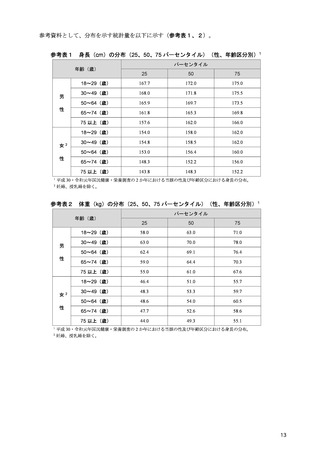
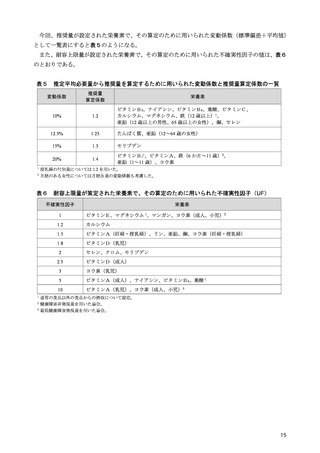
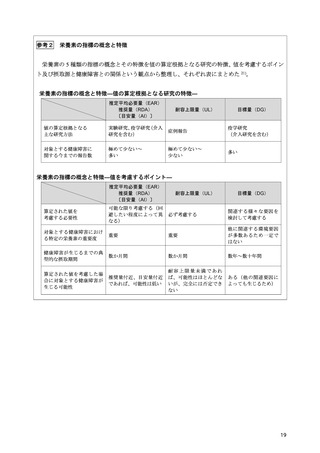
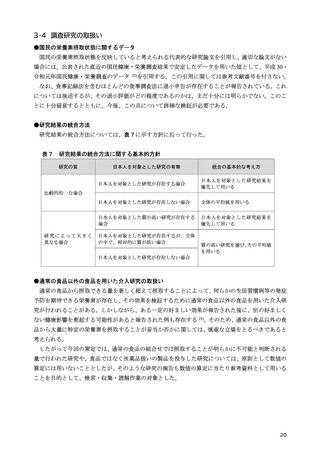
「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書 (347 ページ)
出典
| 公開元URL | https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_44138.html |
| 出典情報 | 「日本人の食事摂取基準(2025年版)」策定検討会報告書(10/11)《厚生労働省》 |
ページ画像
プレーンテキスト
資料テキストはコンピュータによる自動処理で生成されており、完全に資料と一致しない場合があります。
テキストをコピーしてご利用いただく際は資料と付け合わせてご確認ください。
114) Park JH, Hogrebe M, Grüneberg M, et al. SLC39A8 deficiency: A disorder of manganese transport and
glycosylation. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;97(6):894-903.
115) Freeland-Graves JH, Behmardi F, Bales CW, et al. Metabolic balance of manganese in young men
consuming diets containing five levels of dietary manganese. J Nutr. 1988;118(6):764-773.
116) Nishimuta M, Kodama N, Shimada M, et al. Estimated equilibrated dietary intakes for nine minerals (Na,
K, Ca, Mg, P, Fe, Zn, Cu, and Mn) adjusted by mineral balance medians in young Japanese females. J Nutr
Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2012;58(2):118-128.
117) Friedman BJ, Freeland-Graves JH, Bales CW, et al. Manganese balance and clinical observations in young
men fed a manganese-deficient diet. J Nutr. 1987;117(1):133-143.
118) Hardy G. Manganese in parenteral nutrition: who, when, and why should we supplement?
Gastroenterology. 2009;137(5 Suppl):S29-35.
119) Ejima A, Imamura T, Nakamura S, et al. Manganese intoxication during total parenteral nutrition.
Lancet. 1992;339(8790):426.
120) Shinozaki N, Murakami K, Masayasu S, et al. Usual nutrient intake distribution and prevalence of nutrient
intake inadequacy among Japanese children and adults: A nationwide study based on 8-day dietary records.
Nutrients. 2023;15(24):5113.
121) Institute of Medicine. Manganese. In: Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron,
Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. National
Academies Press, Washington D.C.; 2001:394-419.
122) EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference
Values for manganese. EFSA J. 2013;11(11).
123) Ishitsuka K, Sasaki S, Yamamoto-Hanada K, et al. Changes in dietary intake in pregnant women from
periconception to pregnancy in the Japan Environment and Children’s Study: A nationwide Japanese birth
cohort study. Matern Child Health J. 2020;24(3):389-400.
124) Yamamoto M, Sakurai K, Eguchi A, et al. Association between blood manganese level during pregnancy
and birth size: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS). Environ Res. 2019;172:117-126.
125) Yamamoto M, Eguchi A, Sakurai K, et al. Longitudinal analyses of maternal and cord blood manganese
levels and neurodevelopment in children up to 3 years of age: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study
(JECS). Environ Int. 2022;161(107126):107126.
126) EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA), Turck D, Bohn T, et al. Scientific
opinion on the tolerable upper intake level for manganese. EFSA J. 2023;21(12):e8413.
127) Davis CD, Greger JL. Longitudinal changes of manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase and other
indexes of manganese and iron status in women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992;55(3):747-752.
128) Gibson RS. Content and bioavailability of trace elements in vegetarian diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994;59(5
Suppl):1223S-1232S.
129) Yoshida M, Ôgi N, Iwashita Y. Estimation of mineral and trace element intake in vegans living in Japan by
chemical analysis of duplicate diets. Health. 2011;03(11):672-676.
130) Vigeh M, Yokoyama K, Ohtani K, et al. Increase in blood manganese induces gestational hypertension
during pregnancy. Hypertens Pregnancy. 2013;32(3):214-224.
337