1972;68:916-919.
18) 塚本宏. 保険医学からみた体格の諸問題. 日本保険医学会誌. 1985;83:36.
19) 塚本宏, 田村誠. 死亡率からみた日本人の体格―明治生命・標準体重表. 厚生の指標. 1986;33(2):314.
80